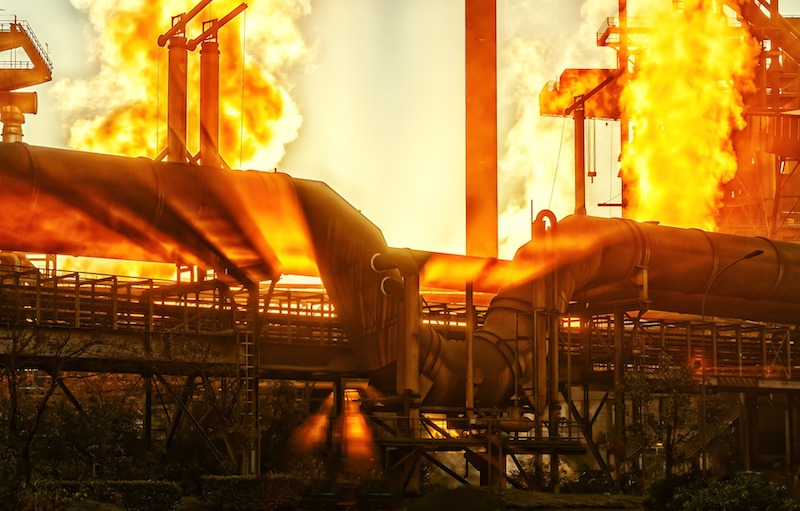
Over the past 90 days, the price of steel that Dallas-based DFW Grating buys from domestic mills to fabricate bar and plate grating has nearly doubled. C. Scott Netherton, DFW Grating’s Vice President of Business Development, added that steel distributors are scaling back their inventories unless they are sure they have a buyer.
“We’re not happy with the current situation,” said Netherton, meaning the uncertainty surrounding tariffs imposed on steel and aluminum imports that have rattled the U.S. market, where prices on some products had been rising since late last year.
“What makes this more difficult is that there’s so much momentum as far as manufacturing is concerned, and no one wants to upset that,” said Edward Youdell, President and CEO of the Fabricators & Manufacturers Association (FMA), which represents 1,500 companies.
Youdell and Netherton were manning booths at last week’s Steel Conference in Baltimore, sponsored by the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) and attended by more than 5,000 people. Like many attendees, they were trying to sort out the ramifications and consequences of the recent 25% tariffs on steel imports and 10% tariffs on aluminum imports imposed by the Trump Administration on March 23. “Anyone who says they’ve got this figured out is BSing you,” said Youdell.
He fears, though, that small fabricators will struggle to compete in this new competitive environment. “What our members would have preferred is no tariffs, let us have access to cheaper parts, and we could compete globally.”
Underutilized domestic mills could get a boost
Imports accounted for an estimated 27% of the 139 million tons of steel consumed in the U.S. in 2017. A year-long investigation by the U.S. Department of Commerce found sufficient evidence of unfair trade practices by foreign suppliers—notably China—to warrant tariffs to protect the American steel industry under the pretext of national security.
However, it didn’t take long for the administration to exempt several countries—including the European Union, Australia, South Korea, Mexico, Canada, Brazil, and Argentina—that by some estimates account for more than three fifths of all imports coming into the United States. Steel and aluminum suppliers are now scrambling to get specific products excluded from the tariffs.
There have been 1,200 applications for waivers from steel tariffs and 125 requests for exemptions from aluminum tariffs, numbers the Commerce Department confirmed to the Washington Post last Friday. “A tsunami is coming,” Kevin Dempsey, general counsel at the American Iron and Steel Institute, told the Post. “I anticipate there will be several thousand exclusion requests filed.”
Just how much protection the U.S. industry needs from imports, though, is a matter of debate. The top five U.S. steel producers—Nucor, U.S. Steel, Steel Dynamics, AK Steel, and Commercial Metals—all reported positive earnings in 2017 (although some were coming off of years when they lost money). Steel Dynamics alone reported record net income, $813 million, a 113% increase over earnings in fiscal 2016. (SDI did not return BD+C’s request for comment.)
It goes without saying, though, that tariffs could be a boon to underutilized American mills. AISC contends that U.S. steel manufacturers would have excess production capacity even in the unlikely event that they had to replace 100% of imports. (For example, domestic mills, with 10 million tons of structural steel capacity, produced 6.3 million tons last year, with another 1.7 million tons imported.)
“With domestic prices rising even before the tariffs went into effect, it’s been a challenge to buy, and it’s forced fabricators to align closer with suppliers and mills,” said Adam Zakeski, Vice President of Sales-decks and joists for Canam Group, an Allentown, Pa.-based producer and fabricator.
The impact of price hikes debated
Zakeski, Youdell, and Netherton expect prices to stabilize by the third quarter of this year. “Domestic mills can only push prices up so far,” said Zakeski, whose company is buying conservatively at the moment. But he’s skeptical of any rationalizations that “trivialize” the impact of price inflation on the industry’s competitiveness.

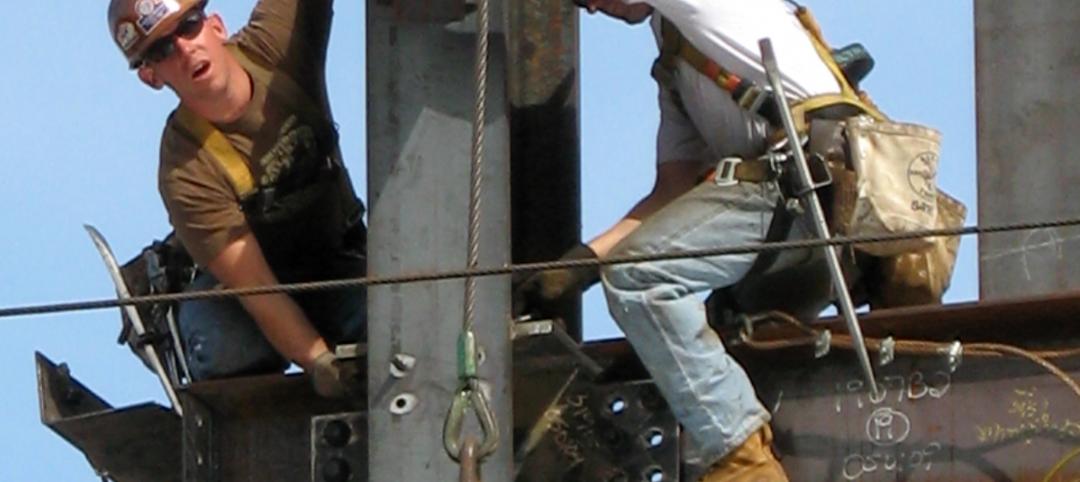
Steel and aluminum tariffs were a hot topic of discussion at last week's Steel Conference. Image: BD+C
In a recent webinar, Brian Raff and Tabitha Stine, AISC’s Director of Government Relations and Vice President, respectively, stated that the structural steel package on a $100 million project accounts for about $12 million, of which 30% is for materials from the mill or distributor. So, a worst-case 25% increase in materials costs would equal around $900,000, or less than 1% of the total project cost.
Raff and Stine were quick to note that a 25% tariff doesn’t typically translate to a 25% price increase. And, they said, until recently mill prices had been relatively stable over the past several years, hovering, with some ups and downs, at around $800 per ton.
While it remained uncertain last week exactly which products would ultimately fall under the tariffs, AISC is pushing hard to have fabricated structural steel imports included. “What we’ve been trying to show is that the tariff on mill steel only is subject to circumvention” by countries that could route their steel to companies in other countries that are exempted from the tariff, explained David Zalesne, President of Owens Steel Company in Columbia, S.C.
Zalesne thinks the tariffs are likely to have less impact, positive or negative, than Trump or his critics believe they will. But what happens next is anybody’s guess. The U.S. has indicated that it might end country exemptions in early May. That could lead to a country-by-country quota system as a prelude to new trade negotiations, suggested Frank Swain with the law firm Faegre Baker Daniels, which represents AISC’s interests in Washington.
He and Zalesne also echoed AISC’s insistence that the U.S. should include a “Buy American” provision as part of any infrastructure spending legislation.
“Right now, it’s a poker game,” observed Youdell.
Related Stories
| Aug 2, 2013
Texas law expected to help reduce construction payroll fraud
Texas lawmakers want to get tough on construction companies that commit a certain form of payroll fraud, passing a new law recently signed by Gov. Rick Perry.
| Jul 26, 2013
AGC launches new coalition to help bring tax relief to construction sector
Associated General Contractor of America (AGC) has launched the Coalition for Fair Effective Tax Rates to bring tax relief to the construction sector.
| Jul 26, 2013
Legislation would revamp federal contracting policy impacting small design and construction firms
Legislation was introduced in the U.S. House of Representative this month to ban reverse auctions when an agency determines small businesses are qualified to bid on the solicitation.
| Jul 17, 2013
U.S. House continues to block enforcement of light bulb standards
The House of Representatives last week voted to block the enforcement of light bulb standards that many say would effectively force people to buy more expensive compact fluorescent bulbs.
| Jul 11, 2013
Bill to borrow more for college spending in Michigan criticized due to ‘higher-ed bubble’
An amendment to a Michigan appropriations budget authorizes an increase in state debt to pay for state university construction projects. But some experts see a “higher education bubble” on the horizon, and said more taxpayer debt for more buildings is a bad idea.
| Jul 11, 2013
Skanska exits U.S. Chamber of Commerce over LEED controversy
Skanska USA resigned from the U.S. Chamber of Commerce over the Chamber’s decision to support the American High-Performance Buildings Coalition.
| Jun 27, 2013
AGC urges Congress, Obama to reject caps on construction workers in immigration legislation
The unemployment rate in the construction sector in May was the lowest it has been in five years, which could signal a coming worker shortage, according to the Associated General Contractors of America.
| Jun 27, 2013
California legislators make push for prevailing wage law
California lawmakers introduced new legislation that would cut off state construction funds from charter cities that don’t mandate the equivalent of union-scale wages on public-works projects. Of the 482 cities in California, 121 are charter cities.
| May 31, 2013
Bond package to fund $2.7 billion in new university construction dies in Texas Legislature
A $2.7 billion state bond package that would have financed expansion projects at more than a half-dozen universities in Texas died on the final day of the legislative session.
| May 31, 2013
Tax break proposal for $1.5 billion expansion of Minnesota’s Mall of America advances
The Minnesota Legislature approved tax breaks worth $250 million for a $1.5 billion project that would double the size of the Mall of America in Bloomington, Minn.