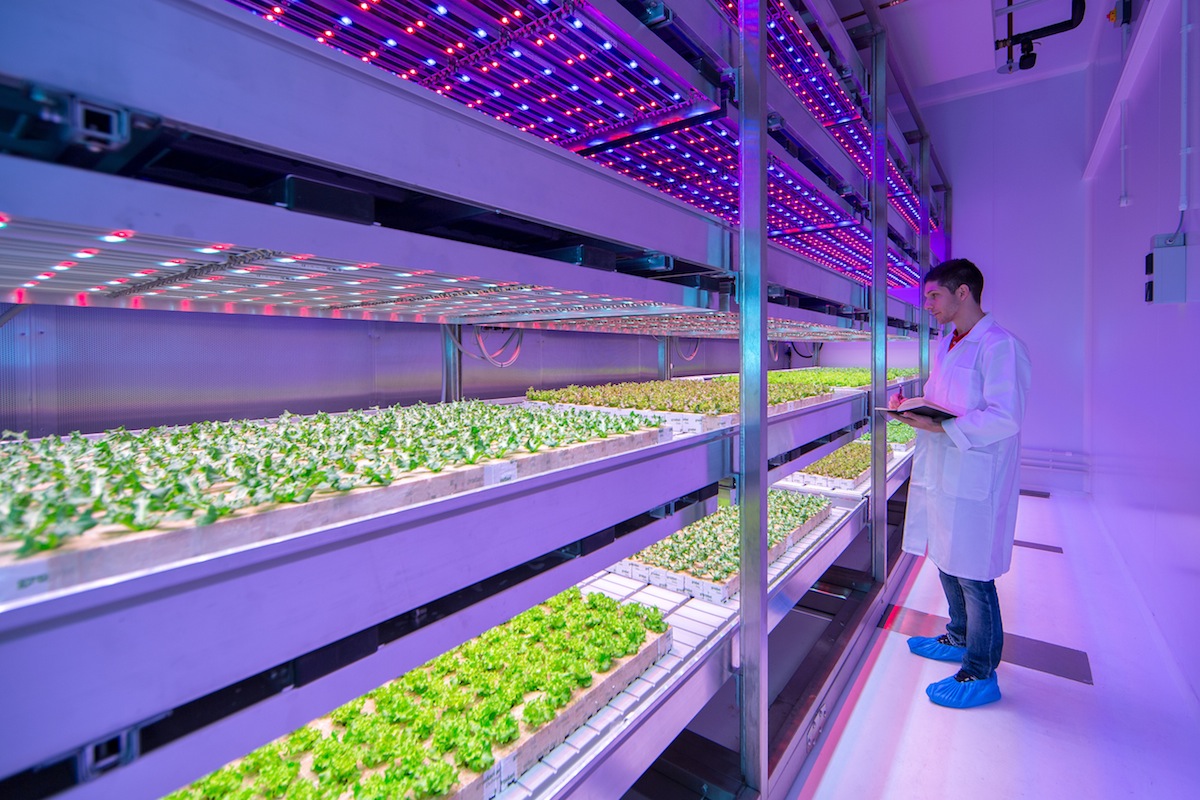
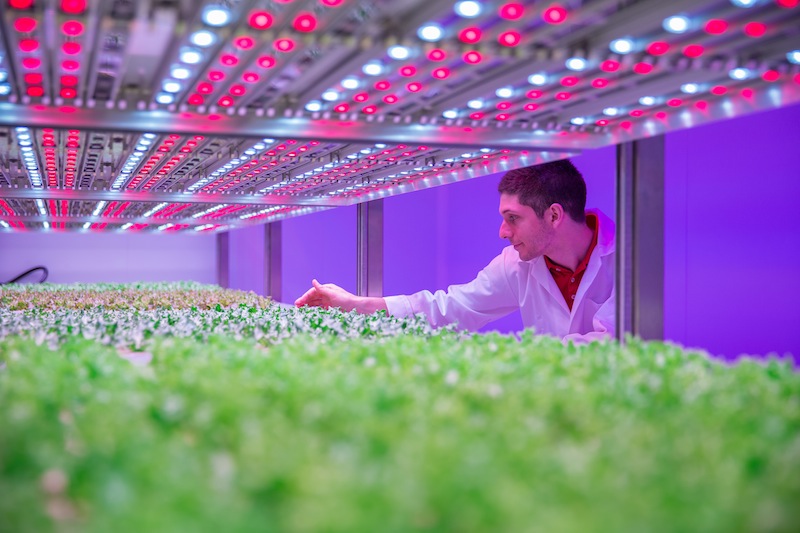
Royal Philips, the global lighting supplier, has opened a 234-sm (2,519-sf) facility at the High-Tech Campus in Eindhoven, The Netherlands, which is conducting research with the goal of providing growers of fruits, vegetables, and herbs with LED light growing solutions. Other areas of research will focus on ways to grow more carbohydrate-rich crops, such as potatoes and wheat, indoors.
The facility, known as the Philips GrowWise City Farming research centre, uses connected LED systems that are customizable, allowing for the development of “growth recipes” tailored to each crop variety or a producer’s requirement, reports Inhabitat.
“Our aim is to develop the technology that makes it possible to grow tasty, healthy, and sustainable food virtually anywhere,” says Gus van der Feltz, Philips’ Global Director of City Farming. “The research we are undertaking will enable local food production on a global scale, reducing waste, limiting food miles, and using practically no land or water.”
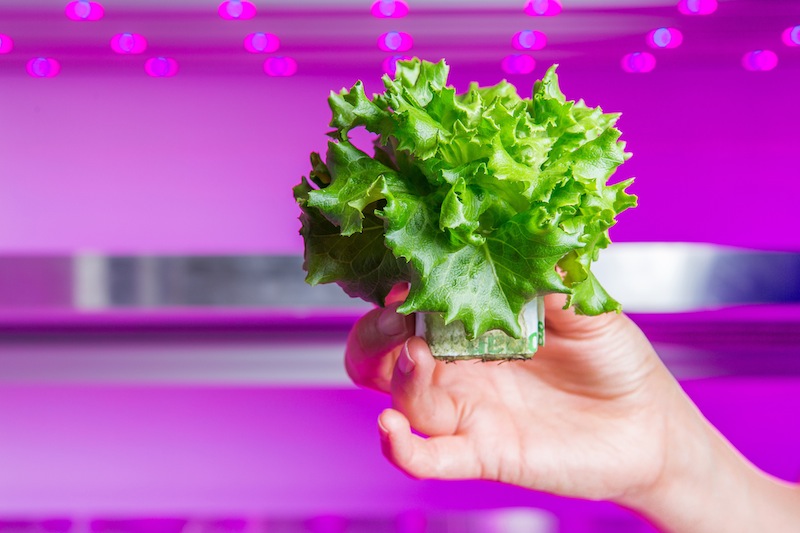
Philips’ team has been able to change the shape, size, productivity and even oil content of many leafy greens and herbs. And because the plants can be stacked in layers, each with its own lighting system, sizable quantities of food can be grown in relatively small spaces.
The research center, one of the largest of its kind in the world, features four-layered mechanized planting racks in each of its eight climate rooms.
Philips’ team has been able to change the shape, size, productivity and even oil content of many leafy greens and herbs. And because the plants can be stacked in layers, each with its own lighting system, sizable quantities of food can be grown in relatively small spaces.
One of Philips’ partners churns out 900 pots of basil per year from one square meter of floor space. And with the cells being sealed and managed under strict hygienic protocol, the need for pesticides and chlorine washing can be significantly reduced, if not eliminated.
Philips, which has been active in horticultural lighting since 1936, has equipped several city farms, including GreenSense in Chicago. (Watch a short YouTube video to see what one of these farms looks like by clicking here.)
The company is hoping that its research facility will unleash lighting and technology innovations that, according to its press release, “will bring farm and fork within a few miles of each other,” and provide year-round growing solutions.
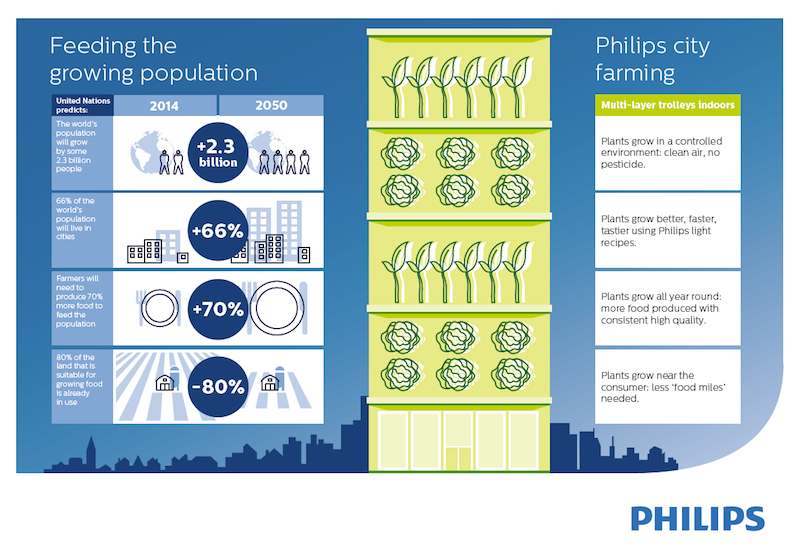
Royal Philips is launching this research center at a time when the world’s food supply is under increasing duress. The United Nations forecasts that by 2050, the world’s population will increase by 2.3 billion people, and that two-thirds of the total population will be living in cities.
In addition, 80% of the world’s arable land is already in use, a good part of which is struggling because of water shortages.


Related Stories
| Nov 11, 2013
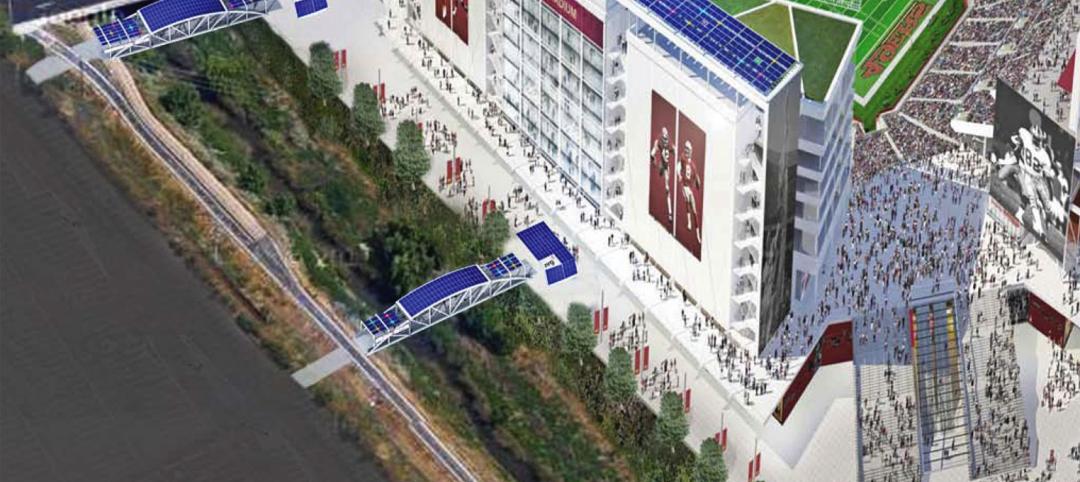
New San Francisco 49ers stadium will achieve net zero thanks to 49 large solar panels
The installation of 49 large rooftop solar panels at the 49ers new stadium outside San Francisco will help the arena achieve net-zero energy use, according to NRG, the company that installed the panels.
| Nov 8, 2013
Can Big Data help building owners slash op-ex budgets?
Real estate services giant Jones Lang LaSalle set out to answer these questions when it partnered with Pacific Controls to develop IntelliCommand, a 24/7 real-time remote monitoring and control service for its commercial real estate owner clients.
| Nov 8, 2013
S+T buildings embrace 'no excuses' approach to green labs
Some science-design experts once believed high levels of sustainability would be possible only for low-intensity labs in temperate zones. But recent projects prove otherwise.
| Nov 8, 2013
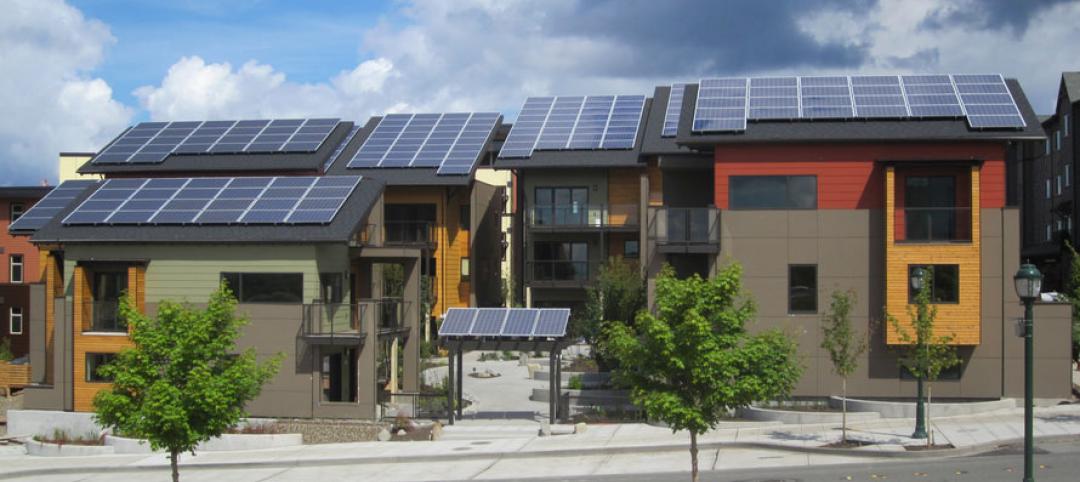
Net-zero bellwether demonstrates extreme green, multifamily style
The 10-unit zHome in Issaquah Highlands, Wash., is the nation’s first net-zero multifamily project, as certified this year by the International Living Future Institute.
| Nov 8, 2013
Exclusive survey: Architects balance ideals, skepticism regarding green strategies
Architects are seeking affirmation that the complex array of programs, systems, and tools at their disposal actually do result in more sustainable buildings, according to a recent survey of architects by Building Design+Construction.
| Nov 6, 2013
Energy-efficiency measures paying off for commercial building owners, says BOMA study
The commercial real estate industry’s ongoing focus on energy efficiency has resulted in a downward trend in total operating expenses (3.9 percent drop, on average), according to BOMA's Experience Exchange Report.
| Nov 5, 2013
Living Building Challenge clarifies net-zero definitions and standards
The Living Building Challenge has released the Net Zero Energy Building Certification to provide clearer definitions regarding what net zero really means and how it is to be achieved.
| Nov 5, 2013
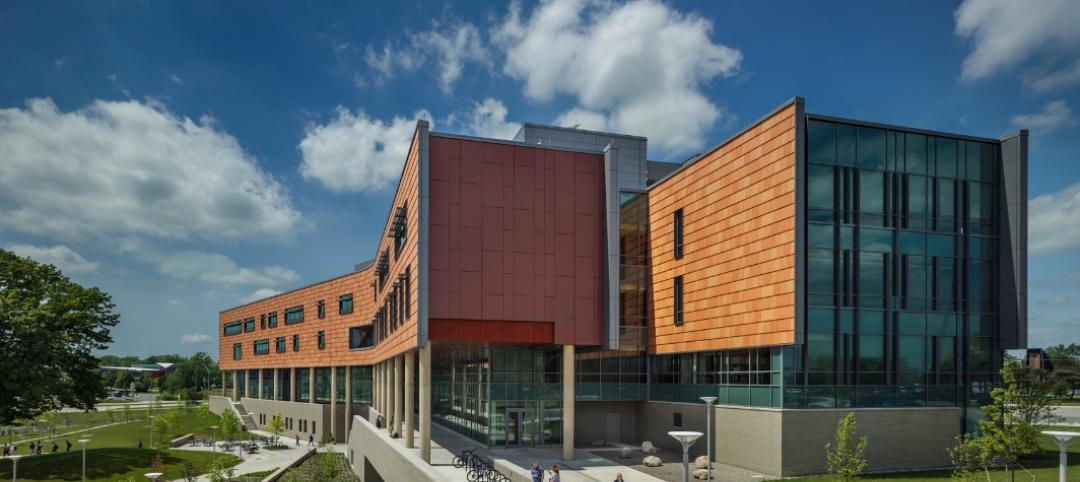
Oakland University’s Human Health Building first LEED Platinum university building in Michigan [slideshow]
Built on the former site of a parking lot and an untended natural wetland, the 160,260-sf, five-story, terra cotta-clad building features some of the industry’s most innovative, energy-efficient building systems and advanced sustainable design features.
| Oct 28, 2013
Packard Foundation’s headquarters receives ILFI Net Zero certification
The Packard Foundation’s 49,000-sf headquarters recently achieved Net Zero Energy Certification through the International Living Future Institute (ILFI), making it the largest such building in the world.
| Oct 21, 2013
University of Queensland’s net-zero building features biomimicry-based design
University of Queensland’s Global Change Institute (GCI) building in Australia showcases on-site solar energy sources, biomimicry-based design features, and the first structural use of low-carbon concrete in the country.