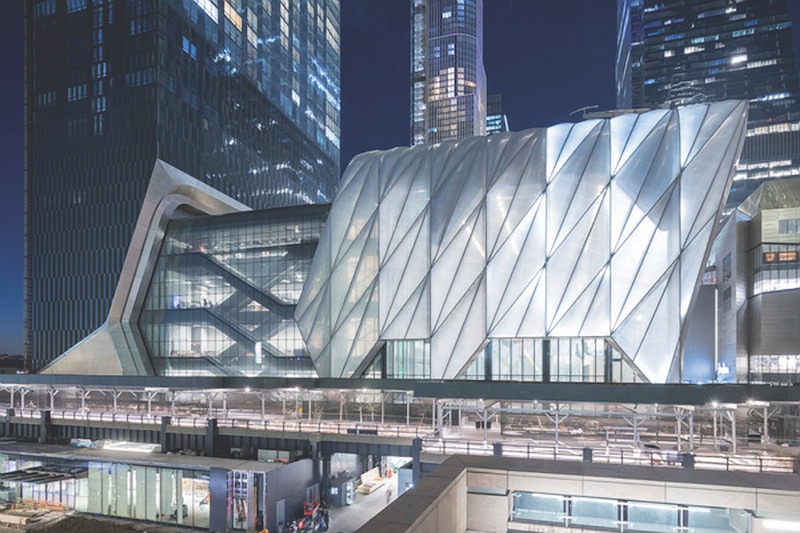
When The Shed, a $435 million arts, education, and entertainment center in New York City, had its grand opening in the spring of 2019, it attracted attention for its 115-foot-tall moveable canopy that, when fully opened, adds 17,000 sf of light-, sound-, and temperature-controlled multipurpose space; and when fully retracted into the 200,000-sf building uncovers an open-air public plaza.
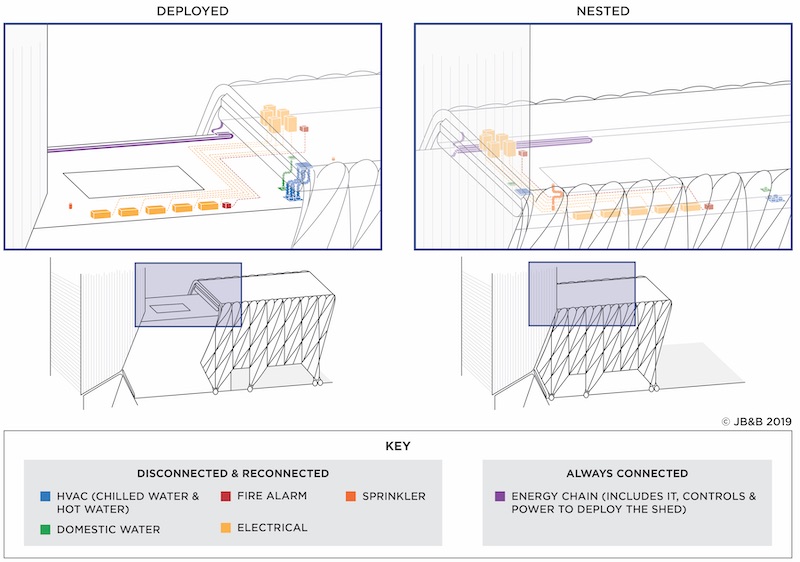
What’s less appreciated, perhaps, by The Shed’s visitors, students, and performers is its electrical interconnection system that powers the building’s nested and deployed positions, and that must be disconnected and connected every time the canopy opens and closes.
“I don’t know of any other moveable building in the world that’s like this. We built it like a Swiss watch,” says Mark Torre, PE, LEED AP, Managing Partner with Jaros, Baum and Bolles (JB&B), the project’s MEP and fire protection consultant.
As originally designed by Diller, Scofidio + Renfro in collaboration with Rockwell Group, The Shed had two moveable features, each of which would have needed to be heated and cooled. (Torre says that design was scotched as being too complex and costly.)
The project team also thought it would have more space below The Shed for its mechanical room, but that didn’t work out, either. At one point, there was some thought given to running air conditioning ducts through manholes, but that idea was rejected because the system would have cooled only about 15% of the performance space.
So the 850,000 lbs of mechanicals—including the building maintenance unit, HVAC, plumbing, conduit, and other equipment—are above the canopy’s lighting rig. Scott Lomax, Senior Principal with Thornton Tomasetti, the project’s structural engineer, says that based on The Shed’s current programming needs, the project team predicted that the 6.1 million-lb canopy will retract about once per month through the life of the building.
See Also: The Shed arts center includes a massive, telescoping outer shell
To facilitate that movement, JB&B created attachment points (both nested and not), which Torre says required precise installation of systems that would be disconnected and reconnected as needed. These systems include normal utility power, legally required standby power, emergency power, fire alarm power and communications, chilled and hot water supply and return, domestic water makeup (which addresses evaporation and maintenance issues), and sprinkler service for the mechanical deck above the event space. The connect/disconnect are performed manually and take about six hours to complete, says Torre. The Shed services that remain connected through the “power chain” include the building management system’s communications and power, information technology, and power for the canopy’s motors and kinetics control system.
Torre notes that nearly all of The Shed’s mechanical systems (for the moveable portions) required variances. These included the energy chain power (for permanent flexible power wiring) as well as the methods for connecting and disconnecting the moveable Shed.
Related Stories
Great Solutions | Aug 30, 2019
An ‘Internet of Beings’? Kinetic flooring promises more than just energy generation
Pavegen says its technology delivers a new level of human engagement in sustainability initiatives.
Great Solutions | Aug 7, 2019
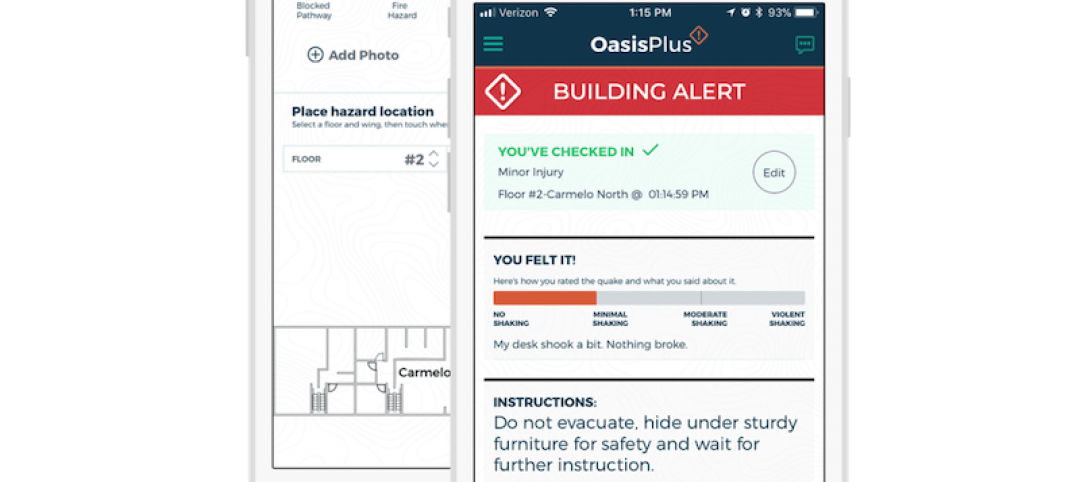
Earthquake response system takes the guesswork out of seismic safety
The platform provides real-time monitoring to help avoid unnecessary evacuations and improve emergency response.
Great Solutions | Jul 12, 2019
Smart sensor maintains privacy, enhances safety in sensitive spaces
The HALO IOT sensor is designed for use in places where cameras are not welcome.
Great Solutions | Apr 9, 2019
Raising the roof is cool again
Upbrella allows for floor-by-floor building construction that is, reportedly, safer and more productive than traditional methods.
Great Solutions | Mar 12, 2019
When is wood not really wood?
Inspired by the look and cellular nature of wood, researchers create 3D-printed “digital wood” and “metallic wood” that is as strong as titanium, with the density of water.
Sustainability | Feb 20, 2019
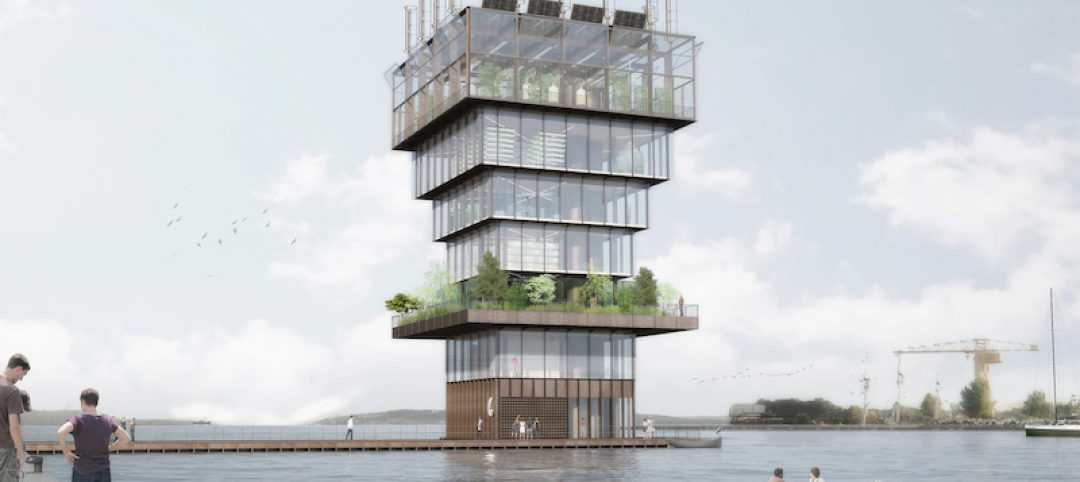
Studio NAB’s Superfarm project creates an entire ecosystem in an urban environment
The Superfarm will go beyond what vertical farms typically produce.
Great Solutions | Feb 7, 2019
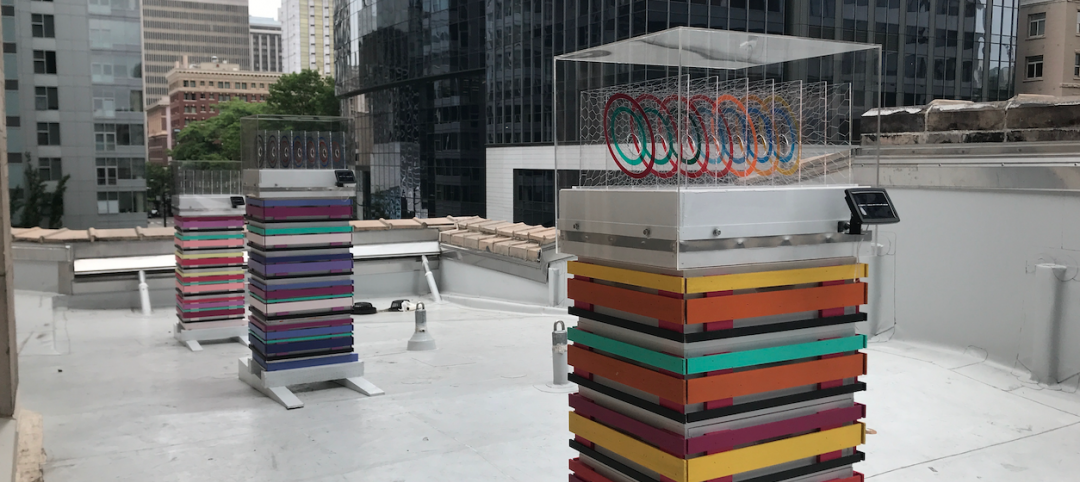
An apiary for the sanctuary
A Seattle events venue, The Sanctuary, has a roof that is literally a hive of sustainability.
Great Solutions | Jan 2, 2019
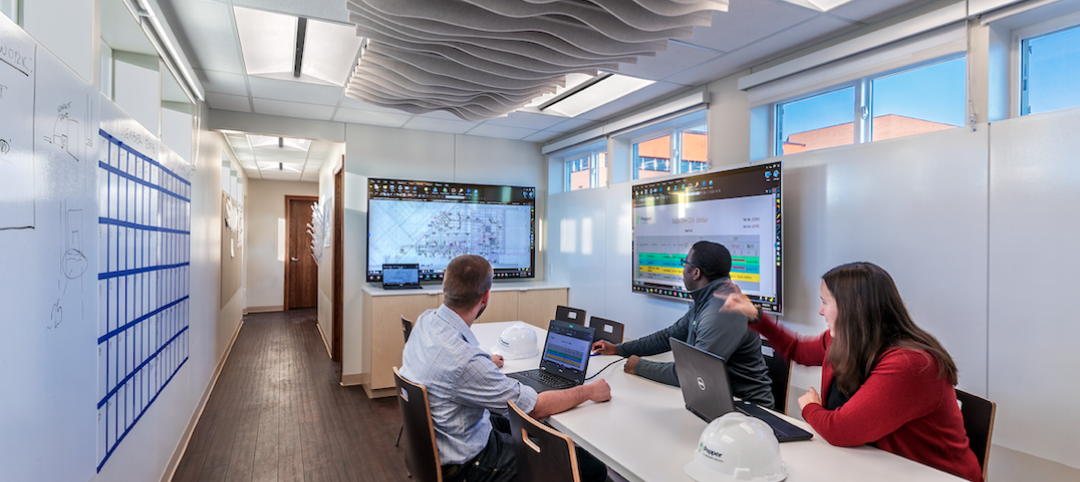
Net zero construction trailer brings health and wellness to the jobsite
As AEC firms scramble to upgrade their offices to maximize occupant wellness and productivity, Pepper Construction asks, What about the jobsite office?
Great Solutions | Dec 12, 2018
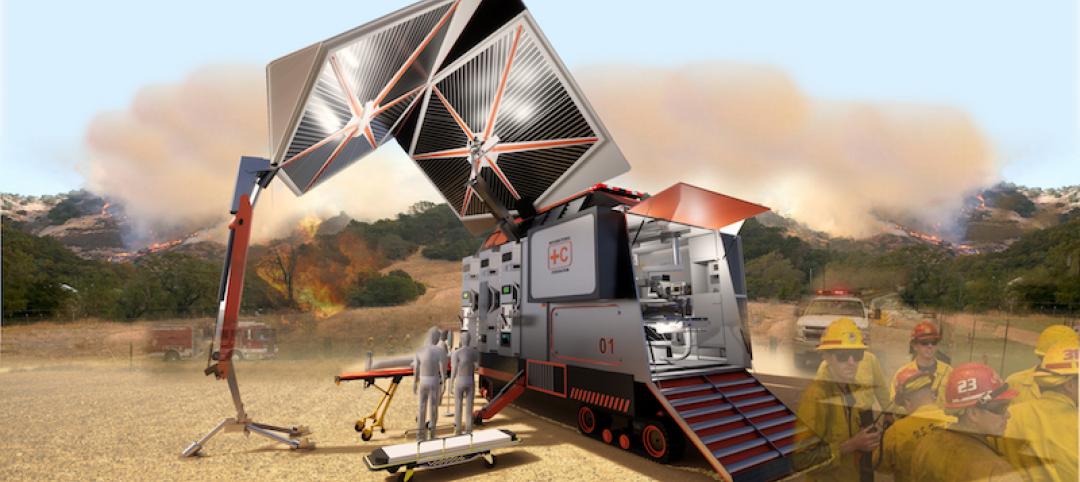
A modular, scalable mobile hospital can quickly respond to natural disasters and crises
CallisonRTKL’s design combines artificial intelligence, electric vehicle technology, and the latest in medical equipment.
Great Solutions | Nov 8, 2018
Public canopy system can be reconfigured by drones on the fly
The installation combines cyber-physical building materials constructed from lightweight carbon fiber filament with a collection of autonomous drones.