In sharp contrast to other types of commercial real estate, the life sciences market is booming, according to SGA, an architecture firm based in Boston and New York that has extensive experience designing life sciences buildings. “There’s increased demand to deliver life sciences towers in dense urban environments,” Brooks Slocum, SGA’s studio director, writes in a blog post.
But while cities need these buildings, urban environments pose a fundamental challenge: “In the past, opportunities to build labs in places like New York City were limited by the lack of square footage on the ground,” Slocum writes.
Traditionally, life sciences buildings have been low-rise facilities. SGA thinks that doesn’t have to be the case.
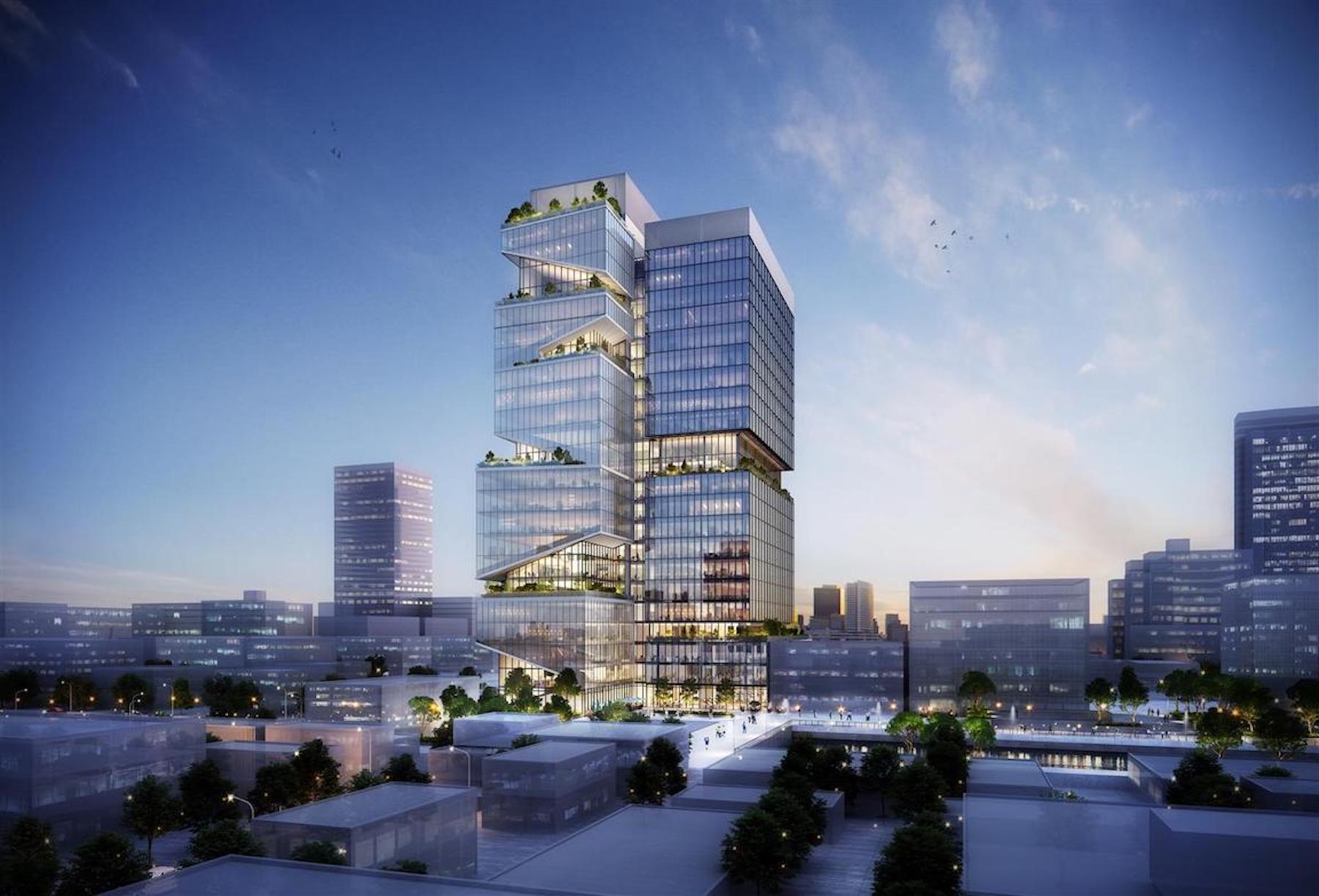
SGA has designed a prototype complex it calls the Vertical Cluster, a proposed 24-story, 750,000-square-foot tower with wet and dry labs. Reflecting local zoning and building codes, the vertical tower can stack diverse programming needs typically found in horizontal life-sciences complexes.
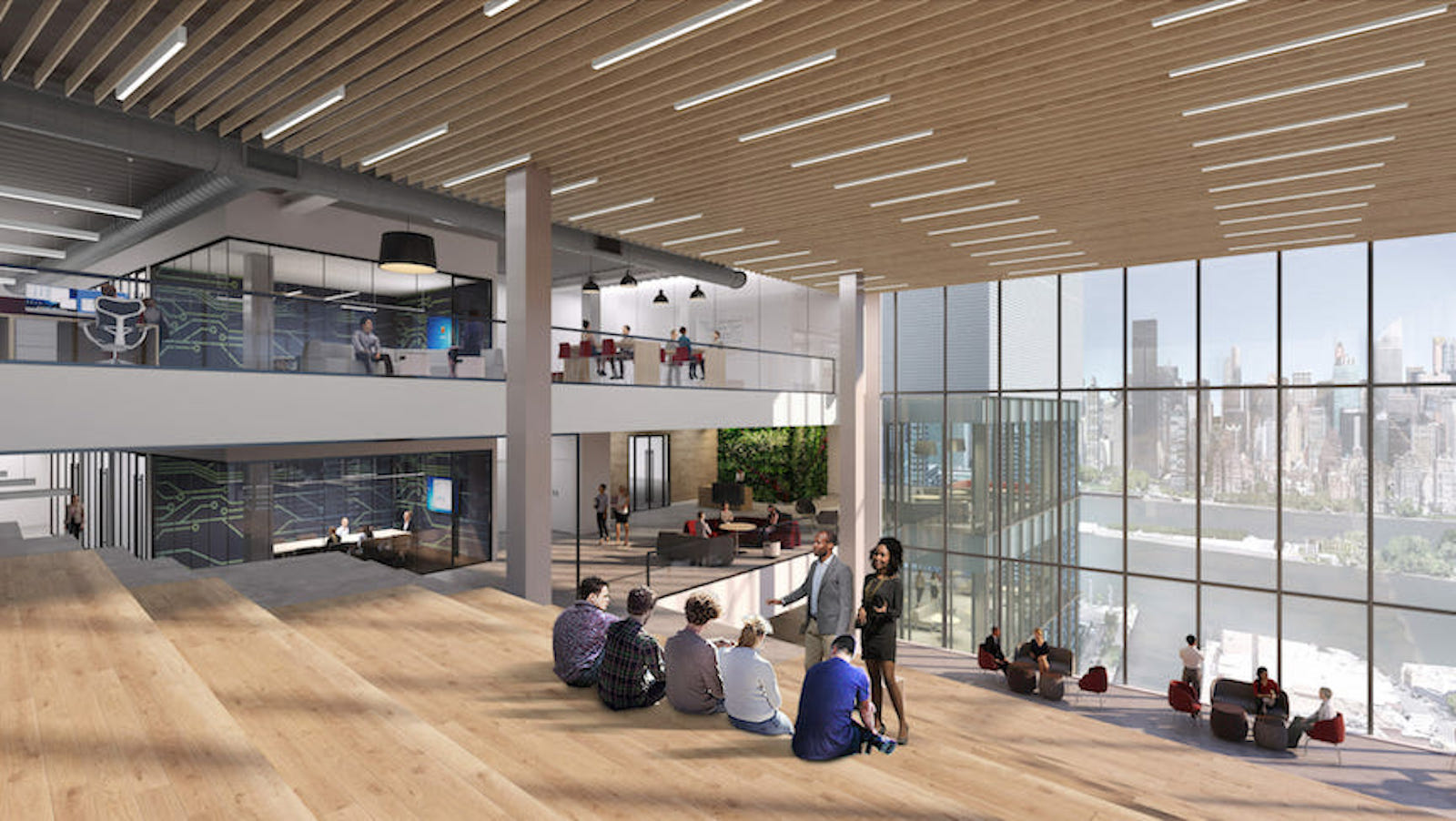

Slocum describes the tower as essentially comprising multiple shorter buildings stacked on top of each other. “Every 10 or 12 floors, we ‘separate’ the building by putting in multi-floor mechanical zones.” This not only isolates the mechanical zones but also avoids overburdening the building with ventilation shafts running from the bottom of the building to the top. This approach allows SGA to design life sciences facilities as tall as zoning allows.
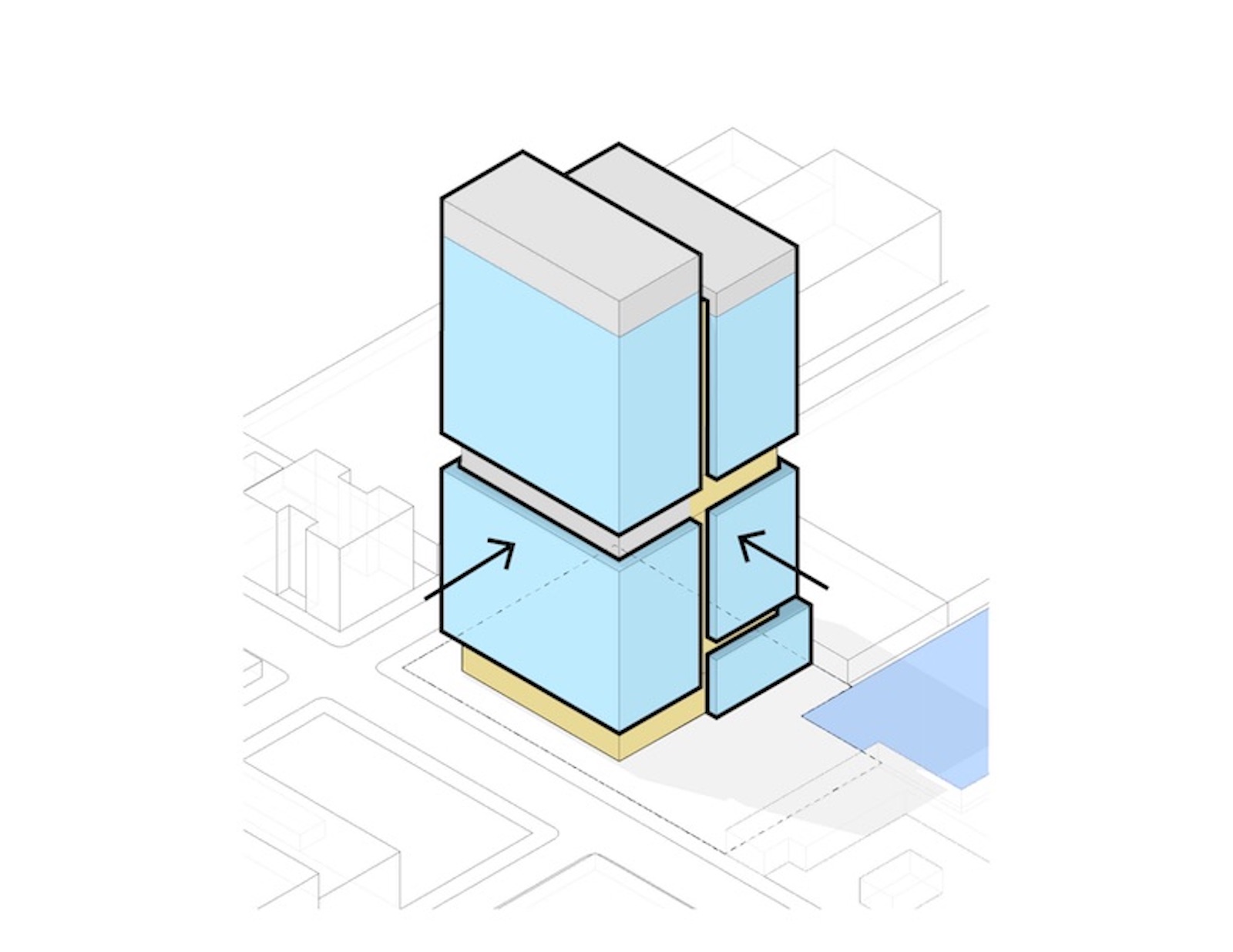
There’s a widespread misconception, according to Slocum, that all lab building exhaust must be moved to a building’s roof. That results in shafts becoming progressively larger on higher floors—with a corresponding reduction in rentable space. But it’s only the exhaust from fume hoods that’s contaminated and requires rooftop exhaust. Most of the air in a lab building comes from the offices—and that air can be recirculated via the mechanical zones.
“With proper design, we can plan the upper floors to have more rentable area available to tenants than on the lower floors, not less,” Slocum writes.
Related Stories
| Jul 12, 2012
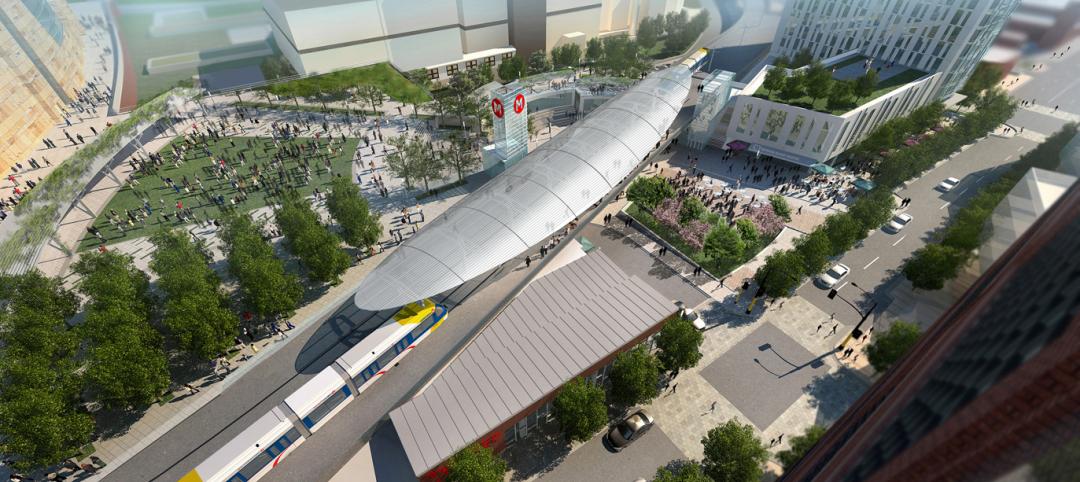
EE&K and Knutson Construction selected for the Interchange in Minneapolis
Design-build contract for $79.3 million transportation hub will connect transit with culture.
| Jul 11, 2012
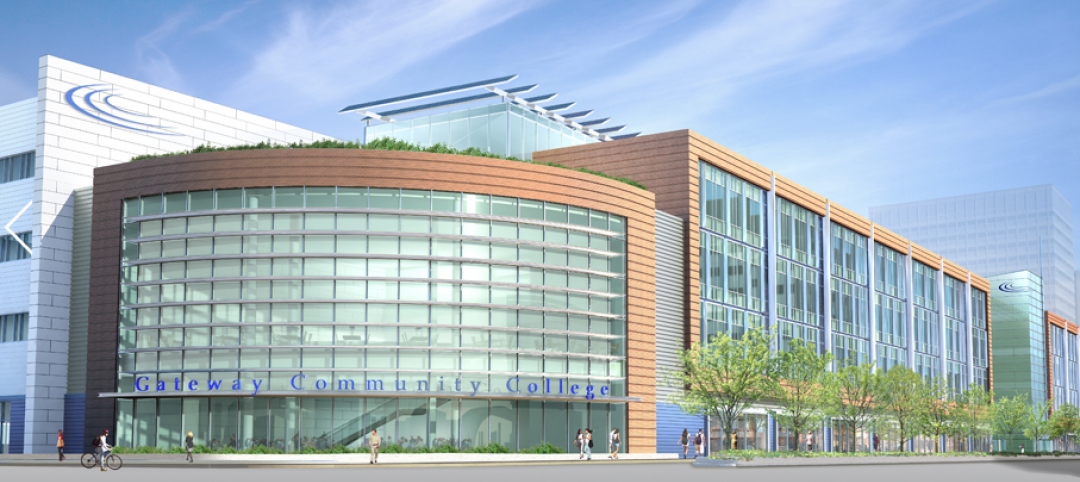
Perkins+Will designs new home for Gateway Community College
Largest one-time funded Connecticut state project and first designed to be LEED Gold.
| Jul 9, 2012
Oakdale, Calif., Heritage Oaks Senior Apartments opens
New complex highlights senior preferences for amenities.
| Jul 3, 2012
Summit Design+Build completes Emmi Solutions HQ
The new headquarters totals 20,455 sq. ft. and features a loft-style space with exposed masonry and mechanical systems, 17-ft clear ceilings, two large rooftop skylights, and private offices with full glass partition walls.











