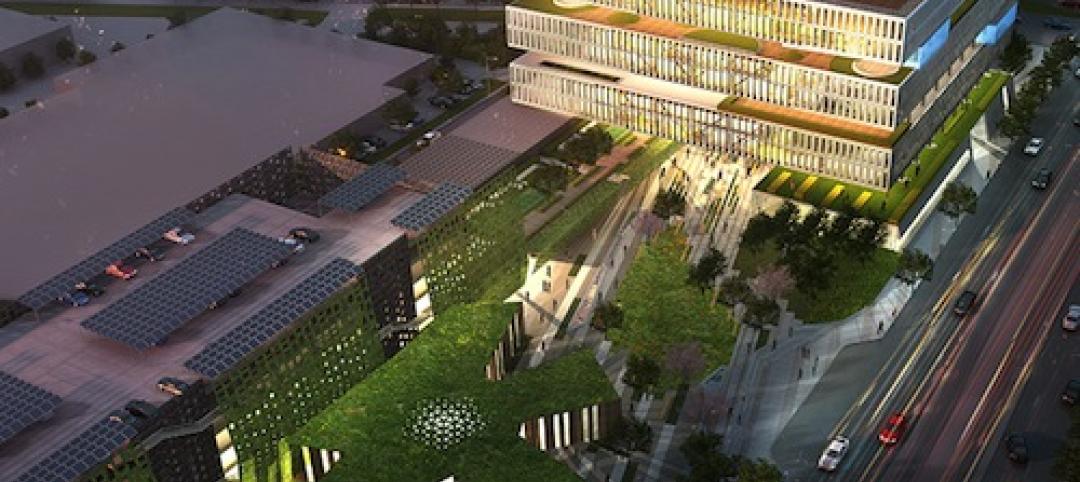
In sharp contrast to other types of commercial real estate, the life sciences market is booming, according to SGA, an architecture firm based in Boston and New York that has extensive experience designing life sciences buildings. “There’s increased demand to deliver life sciences towers in dense urban environments,” Brooks Slocum, SGA’s studio director, writes in a blog post.
But while cities need these buildings, urban environments pose a fundamental challenge: “In the past, opportunities to build labs in places like New York City were limited by the lack of square footage on the ground,” Slocum writes.
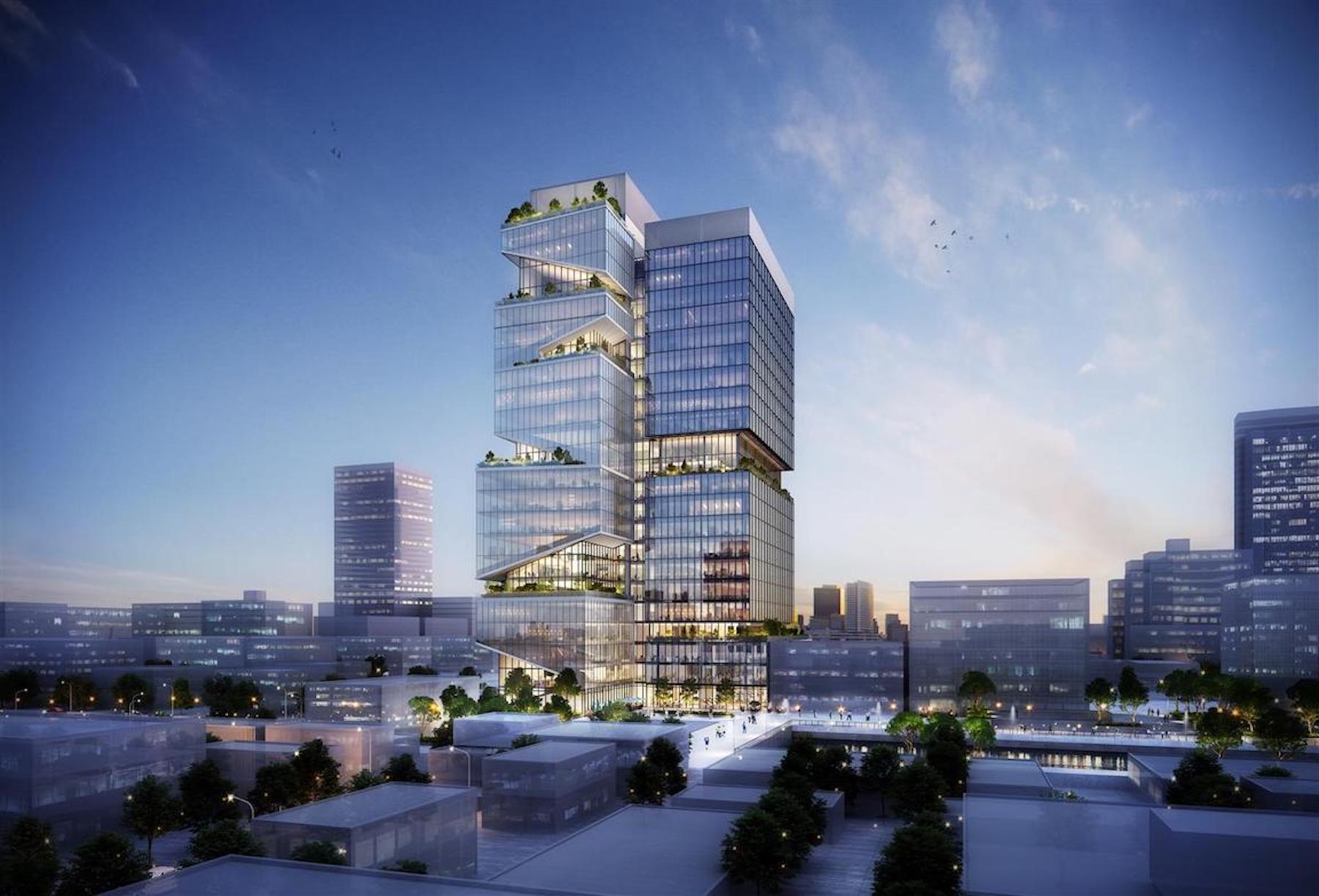
Traditionally, life sciences buildings have been low-rise facilities. SGA thinks that doesn’t have to be the case.
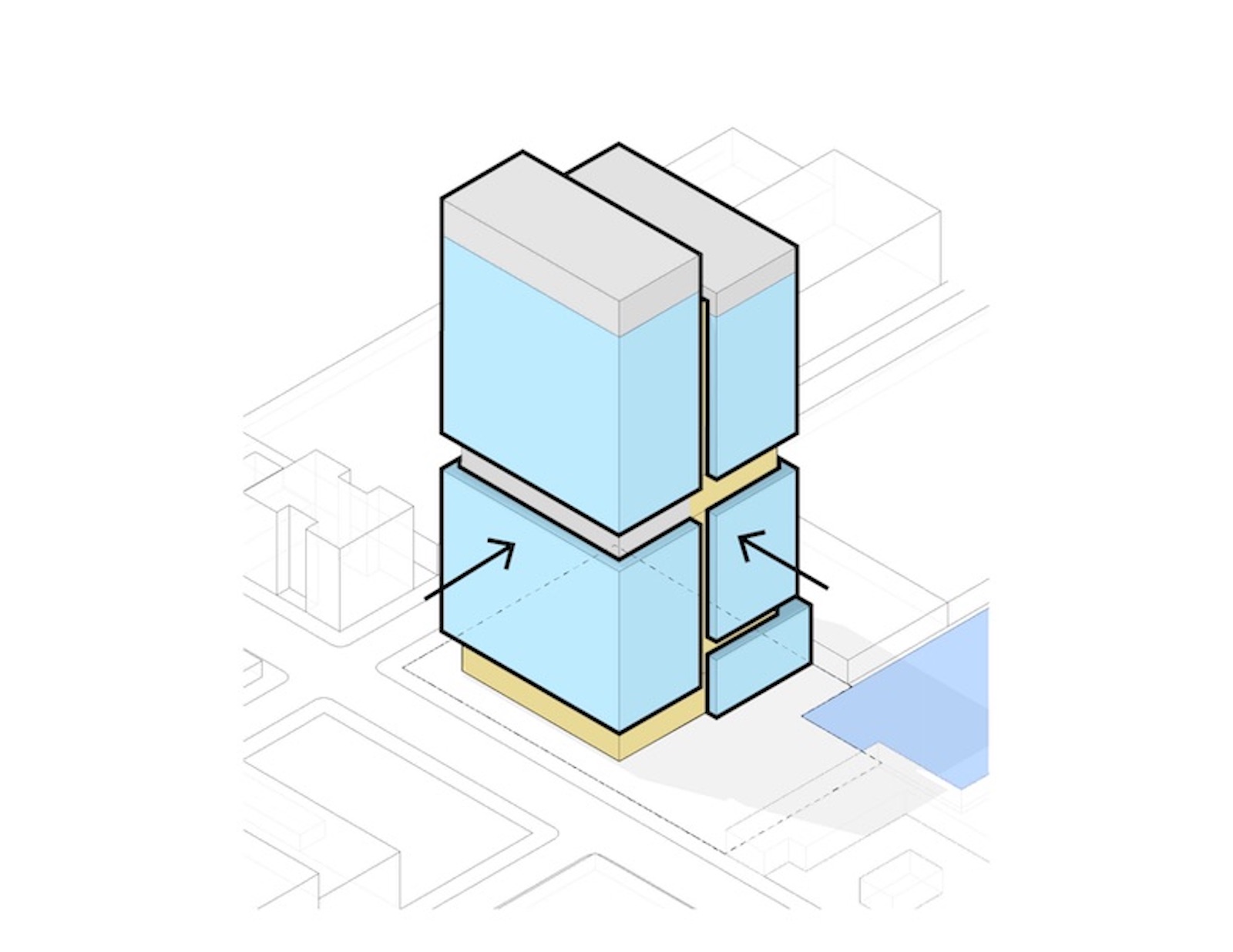
SGA has designed a prototype complex it calls the Vertical Cluster, a proposed 24-story, 750,000-square-foot tower with wet and dry labs. Reflecting local zoning and building codes, the vertical tower can stack diverse programming needs typically found in horizontal life-sciences complexes.

Slocum describes the tower as essentially comprising multiple shorter buildings stacked on top of each other. “Every 10 or 12 floors, we ‘separate’ the building by putting in multi-floor mechanical zones.” This not only isolates the mechanical zones but also avoids overburdening the building with ventilation shafts running from the bottom of the building to the top. This approach allows SGA to design life sciences facilities as tall as zoning allows.
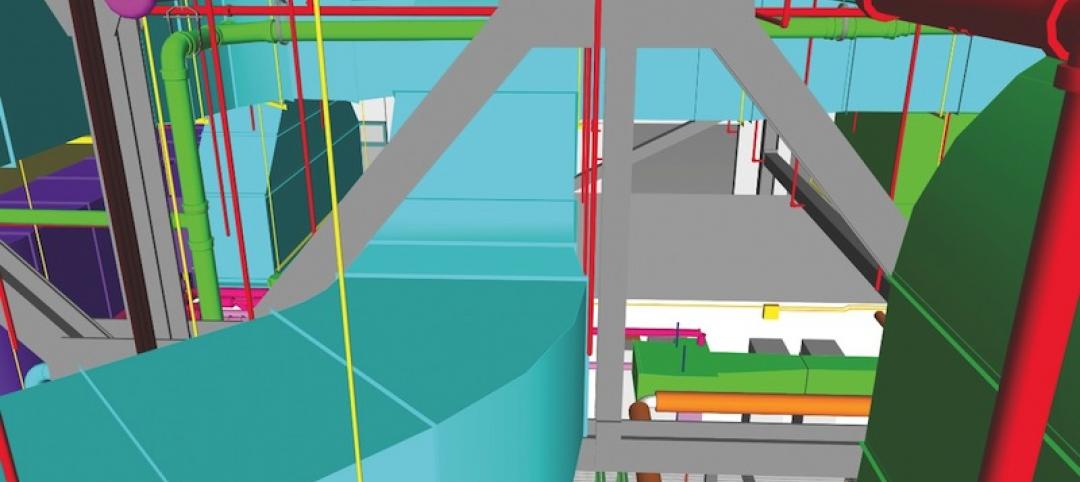
There’s a widespread misconception, according to Slocum, that all lab building exhaust must be moved to a building’s roof. That results in shafts becoming progressively larger on higher floors—with a corresponding reduction in rentable space. But it’s only the exhaust from fume hoods that’s contaminated and requires rooftop exhaust. Most of the air in a lab building comes from the offices—and that air can be recirculated via the mechanical zones.
“With proper design, we can plan the upper floors to have more rentable area available to tenants than on the lower floors, not less,” Slocum writes.
Related Stories
| Jun 11, 2014
David Adjaye’s housing project in Sugar Hill nears completion
A new development in New York's historic Sugar Hill district nears completion, designed to be an icon for the neighborhood's rich history.
| Apr 8, 2014
Fire resistive curtain wall helps The Kensington meet property line requirements
The majority of fire rated glazing applications occur inside a building to allow occupants to exit the building safely or provide an area of refuge during a fire. But what happens when the threat of fire comes from the outside? This was the case for The Kensington, a mixed-use residential building in Boston.
| Mar 25, 2014
Sydney breaks ground on its version of the High Line elevated park [slideshow]
The 500-meter-long park will feature bike paths, study pods, and outdoor workspaces.
| Jan 28, 2014
2014 predictions for skyscraper construction: More twisting towers, mega-tall projects, and 'superslim' designs
Experts from the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat release their 2014 construction forecast for the worldwide high-rise industry.
| Jan 21, 2014
2013: The year of the super-tall skyscraper
Last year was the second-busiest ever in terms of 200-meter-plus building completions, with 73 towers, according to a report by the Council on Tall Buildings and Urban Habitat.
| Sep 23, 2013
Six-acre Essex Crossing development set to transform vacant New York property
A six-acre parcel on the Lower East Side of New York City, vacant since tenements were torn down in 1967, will be the site of the new Essex Crossing mixed-use development. The product of a compromise between Mayor Michael Bloomberg and various interested community groups, the complex will include ~1,000 apartments.
| May 1, 2013
World’s tallest children’s hospital pushes BIM to the extreme
The Building Team for the 23-story Lurie Children’s Hospital in Chicago implements an integrated BIM/VDC workflow to execute a complex vertical program.
| Apr 22, 2013
Top 10 green building projects for 2013 [slideshow]
The AIA's Committee on the Environment selected its top ten examples of sustainable architecture and green design solutions that protect and enhance the environment.
| Feb 28, 2013
Greeening Silicon Valley: Samsung's new 1.1 million-sf HQ
Samsung Electronics' new 1.1 million sf San Jose campus will support at least 2,500 sales and R&D staff in the company's semiconductor and display businesses.
| Feb 27, 2013
Bronx residents get LEED Platinum public housing complex, rooftop farm
The New York City Housing Authority has opened Arbor House, a 124-unit LEED Platinum complex in the Morrisania neighborhood of the Bronx.