Two of the construction industry’s heavyweights were instrumental in the development of new tools that measure embedded carbon in building materials, with an eye toward significantly reducing the carbon footprint of nonresidential buildings in the future.
On Nov. 19, the University of Washington's Carbon Leadership Forum used the Greenbuild expo in Atlanta to officially launch its Embodied Carbon in Construction Calculator (EC3), a free tool for calculating and evaluating carbon emissions embodied within an array of building products. Skanska co-conceived this open-source tool with C Change Labs, and with Microsoft provided seed funding. To accelerate its development, The Carbon Leadership Forum incubated EC3 with financial support from more than 30 industry leaders that included Autodesk, Interface, the MKA Foundation, and the Charles Pankow Foundation, which was the lead sponsor and grant manager.
EC3 is designed to allow contractors, owners, and designers to work together to examine data for common building materials and create an overall embodied carbon footprint for a project as well as a procurement strategy. EC3 is also the first tool to create a digital Environmental Product Declaration form and to translte all EPDs into that form for viewing and analyzing data.
“It is critical that owners, designers, engineers, contractors, and policy makers turn their attention to building materials, and seek information that will pave the wat to reduce embodied carbon,” says Kate Simonen, director of the Carbon Leadership Forums and a professor in the College of Built Enviornments at the University of Washington.
By the end of this year, the engineering firm Thornton Tomasetti will release its own embedded carbon measuring tool, called Beacon, which it created in-house for use in the Revit environment. Beacon, on the other hand, is more of a parametric tool, customized for structural engineers to measure how they are doing while they are working on a project.
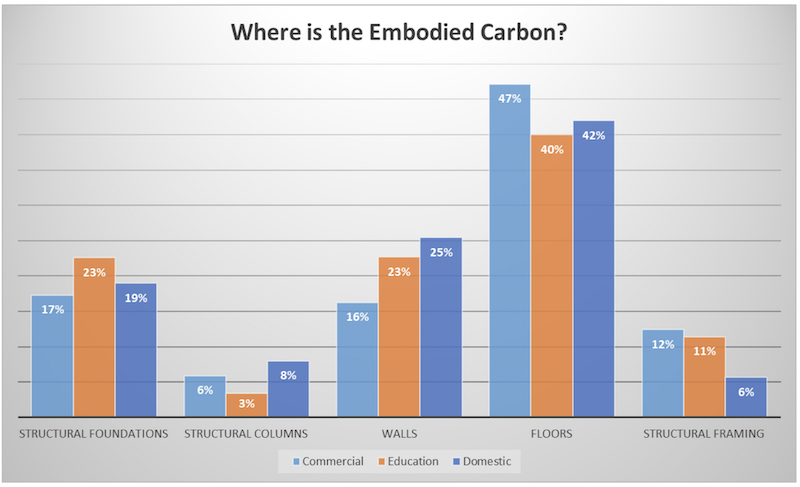
The data in these two charts were derived from a seven-year analysis that Thornton Tomasetti conducted on more than 600 structures.
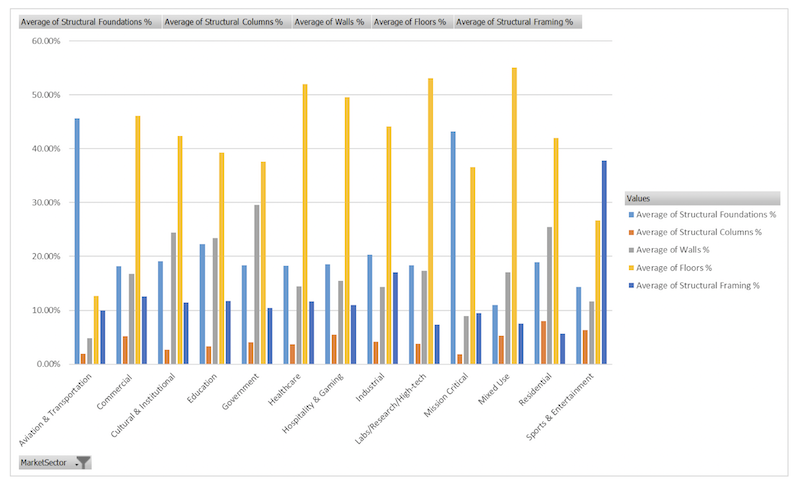
This week, Thornton Tomasetti released the findings of a seven-year study based on the measurement of embedded carbon in more than 600 projects. The findings from that study include the following:
•The largest driver of embodied carbon reduction in structures in the last seven years has been a market-driven trend toward using more recycled steel and supplementary cementitious materials such as fly ash.
•LEED-certified buildings show slightly lower embodied carbon levels than non-LEED buildings.
•Concrete structures show less embodied carbon levels than steel buildings.
•All building types—with the exception of aviation, sports and mission critical facilities—have the highest proportion of embodied carbon in their slabs. Alternative, low-carbon slabs such as hollow core, voided slabs or timber floors may be considered to reduce embodied carbon. In aviation and mission critical structures, the foundations hold the greatest embodied carbon, while in sports structures, the most embodied carbon is in the structural framing.
•Mission critical structures such as hospitals and data centers have the overall highest levels of embodied carbon of any asset category. Skyscrapers show the highest proportion of embodied carbon in their columns rather than foundations.
“We are sharing the first results of our ongoing study in the hope that it will serve to educate our peers and encourage them to contribute data so we can expand our research and support the development of more sustainable and better performing structures,” said Amy Seif Hattan, Thornton Tomasetti’s Corporate Responsibility Officer.
This study follows the launch of the Carbon Leadership Forum’s Structural Engineers 2050 Challenge, whose goal is to establish progressive steps to achieve zero-carbon buildings by 2050.
In that regard, the industry has its work cut out for it. Two trillion sf of buildings will be constructed or undergo significant renovation between 2015 and 2050 worldwide, according to the independent non-profit Architecture 2030. Over the average 30-year lifecycle of a new building completed in 2019, roughly half of its carbon will come from embodied carbon—or the emissions associated with building construction, including extracting, transporting and manufacturing materials.
“Considering that materials used for construction are estimated to consume 75% of all new materials annually by volume, the case for reducing the carbon emissions embodied in building materials is clear,” asserted Thornton Tomasetti in a prepared statement.
“It may not matter how efficiently we operate our buildings over time if we don’t immediately address the carbon embodied in what and how we build,” said Beth Heider, FAIA, Skanska USA’s Chief Sustainability Officer. “We have only a short time to actionably reduce carbon emissions as a society. With our benchmarking and the EC3 tool, we more fully understand the emissions footprint of how and what we build—and can chart an urgent course toward its reduction.”
Skanska is a signatory to the Paris Climate Accord, which has set aggressive global goals for carbon emissions reduction.
Skanska USA’s investment in addressing embodied carbon dates back to 2016, through its internal innovation grant program. EC3 is an open-source database with nearly 17,000 building materials including concrete, steel, and gypsum. During its pilot stage, participating development projects realized embodied carbon reductions of up to 30%, without significant additional financial impacts on the piloting companies.
Editor's note: This article revises the original posted version with new information, and correctly identifies that the Carbon Leadership Forum launched EC3. (The original stated it was Skanska, which is not directly involved in the launch, but was playing up the tool at its exhibit booth during Greenbuild.)
Related Stories
Products and Materials | Sep 29, 2023
Top building products for September 2023
BD+C Editors break down 15 of the top building products this month, from smart light switches to glass wall systems.
Building Owners | Aug 23, 2023
Charles Pankow Foundation releases free project delivery selection tool for building owners, developers, and project teams
Building owners and project teams can use the new Building Owner Assessment Tool (BOAT) to better understand how an owner's decision-making profile impacts outcomes for different project delivery methods.
Fire-Rated Products | Aug 14, 2023
Free download: Fire-rated glazing 101 technical guide from the National Glass Association
The National Glass Association (NGA) is pleased to announce the publication of a new technical resource, Fire-Rated Glazing 101. This five-page document addresses how to incorporate fire-rated glazing systems in a manner that not only provides protection to building occupants from fire, but also considers other design goals, such as daylight, privacy and security.
Green | Aug 7, 2023
Rooftop photovoltaic panels credited with propelling solar energy output to record high
Solar provided a record-high 7.3% of U.S. electrical generation in May, “driven in large part by growth in ‘estimated’ small-scale (e.g., rooftop) solar PV whose output increased by 25.6% and accounted for nearly a third (31.9%) of total solar production,” according to a report by the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
Digital Twin | Jul 31, 2023
Creating the foundation for a Digital Twin
Aligning the BIM model with the owner’s asset management system is the crucial first step in creating a Digital Twin. By following these guidelines, organizations can harness the power of Digital Twins to optimize facility management, maintenance planning, and decision-making throughout the building’s lifecycle.
Sustainability | Jul 26, 2023
Carbon Neutrality at HKS, with Rand Ekman, Chief Sustainability Officer
Rand Ekman, Chief Sustainability Officer at HKS Inc., discusses the firm's decarbonization strategy and carbon footprint assessment.
Mass Timber | Jul 11, 2023
5 solutions to acoustic issues in mass timber buildings
For all its advantages, mass timber also has a less-heralded quality: its acoustic challenges. Exposed wood ceilings and floors have led to issues with excessive noise. Mass timber experts offer practical solutions to the top five acoustic issues in mass timber buildings.
Green | Jun 26, 2023
Federal government will spend $30 million on novel green building technologies
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies. The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance.
3D Printing | Jun 20, 2023
World's largest 3D-printed building completed in Florida
Printed Farms, known for completing Florida’s first permitted 3D-printed house in Tallahassee, announces the completion of the world’s largest 3D-printed building: a luxury horse barn.
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?