There are three things that are certain in life: death, taxes, and employees being uncomfortable with the ambient temperature of their offices. While some reach for Sherpa-lined blankets and cups of hot tea, others work up a lather that would give Paul Newman in “Cool Hand Luke” a run for his money. Not only is it difficult to find a temperature where everyone is comfortable, heating and cooling a building is also costly.
But what if you could heat the individual building occupants instead of the building itself? Not only would everyone be more comfortable, but it would also present an opportunity to conserve energy.
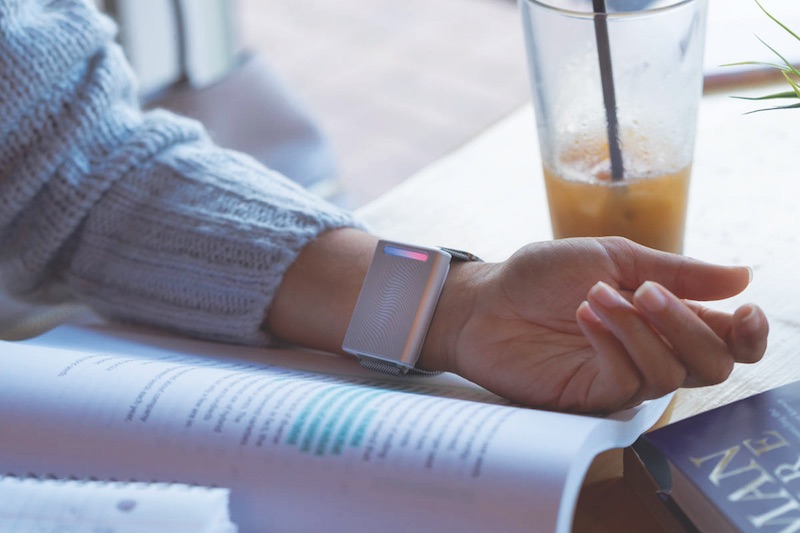
New wearable technology from Embr Labs, known as the Embr Wave, gives each wearer direct control over their own temperature. It utilizes the human body’s natural response to temperature to provide thermal relief by warming and cooling the user’s wrist.
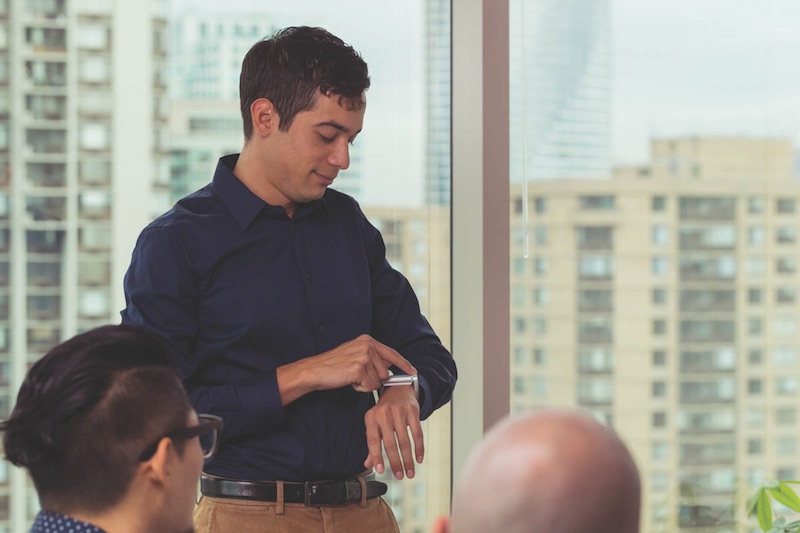 Photo: Embr Labs.
Photo: Embr Labs.
Founded at MIT, the Embr Wave uses a cooling and warming thermoelectric module to help a user feel more comfortable. The temperature is controlled via a light bar located on a nickel-free anodized aluminum body.
Say a user is feeling a bit on the warm side. All they need to do is press the left side of the Embr Wave, and a cooling sensation will begin to spread across their wrist. As the Embr Wave is cooling, the aluminum heat sink warms up to dissipate heat. Press the right side and the Embr Wave will turn up the heat to warm a cold user. Because the device uses conduction heating and cooling, it can be more efficient, precise, and immediate than traditional air-conditioning or heaters.
EYP Architecture and Engineering recently equipped some of its employees with the Embr Wave and embarked on a five-week pilot study to collect product feedback and data. Nearly three-quarters (72%) of the participants said they felt more in control of their own thermal comfort while using the Embr Wave. Factors such as environmental space metrics, temperature, humidity, and other thermal data were collected and analyzed against participant surveys throughout the duration of the study.
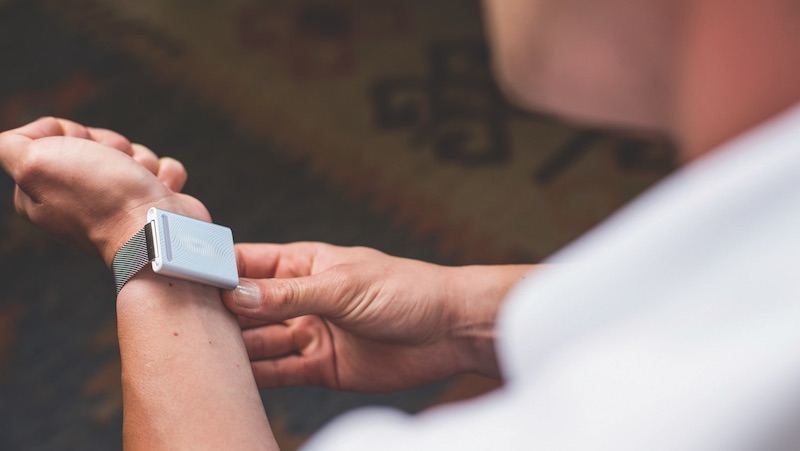 Photo: Embr Labs.
Photo: Embr Labs.
EYP’s main goals of the study were to discover if the Embr Wave could improve human comfort, fuel productivity, and present opportunities to conserve officewide energy consumption. With the vast majority of participants saying they felt more in control of their own thermal comfort while wearing the device, EYP believes there is a potential opportunity to incorporate personal comfort devices, such as the Embr Wave, in building design planning.
EYP's participation in this study showcases how many architecture and design firms are taking an interest in their buildings long after construction has been completed in order to gain insight into how to plan more comfortable, energy-efficient, and sustainable spaces in the future.
Related Stories
Great Solutions | Sep 14, 2017
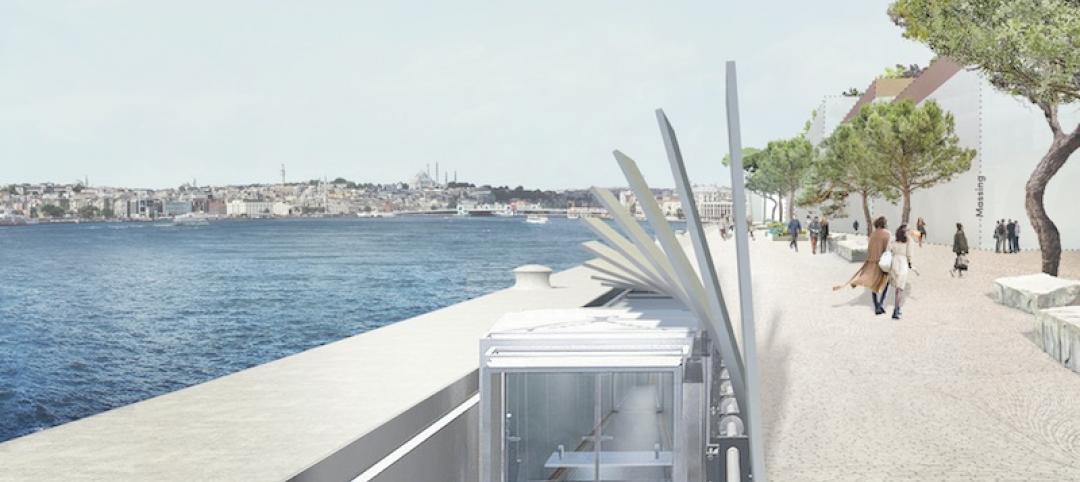
Hydraulic underground boardwalk and gangway system reunites the public with the coastline in Istanbul
The bespoke system is part of a master plan by Dror and Gensler that creates the world’s first underground cruise operation.
Great Solutions | Aug 14, 2017
Transmogrifying ‘E ink,’ energy-harvesting paint remove the ‘fiction’ from ‘science fiction’
These materials can turn an ordinary wall into dynamic real estate.
Great Solutions | Jul 12, 2017
The writing on the wall: Maker spaces encourage students to take an active role
Maker spaces, dry-erase walls, and flexible furniture highlight Kinkaid’s new Learning Center.
Great Solutions | Jun 6, 2017
Good vibrations: Portable tuned mass damper provides lightweight, cost-effective way to reduce structural vibrations
Developed by a team at Virginia Tech, the PTMD has been shown to reduce vibrations by as much as 75%.
Great Solutions | May 5, 2017
No nails necessary: Framing system comes together with steel zip ties and screws
Clemson University’s School of Architecture develops a patent-pending construction method that is gaining attention for its potential use in rapid, low-tech sustainable housing.
Great Solutions | Apr 6, 2017
Phone booths for the 21st century
Spotting a phone booth on a public street may not become any less rare, but they may soon become fixtures in the modern office.
Great Solutions | Mar 8, 2017
Pop-out balcony is a breath of fresh air for stuffy hotel rooms and apartments
In less than one minute, Bloomframe transforms from an insulated picture window to an open balcony.
Great Solutions | Feb 3, 2017
Drone-based hospitality concept looks to make nomads of us all
Driftscape could take the resort industry to places no hotel has ventured before.
AEC Tech | Sep 6, 2016
Innovation intervention: How AEC firms are driving growth through R&D programs
AEC firms are taking a page from the tech industry, by infusing a deep commitment to innovation and disruption into their cultural DNA.
Great Solutions | Aug 23, 2016
GBBN designers take on wellness research
In a new research paper, three healthcare specialists present factors that contribute to a psychological state that is receptive to healing.
















