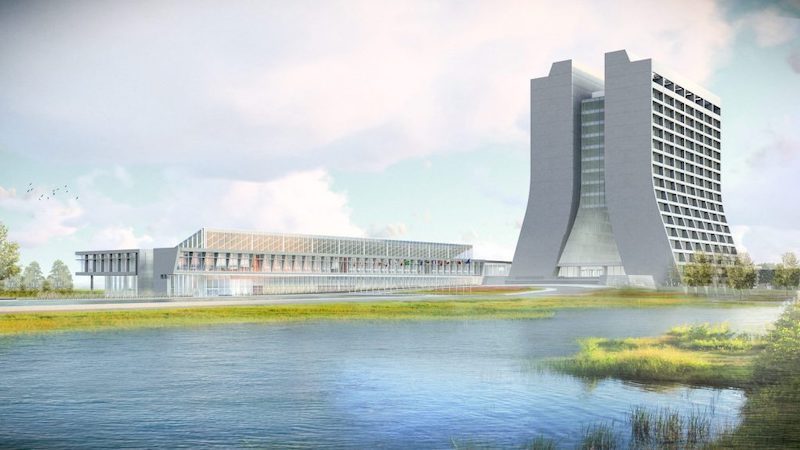
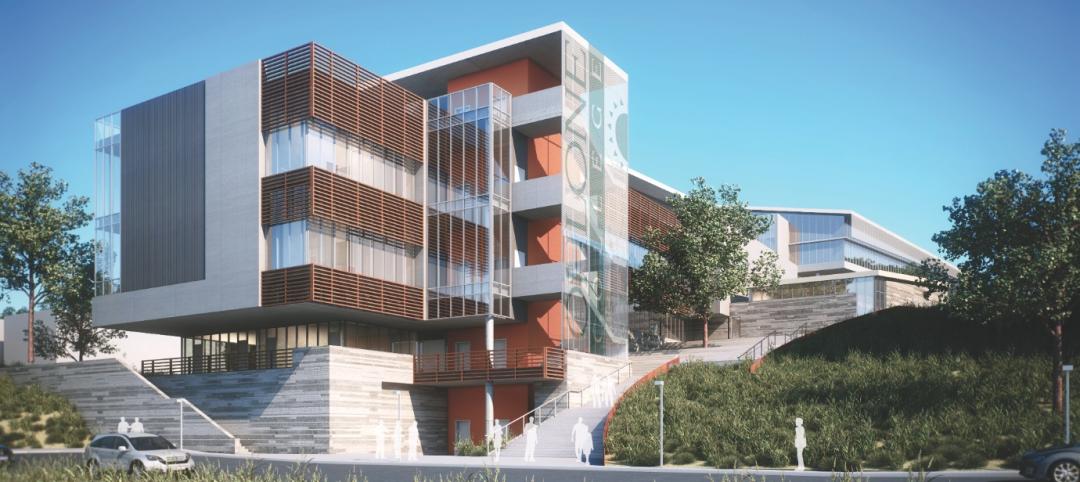
This fall, construction is scheduled to begin on the Integrated Engineering Research Center (IERC), an $86 million, 85,000-sf infrastructure project on the 6,800-acre campus of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory in Batavia, Ill., the nation’s premier particle physics lab.
IERC has been in the works since the summer of 2015, and at one time was conceived as a 100,000-sf building that dedicated two of its three floors to office space. That concept changed after a team comprised of Arup and Perkins and Will won a design competition that Fermilab conducted in 2017.
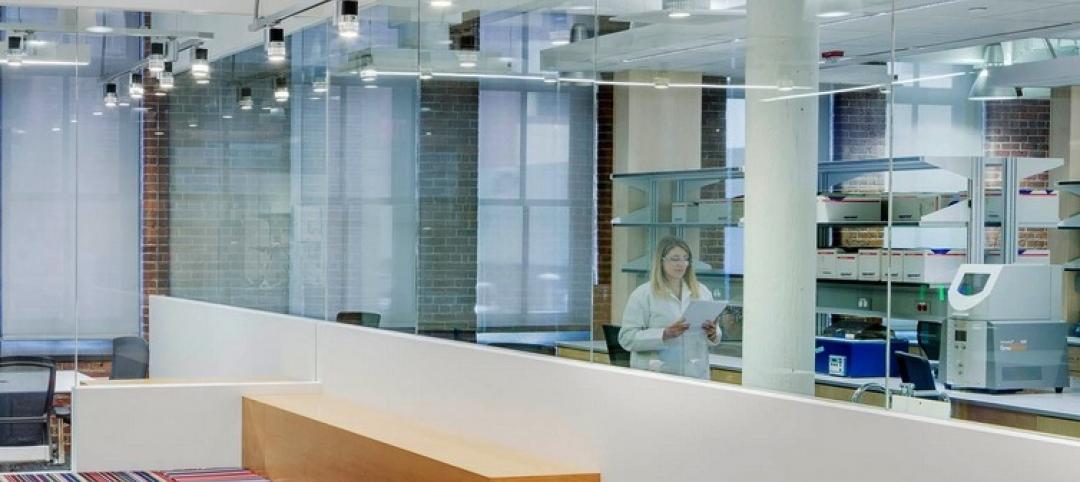
That team’s concept scales back the building to two floors, and includes more lab space. What emerges are “hybrid labs” that, essentially, remove the walls separating labs and offices for the purposes of colocation and collaboration. There are two hybrid zones on the ground floor, in one big open area “that just about anyone can walk through,” explains Aaron Tabares, a Senior Electrical Engineer for Arup’s offices in Chicago, which provides the SE, MEP, F/LS, AV, and IT services to the IERC project.
(He notes, parenthetically, that Arup’s acoustics expertise came in handy to help design these hybrids with quiet features for researchers when needed.)
Brian Rubik, SE, Fermilab’s project manager, adds that Perkins and Will, the designer and AOR on the IERC project, championed bringing more natural light into the new building, whose sloped roof includes clerestories that angle toward the campus’s iconic Wilson Hall.
Rubik notes that IERC’s mechanicals were moved to the center of its upper floor so that more offices could be positioned on the interior perimeter to receive more light. Fermilab calls the hallways and windows around the perimeter of the ground floor “science on display,” says Rubik.
“A lot of the building’s systems are discrete,” adds Tabares. “The form of the building considered just about every angle for the occupants.”
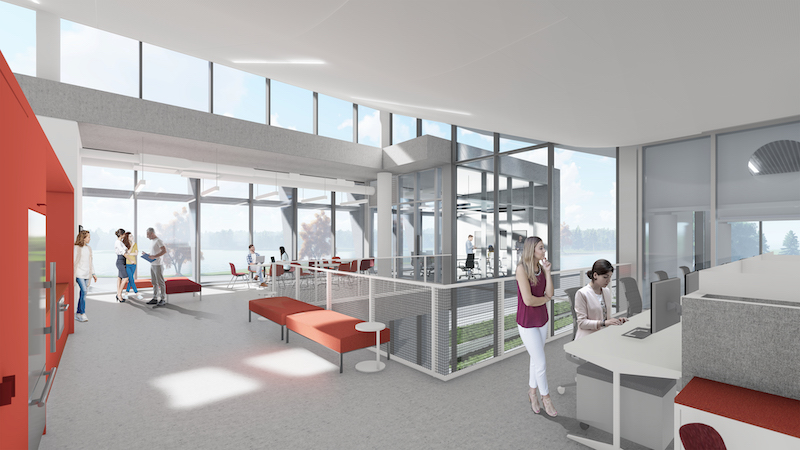

Open, collaborative spaces, designed modularly for maximum flexibility, are IERC's hallmarks.
Keeping the mechanicals off the roof will present a more aesthetically pleasing appearance for a building that, when it’s completed in October 2022, will be a centerpiece of Fermilab’s campus. Prominently featured in IERC’s design is its glassed-in Argon Cube, located at the northeast corner of the building. The Argon Cube is an R&D space related to Liquid Argon (Lar) in support of the DUNE (Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment) and the LBNF (Long Neutrino Baseline Facility). It houses the Liquid Argon cryostat vessel, where Fermilab will test the detector components and advance study related to using Lar cryogenics in filtration and air contamination recovery.
A TIGHT JOBSITE
This project presented an array of physical challenges to the Building Team, which includes Mortenson (GC/CM) and Terra Engineering (CE).
“Terra’s role was especially important, as there were a lot of utilities running into this building,” says Thomas Mozina, Design Principal for Perkins and Will, whom BD+C interviewed last week with Adana Johns, AIA, LEED AP, the firm’s Associate Principal and Science + Technology Practice Leader.
Mortenson has been prepping IERC’s site, adjacent to Wilson Hall, since July 2019. The location is constrained by the formal “horseshoe” entry drive and a raised (8- to 10-ft-tall) berm that had been a radiation shield for a 1.25-mile-diameter Tevatron beam line, the main ring around the particle accelerator, which was deactivated in 2011. Tabares says that excavation was dictated by another, active particle accelerator beam. An electrical artery outside of the building also needed to be relocated.
“We’re kind of jammed into there,” says Rubik about the Center’s location.
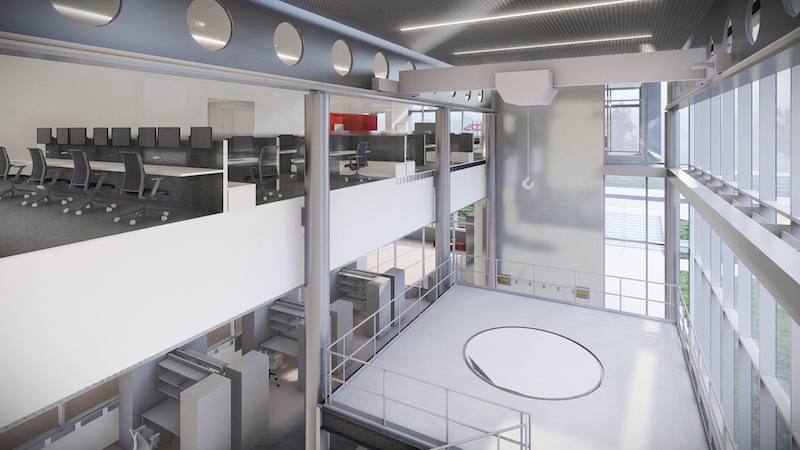

The Argon Cube, enclosed in glass for exterior visibility, is an example of IERC's “science on display.”
MODULAR DESIGN FOR FLEXIBILITY
Inside the IERC, Perkins and Will designed office and lab space “with a certain sense of modularity,” says Mozina, in order to provide Fermilab with the flexibility it needs as research evolves. (He describes the design as a kit of parts, and Johns doesn’t think the client will require many more changes in that design, “having already gone through so many iterations in the planning process.”)
Wilson Hall, which dates back to 1971, has 800 employees. It will connect with IERC at the former’s ground floor and 16-atory atrium level via a 20-ft-long enclosed runway.
Related Stories
| Oct 16, 2014
Perkins+Will white paper examines alternatives to flame retardant building materials
The white paper includes a list of 193 flame retardants, including 29 discovered in building and household products, 50 found in the indoor environment, and 33 in human blood, milk, and tissues.
| Oct 15, 2014
Harvard launches ‘design-centric’ center for green buildings and cities
The impetus behind Harvard's Center for Green Buildings and Cities is what the design school’s dean, Mohsen Mostafavi, describes as a “rapidly urbanizing global economy,” in which cities are building new structures “on a massive scale.”
| Oct 14, 2014
Proven 6-step approach to treating historic windows
This course provides step-by-step prescriptive advice to architects, engineers, and contractors on when it makes sense to repair or rehabilitate existing windows, and when they should advise their building owner clients to consider replacement.
| Oct 12, 2014
AIA 2030 commitment: Five years on, are we any closer to net-zero?
This year marks the fifth anniversary of the American Institute of Architects’ effort to have architecture firms voluntarily pledge net-zero energy design for all their buildings by 2030.
| Oct 9, 2014
Beyond the bench: Meet the modern laboratory facility
Like office workers escaping from the perceived confines of cubicles, today’s scientists have been freed from the trappings of the typical lab bench, writes Perkins+Will's Bill Harris.
| Oct 6, 2014
Frank Gehry's $100 million Eisenhower Memorial gets preliminary approval
After a rejection earlier in the year, Frank Gehry has gotten some good news: his revised design for the Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial has received approval from the National Capital Planning Commission.
| Oct 2, 2014
Budget busters: Report details 24 of the world's most obscenely over-budget construction projects
Montreal's Olympic Stadium and the Sydney Opera House are among the landmark projects to bust their budgets, according to a new interactive graph by Podio.
| Sep 24, 2014
Architecture billings see continued strength, led by institutional sector
On the heels of recording its strongest pace of growth since 2007, there continues to be an increasing level of demand for design services signaled in the latest Architecture Billings Index.
| Sep 22, 2014
4 keys to effective post-occupancy evaluations
Perkins+Will's Janice Barnes covers the four steps that designers should take to create POEs that provide design direction and measure design effectiveness.
| Sep 22, 2014
Sound selections: 12 great choices for ceilings and acoustical walls
From metal mesh panels to concealed-suspension ceilings, here's our roundup of the latest acoustical ceiling and wall products.