As experienced designers, contractors, and owners know, most paint and coating problems are correctable, but some are especially stubborn to address. The following is a partial compendium of typical failure modes and methods for addressing the problem, as provided by paint and coatings manufacturer Benjamin Moore & Co. (www.benjaminmoore.com):
1. Surface imperfections.
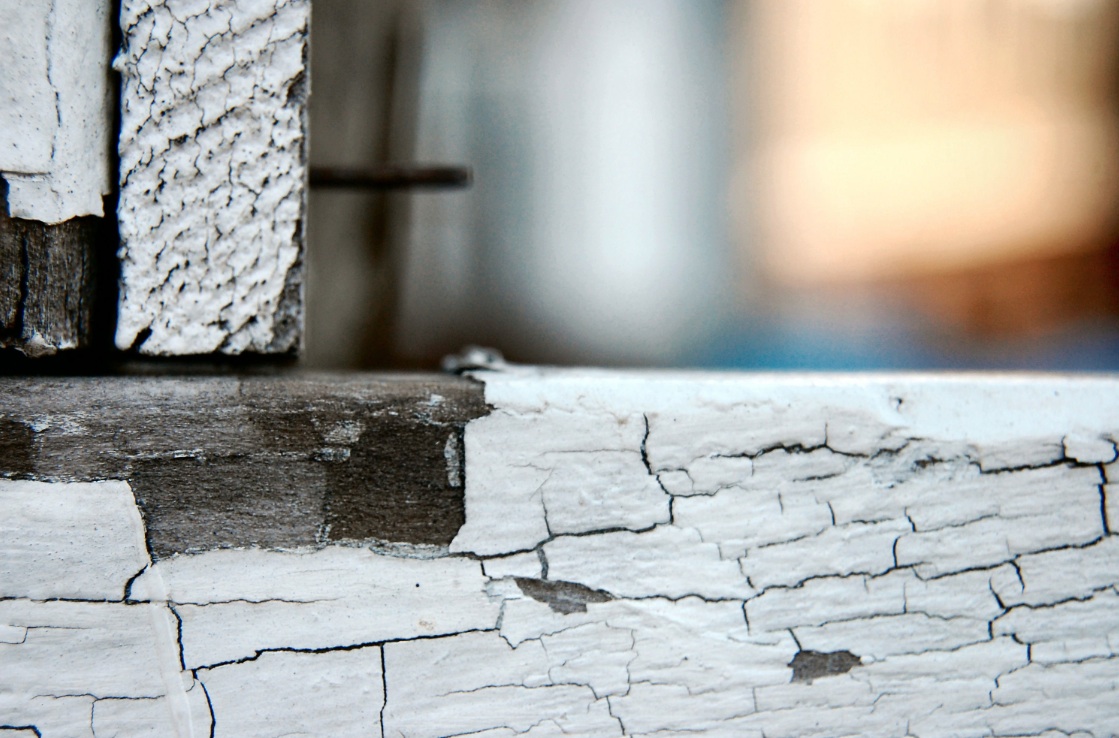
There are many types of imperfections that can be visible on painted or sealed surfaces. Alligatoring occurs when the paint film takes on the appearance of alligator hide. (A similar problem is known as wrinkling, which appears as a rough creased or crinkled pattern.) Alligatoring usually occurs when a topcoat is applied before an undercoat is dry, or if an alky enamel or other hard, rigid coating is applied over a latex primer or another more flexible finish layer. Some oil-based coats will lose elasticity as they age, causing this familiar cracking pattern.
2. Blistering.
Blistering (or bubbling) is caused by a localized loss of adhesion and lifting of the paint film from the underlying surface, sometimes when solvent gas expands on sunny façades. Blistering tends to occur in fresh coats of paint.
Both problems require removing as much paint as possible and repainting. However, blistering can immediately reappear if the problem is caused by moisture; to mitigate this problem, the contractor should repair loose caulk and retrofit drainage and drying details, if possible. Installing vents or exhaust fans can also reduce moisture by evaporation before it wets enclosure materials.
For alligatoring, most paint contractors will recommend completely remove the existing oil paint by using a heat gun, scraping, and sanding. After priming the reworked surface with a high-quality latex or oil-based primer, the area can then be recoated with exterior latex or similar paint.
3. Flaking and chalking.
In some cases, a painted or coated surface will exhibit a loose powder or flaking surface. These problems are caused by decomposing paint and are different from efflorescence or mottling, which display white, crusty mineral salt deposits that have leached from mortar, concrete, or masonry surfaces behind the paint. A similar problem known as frosting is often seen on dark paints and coatings; in this case, a white discolored substance appears on the surface, similar to salt staining.
Chalking paint may be washed by rain and cause patterns, or it may wash across other surfaces, an effect called chalk rundown.
4. Miscoloring and staining.
Other sources of miscoloration on exterior and interior surfaces include nailheads and other penetrations that leach a rust-colored stain onto a surface, which often trails down from the location of the hardware. Mildew appears as black, gray, or brown spots or areas on the paint film or caulk bead.
5. Surfactant leaching.
Another source of undesired color change is surfactant leaching, in which concentrated, water-soluble ingredients in latexes seep to the paint surface, often creating a brownish blotchy or shiny appearance. Tannin staining can also be a brownish or tan discoloration on the paint surface, caused by wood tannins that leach through the paint film.
When applied properly onto suitably prepared substrates, architectural coatings will rarely exhibit these kinds of failures. Even better, when integrated into a thoughtful sustainability program, paints and coatings can be a partner in effective building designs that promote improvements to project economics and social considerations as well as protecting the environment.
Related Stories
| Mar 14, 2012
Firestone names 2012 Master Contractor Award Winners
Annual award acknowledges industry’s top roofing professionals.
| Mar 14, 2012
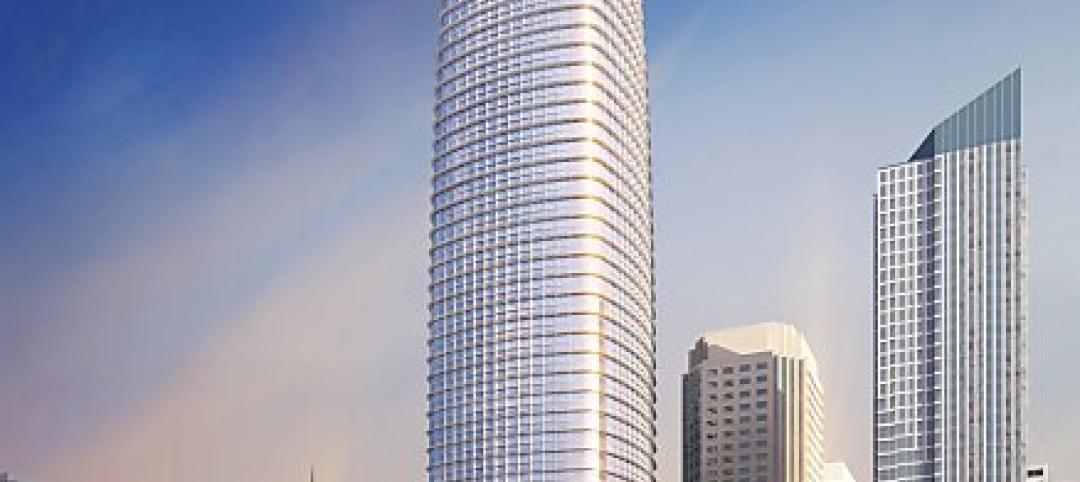
Plans for San Francisco's tallest building revamped
The glassy white high-rise would be 60 stories and 1,070 feet tall with an entrance at First and Mission streets.
| Mar 13, 2012
China's high-speed building boom
A 30-story hotel in Changsha went up in two weeks. Some question the safety in that, but the builder defends its methods.
| Mar 13, 2012
Commercial glazer Harmon expanding into Texas
Company expanding into the Texas market with a new office in Dallas and a satellite facility in Austin.
| Mar 13, 2012
Worker office space to drop below 100-sf in five years
The average for all companies for square feet per worker in 2017 will be 151 sf, compared to 176 sf, and 225 sf in 2010.
| Mar 7, 2012
Firestone iPad app offers touch technology
Free app provides a preview of Firestone’s Roots to Rooftop Building Envelope Solution with an overview of all the products from ground and stormwater management solutions, to complete wall panel and commercial roofing system applications.
| Mar 7, 2012
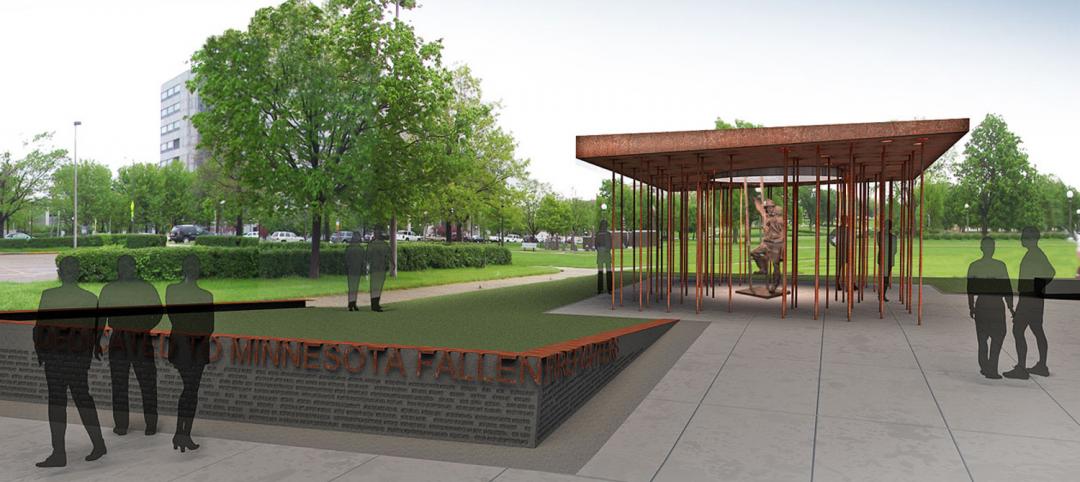
LEO A DALY selected to design Minnesota Fallen Firefighters Memorial
The bronze, figurative sculpture of a firefighter rescuing a child, which is currently on display at the Minneapolis/St. Paul International Airport, is lit by natural light through a circular void in the monolith.
| Mar 6, 2012
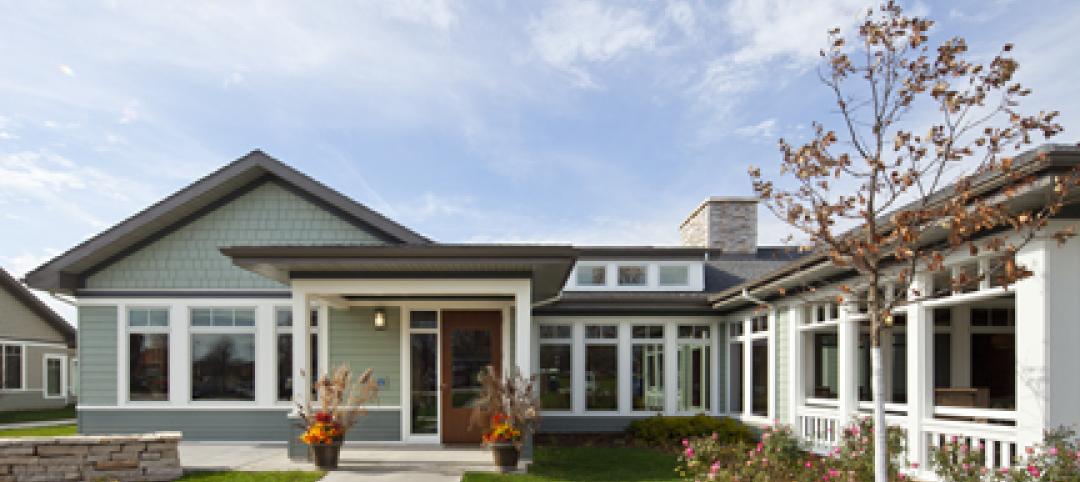
Country’s first Green House home for veterans completed
Residences at VA Danville to provide community-centered housing for military veterans.
| Mar 6, 2012
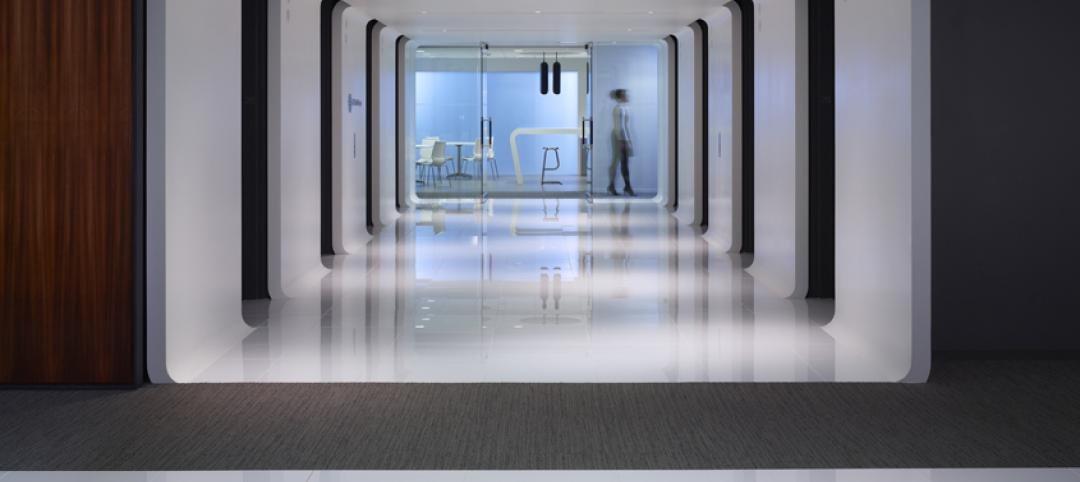
Gensler and Skender complete new corporate headquarters for JMC Steel in Chicago
Construction was completed by Skender in just 12 weeks.
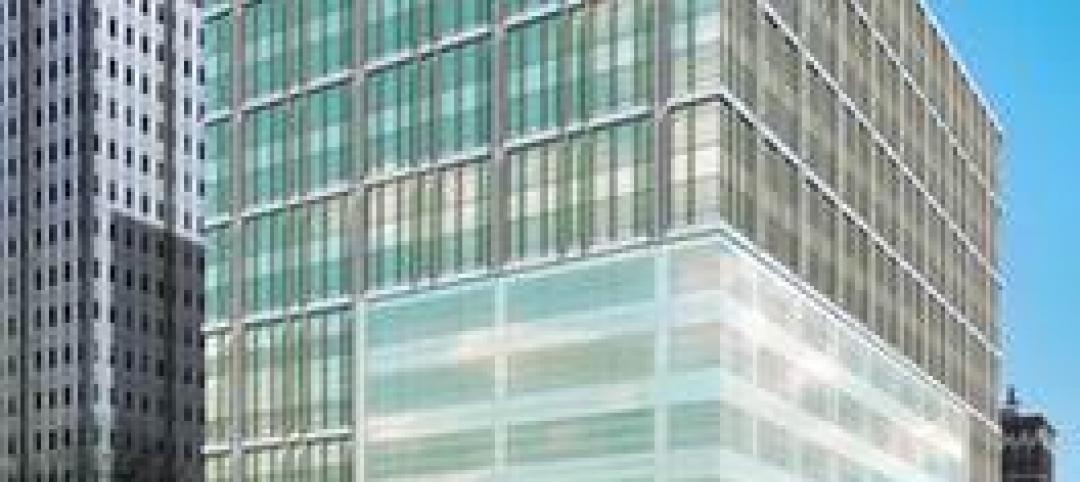
| Mar 5, 2012
Tishman constructing new courthouse in Philadelphia
Construction is underway for the Pennsylvania Department of General Services’ 510,000-sf facility.