The recent report of the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis, is not a happy read.
The IPCC report provides new estimates of the chances of crossing the crucial global warming level of 1.5°C in the coming decades. It finds that “unless there are immediate, rapid, and large-scale reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, limiting warming to close to 1.5°C or even 2°C will be beyond reach.” A 1.5°C increase in global warming is believed to be the point at which climate change would be irreversible. To quote the report’s chief author, Joeri Roejl, PhD, “The greater weight of evidence has confirmed the trend, as expected, and it’s not really good news.”
As you’ve heard many times, existing and new-construction buildings and homes are the biggest source of global carbon emissions: 39%—28% for operations (heating and cooling, lighting, etc.), 11% for building materials and construction. (“Industry” contributes 32%; “transportation,” 23%.) Clearly, the building sector plays the leading role in this global drama.
SUSTAINABILITY AND CLIMATE CHANGE, CIRCA 2003
At Building Design+Construction, we’ve been writing about ways AEC professionals and building product manufacturers have improved energy and water efficiency in buildings since well before the scientific community had firmly established humankind’s role in climate change.
In 2003, as the U.S. Green Building Council and its powerful new green building certification system, LEED, were ramping up, we published our “White Paper on Sustainability,” the first in-depth investigation of the fast-emerging green building movement, and followed it up in 2004 with a “Progress Report on Sustainability.”
Each of these reports offered specific recommendations for action, such as “launch a pilot program in 10 large public school districts to measure the impact of green schools on student achievement and health,” and named the parties who should be responsible for carrying out these measures (in this case, six schools organizations and government entities) and "promote a national program to reduce construction and demolition waste by 50% in five years" (progressive GC firms would be hitting 90-95% C+D waste reduction in very short order).

BD+C PUBLISHES ‘GREEN BUILDINGS + CLIMATE CHANGE’ WHITE PAPER
In 2008, we published our most ambitious white paper, a 40,000-word, 64-page report, “Green Buildings + Climate Change,” which spelled out 22 practical steps that design and construction firms could take to flatten the GHG growth curve.
Some of our recommendations were fairly easy for the AEC community to undertake; for example, AEC firms should “fit out your own office to reduce GHG emissions”—a practical step many AEC firms have taken in the interim, often at the LEED Platinum level.
Other recommendations had more bite and required considerably greater investment of time, money, and thinking by larger and more extensive constituencies:
- “Give much greater attention to special threats to waterfront developments and buildings in severe-weather zones”—as evidenced by 2012’s Superstorm Sandy and, recently, more frequent and powerful superstorms and hurricanes.
- “Cities and counties should plug the leaks in the 72,000 miles of water pipes and sewer mains” that were 80 years old or more at that time (sounds like an early call for an infrastructure program, doesn’t it?)
ENCOURAGING THE USE OF SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTS
Two recommendations from the 2008 report merit further consideration today.
The first advised AEC firms to “work with your clients to encourage them to use the most energy-efficient products and systems in their [building] projects.”
Since the early days of LEED, we have seen the proliferation of certification programs for building products—Greenguard, Greenseal, Cradle to Cradle, FSC and SFI (for wood), Red List Free, etc. There are now more than 50 certification programs for building products, buildings, homes, whole neighborhoods, sites, parking structures, schools, and more.
The second recommendation from 2008 encouraged AEC firms to “leverage your supply chain to achieve GHG reductions.” We noted that Turner Construction, the largest building contractor in the U.S. (currently, $14 billion/year in construction), purchases many building products and equipment in high volume to achieve dollar savings for its clients.
We recommended that “giant GCs” like Turner—as well as states, counties, and cities—take this tool one step further and use their purchasing power to “encourage (or require) suppliers to post the carbon emissions of their products and systems online or in their purchase orders.” Many suppliers are doing that in one form or other, via environmental or health product declarations) or via so-called ESG (environmental, social, and governance) impact reports.
Recommendations like these from 13 years ago may seem modest in the context of the current climate crisis, but they were fairly radical at the time and often drew criticism from some in the AEC world who denied that human activity had any role in climate change.
AECO FIRMS TAKING ACTION ON CLIMATE CHANGE
Today, there is a burning desire among progressive architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as well as among forward-thinking real estate development companies, to address climate change.
Eight hundred architecture irms have signed on to the AIA 2030 Commitment to achieve carbon neutrality in their building projects by 2030. The Carbon Leadership Forum is shedding light on the embodied carbon content of building materials and products. The ILFI’s Living Building Challenge 4.0 is pushing AEC firms higher and higher in terms of sustainable design, especially regarding materials.
Just 10 years ago, net-zero buildings were thought to be impossible to achieve. (See “Zero + Net-Zero Energy Buildings + Homes,” March 2011.) Today, net-positive buildings — those that make more energy than they use — are being built.
LATEST CONCERN: CUTTING JOB-SITE CARBON EMISSIONS
This past July, AGC of America formed a Climate Change Task Force to hone in on “the top impacts associated with climate change for construction markets and construction firms.”
Among the task force members are The Beck Group, Clark Construction Group, Linbeck Group, McCarthy Holdings, and Swinerton.
One of the “discussion points” that the AGC Task Force plans to undertake is to “engage with equipment manufacturers to improve energy efficiency and emissions performance without sacrificing safety or power output.”
“Construction activity” accounts for less than 2% of global GHG emissions, but that’s not stopping the nation’s major contractors from pushing construction equipment manufacturers and suppliers to slash carbon emissions on the job site. One sustainability director told me that their firm was committed to cutting on-site GHG emissions by 50% by the end of this decade.
In Northern California, a coalition of GCs called the Bay Area Sustainable Construction Leaders is asking equipment manufacturers and rental companies what they’re doing to electrify their fleets. All the major equipment makers, from Caterpillar to Volvo, know they have to electrify as quickly as possible. Ford has introduced the all-electric F-150 Lightning work truck. Sunbelt Rentals has issued a “Sustainability Plan 2030” that aligns with eight of the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals. It’s a movement that would have been unheard of 10 years ago,
‘SUSTAINABILITY’ NOW ALSO MEANS ‘WELLNESS’ AND ‘RESILIENCE’
These days, “sustainability” is much more than energy savings (although saving energy remains crucial to reducing carbon emissions). Protecting the health and wellness of building occupants, visitors, and staff has become a huge component of sustainability, especially in light of the Covid pandemic. Programs like WELL Certified and Fitwel Ambassadors are addressing AECO professionals’ concerns about healthy buildings, just as the RELi standard is taking on building resilience. The climate change landscape is getting wider and deeper than ever.

NEW ‘PROCONNECT’ PROGRAM ADDRESSES SUSTAINABILITY
This year, in response to the rapidly developing global warming landscape, Building Design+Construction and our parent company, SGC Horizon, have introduced ProCONNECT Sustainability | Wellness | Resilience (Nov 2-3, 2021, 11am to 4:25pm ET).
ProCONNECT Sustainability gives AEC Professionals and Developers with responsibility for high-performance buildings — Chief Sustainability Officers, Directors of Sustainability, LEED Fellows, LFAs, WELL APs, resilience directors, net-zero building experts, and other “climate-action champions” — the opportunity to meet one-on-one with top product manufacturers to discuss their firms’ climate-action, wellness, and resilience agendas and discover practical solutions that can enhance their firms’ high-performance projects.
More than 40 AEC firms, developers, and consultants have committed to participating in ProCONNECT Sustainability. There is no charge for Attendees. To learn more, click here.
Building product manufacturers and suppliers who would like more information about sponsoring ProCONNECT Sustainability can contact: Dan Gardner, dgardner@sgcmail.com, 989.860.7930, or click here.
Related Stories
Higher Education | Mar 23, 2015
Hong Kong university building will feature bioclimatic façade
The project's twin-tower design opens the campus up to the neighboring public green space, while maximizing the use of summer winds for natural ventilation.
Codes and Standards | Mar 12, 2015
Energy Trust of Oregon offers financial incentives for net-zero buildings
The organization is offering technical assistance along with financial benefits.
Codes and Standards | Mar 5, 2015
AEC industry groups look to harmonize green building standards, codes
The USGBC, ASHRAE, ICC, IES, and AIA are collaborating on a single green code.
Green | Feb 23, 2015
State of the green union, and the next big shift in sustainability
The history of the green movement offers cues that we are on the precipice of another significant shift in the green union.
Codes and Standards | Feb 18, 2015
USGBC concerned about developers using LEED registration in marketing
LEED administrators are concerned about a small group of developers or project owners who tout their projects as “LEED pre-certified” and then fail to follow through with certification.
Codes and Standards | Feb 12, 2015
ASHRAE, USGBC, IES consider biomass requirements in green building standard
The proposal would add biomass to approved renewables.
Sponsored | Green | Jan 26, 2015
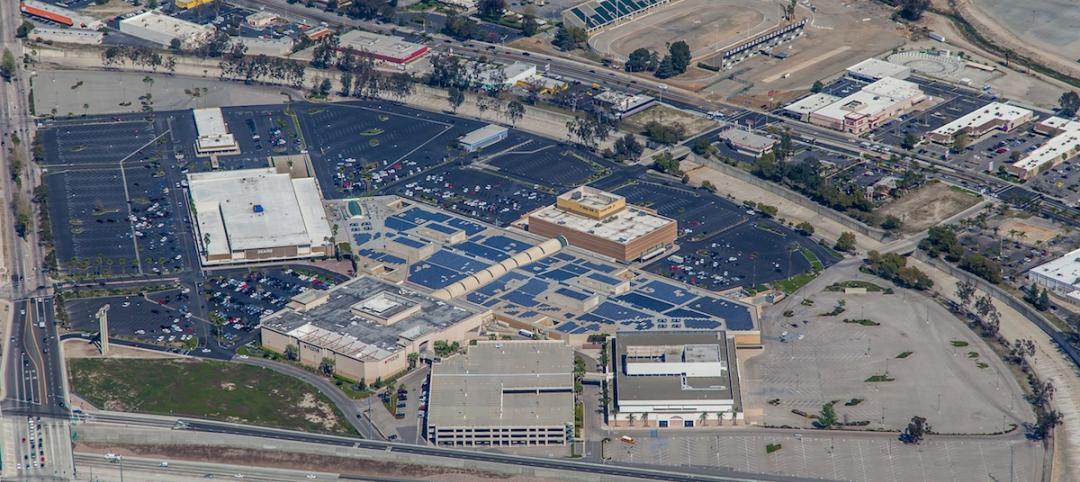
Shopping centers set their sight on solar
As part of its pledge to environmentally sound practices, real estate investment trust Macerich is implementing solar across its portfolio of 85-plus properties in 19 states.
| Jan 21, 2015
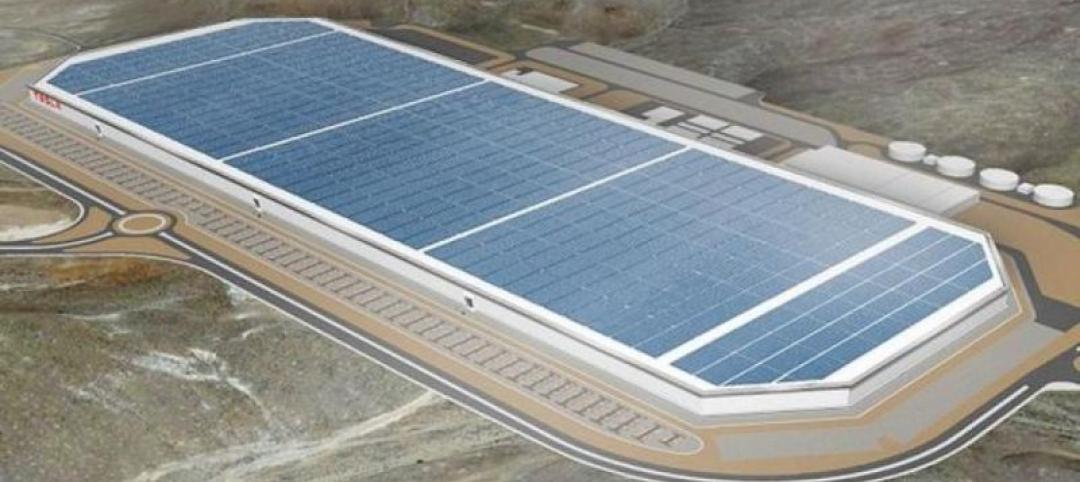
Tesla Motors starts construction on $5 billion battery plant in Nevada
Tesla Motors’ “gigafactory,” a $5 billion project on 980 acres in Sparks, Nev., could annually produce enough power for 500,000 electric cars.
| Dec 29, 2014
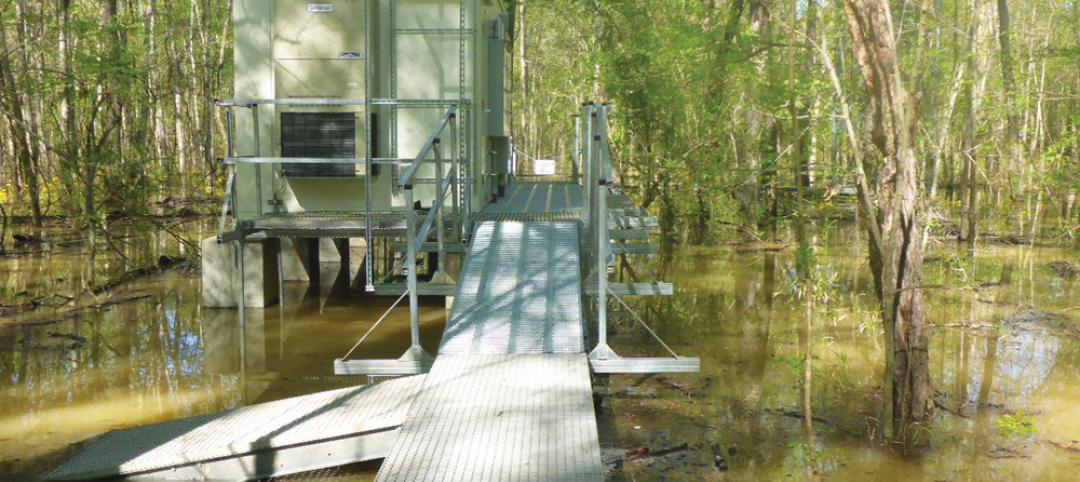
Leo A Daly's minimally invasive approach to remote field site design [BD+C's 2014 Great Solutions Report]
For the past six years, Leo A Daly has been designing sites for remote field stations with near-zero ecological disturbance. The firm's environmentally delicate work was named a 2014 Great Solution by the editors of Building Design+Construction.
| Dec 28, 2014
Using energy modeling to increase project value [AIA course]
This course, worth 1.0 AIA LU/HSW, explores how to increase project value through energy modeling, as well as how to conduct quick payback and net present value studies to identify which energy strategies are most viable for the project.