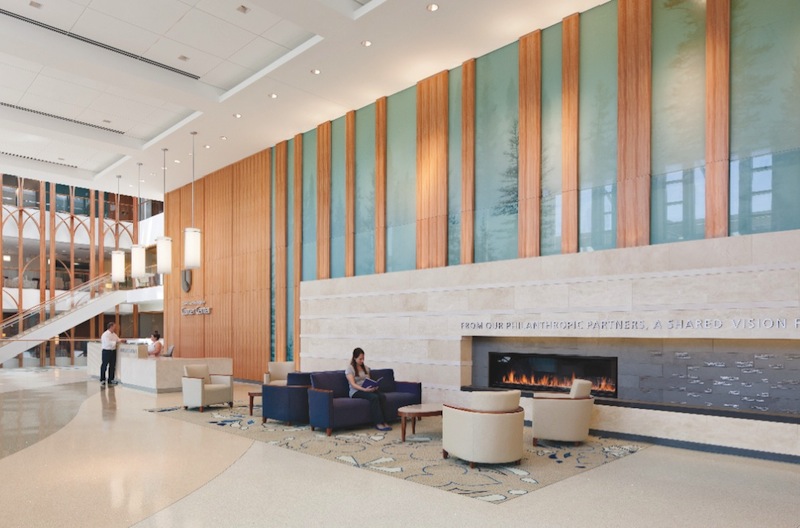
Editor's note: This article was published as part of our March 2013 report on hospital lobby design stategies.
If you do hotels, schools, student unions, office buildings, performing arts centers, transportation facilities, or any structure with a lobby, here are six principles from healthcare lobby design that make for happier users—and more satisfied owners.
1. Select durable furnishings. Fancy chairs can be appealing, but not if they quickly turn shabby with use. TK&A’s Kate Wendt suggests high-wearing polyester and vinyl materials. “The seat takes the most abuse,” says Wendt. “You can usually do something different on the back, but it all has to be cleanable.”
2. Manage traffic. Hospital access and egress are often complex, due to a higher-than-usual percentage of disabled visitors. Healthcare Building Teams typically make extensive provisions for wheelchair access and storage, and for vehicular drop-off and drive-up. Beyond minimal ADA compliance, how welcoming is your facility to people with disabilities?
3. Emphasize wayfinding. Many hospitals have a public mission to serve a diverse population. For them, multilingual signage is just the start of a good wayfinding strategy. Dedicated volunteer greeters often make life easier for visitors in healthcare environments. How hard is it for non-English-speaking visitors to navigate in public facilities you’re creating?
4. Control germs. Hospital clients may reject water features, live plants, and other design elements that could pose a sanitation risk, but such elements may be an asset to your client’s project. What can you do to help end users and visitors avoid spreading germs and keep maintenance to a minimum?
5. Keep floors dry. Because patients may be unsteady on their feet, hospitals pay strict attention to the location and length of walk-off mats. Puddles are hazardous, regardless of user groups. Do your projects make room for mats that are long and wide enough to sop up water and slush?
6. Match scale, budget, and need. TK&A’s Chu Foxlin says that many healthcare clients are questioning if it is necessary to have multiple-floor atrium spaces and large, open, idle program space, just to convey a sense of grandeur. “They are pushing us to give them an efficient lobby that is the right size for the traffic, with spaces that are flexible and multifunctional,” she says. What do your non-healthcare clients think about this?
Related Stories
| Jun 30, 2014
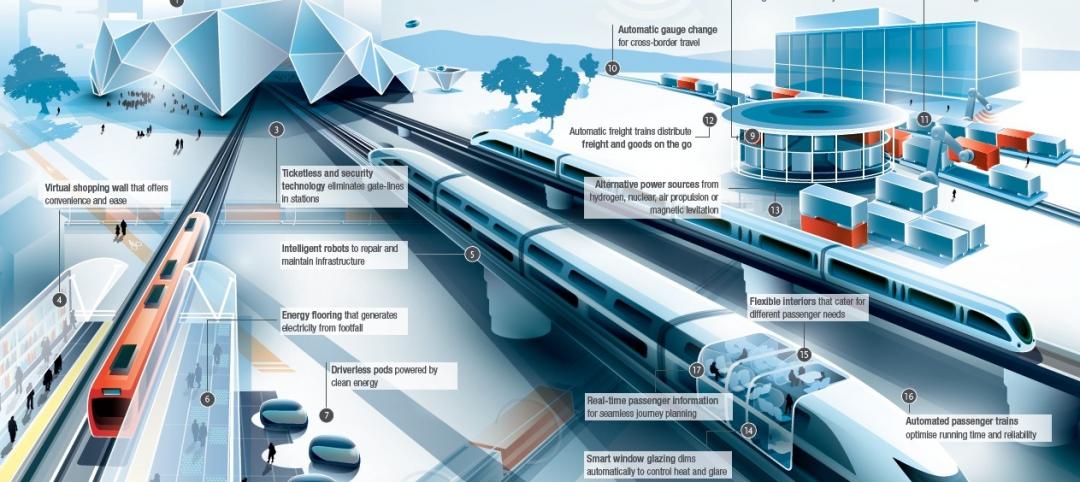
Arup's vision of the future of rail: driverless trains, maintenance drones, and automatic freight delivery
In its Future of Rail 2050 report, Arup reveals a vision of the future of rail travel in light of trends such as urban population growth, climate change, and emerging technologies.
| Jun 18, 2014
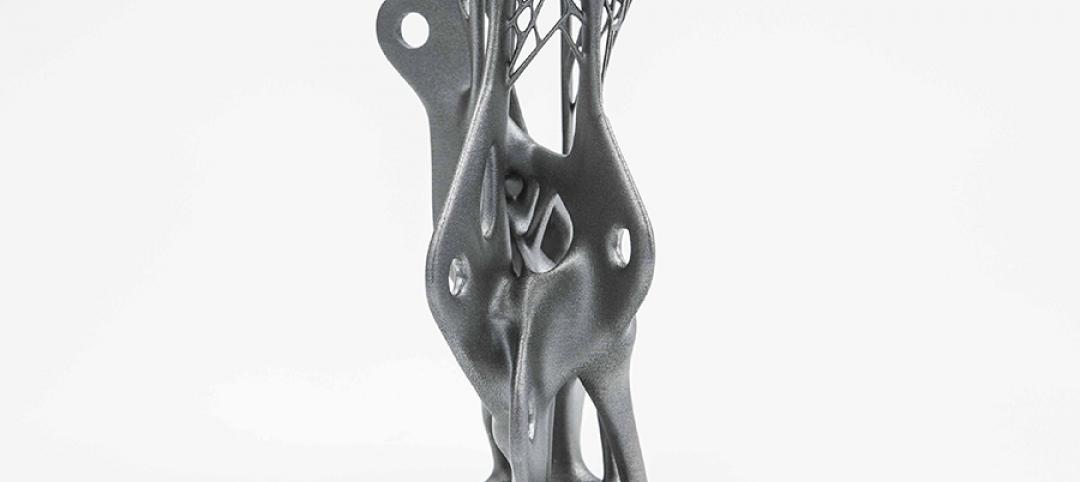
Arup uses 3D printing to fabricate one-of-a-kind structural steel components
The firm's research shows that 3D printing has the potential to reduce costs, cut waste, and slash the carbon footprint of the construction sector.
| Jun 12, 2014
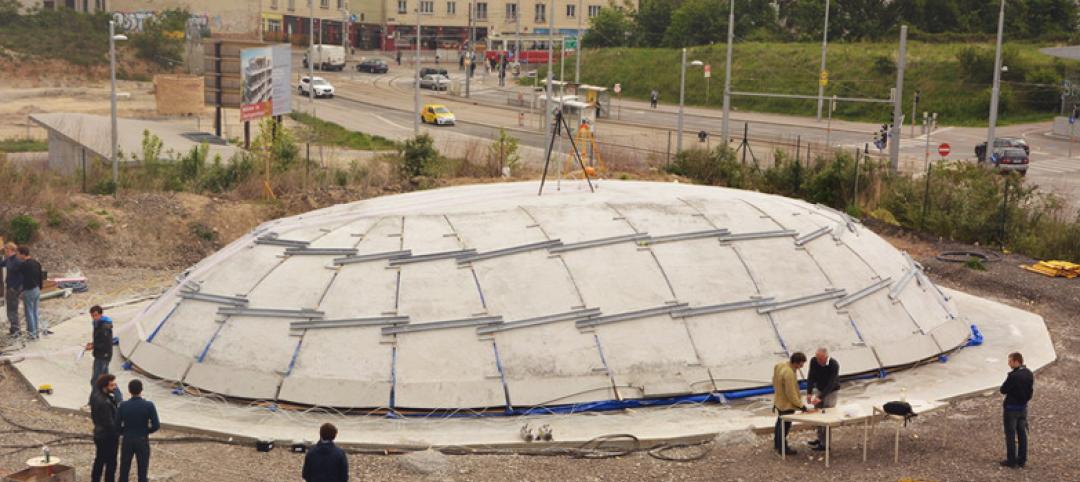
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 2, 2014
Parking structures group launches LEED-type program for parking garages
The Green Parking Council, an affiliate of the International Parking Institute, has launched the Green Garage Certification program, the parking industry equivalent of LEED certification.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 23, 2014
Top interior design trends: Gensler, HOK, FXFOWLE, Mancini Duffy weigh in
Tech-friendly furniture, “live walls,” sit-stand desks, and circadian lighting are among the emerging trends identified by leading interior designers.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.