U.S. school districts are widely planning to use funds from last year’s American Rescue Plan (ARP) to upgrade or improve air filtration and heating/cooling systems, according to a report from the Center for Green Schools at the U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC).
The report, School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic, says air filtration and HVAC upgrades are the top facility improvement choice for the 5,004 school districts included in the analysis. The top choice for spending federal funds was for staffing, followed by air filtration/HVAC at $5.5 billion.
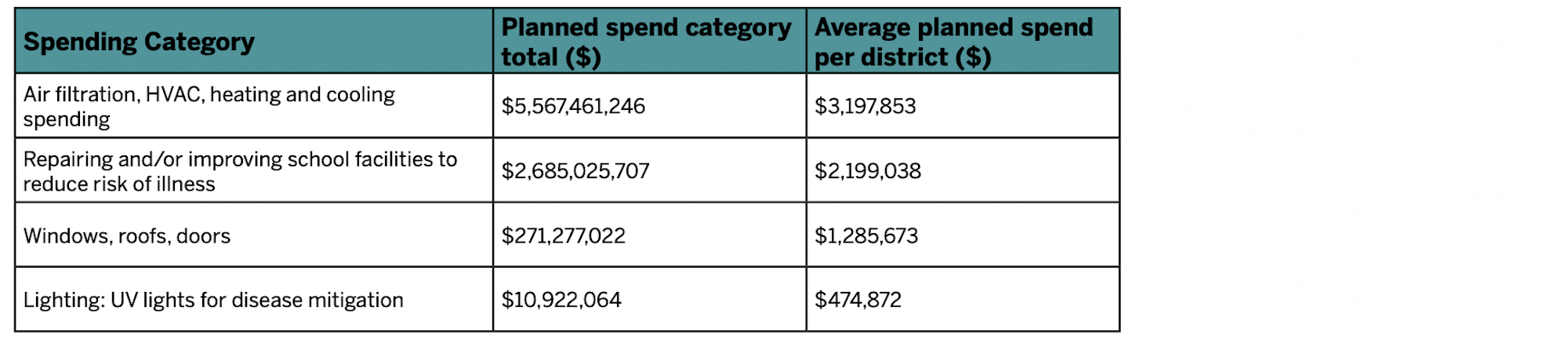
Other categories of planned spending include $2.6 billion for repairing/improving school facilities; $271 million for upgrading windows, roofs, and doors; and nearly $11 million for UV lighting for disease mitigation. The average planned spending for air filtration and HVAC is about $260,000 per school. Around 500 school districts plan to spend over $1 million per school on one or more of these categories.
District interviewees said having substantial federal dollars was important to be able to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases. They also noted that they face constraints on their projects caused by the pandemic, associated supply chain issues, and the rising rate of inflation.
District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems.
More findings from the School Facilities Funding in the Pandemic study
- Although staff capacity, inflation and supply chain shortages are affecting infrastructure projects, school districts have prioritized significant ESSER III funding to support indoor air quality for their students and staff. Of all the funding categories tracked by Burbio, air filtration/HVAC was the second-highest category for district planned spending at $5.5 billion, just behind staffing/teachers/academic interventionists/guidance counselors.
- Of the 2,379 school districts that planned to spend any ESSER III funding on facilities, large districts planned to spend the lowest percentage (on average 22%) and small districts planned to spend the highest percentage of their total allocation (on average 30%).
- Small and medium-size districts (those with 20 or fewer schools) consistently reported more spending per school on facilities categories than their larger counterparts.
- In addition to filtration and HVAC improvements, in most cases, districts that planned to spend in this category also indicated plans to spend in at least one other facilities category, displaying a layered approach to addressing COVID at the building infrastructure level.
- The district interviewees highlighted the importance of having substantial federal dollars to invest in costly HVAC infrastructure projects, which would otherwise be delayed or addressed in phases.
- District interviewees noted that where HVAC upgrades were made in their schools, they were able to keep energy usage and costs to a minimum compared to schools with outdated systems. Similarly, interviewees reported positive results from spending in other facilities categories to reduce the spread of COVID.
The analysis included qualitative interviews with three school district facilities personnel and a quantitative analysis based on a data set of 5,004 school districts’ ESSER-III spending plans by the Burbio data service. The dataset contained information from school districts from all 50 states and the District of Columbia, representing approximately 74% of public-school students and roughly $83.1 billion in ESSER III funds.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
7 Keys to Unlocking Energy Efficiency in Schools
Today’s best K-12 schools are embracing the sustainability ethos in their design and construction, and that can mean a healthier, more comfortable indoor environment and improved learning. Some studies contend that ample amounts of daylighting, for example, lead to higher test scores. High-performance HVAC systems that constantly draw fresh air into a classroom seem to help both teachers ...
| Aug 11, 2010
Blue-Light Schoolhouses
Add the explosion in the number of school-aged kids nationally to the glut of huge, vacant stores in many communities and what do you get? Big boxes being turned into schools. For districts facing population pressure, these empty retail buildings can be the key to creating classrooms quickly, and at a significant cost advantage.
| Aug 11, 2010
Great Solutions: Green Building
27. Next-Generation Green Roofs Sprout up in New York New York is not particularly known for its green roofs, but two recent projects may put the Big Apple on the map. In spring 2010, the Lincoln Center for the Performing Arts will debut one of the nation's first fully walkable green roofs. Located across from the Juilliard School in Lincoln Center's North Plaza, Illumination Lawn will consist ...
| Aug 11, 2010
Dream Fields, Lone Star Style
How important are athletic programs to U.S. school districts? Here's one leading indicator: In 2005, the National Football League sold 17 million tickets. That same year, America's high schools sold an estimated 225 million tickets to football games, according to the American Football Coaches Association.
| Aug 11, 2010
Back to Nature: Can wood construction create healthier, more productive learning environments?
Can the use of wood in school construction create healthier, safer, more productive learning environments? In Japan, there's an ongoing effort by government officials to construct school buildings with wood materials and finishes—everything from floors and ceilings to furniture and structural elements—in the belief that wood environments have a positive impact on students.
| Aug 11, 2010
High School in a Hurry
One of the more compelling arguments for charter schools is their theoretical ability to streamline decision making. Eliminate all those layers of bureaucratic fat that clog the arteries of most public school systems, the argument goes, and decisions can be made to flow much more smoothly, even when it comes to designing and building a major school project.
| Aug 11, 2010
Bronze Award: Garfield High School, Seattle, Wash.
Renovations to Seattle's historic Garfield High School focused mainly on restoring the 85-year-old building's faded beauty and creating a more usable and modern interior. The 243,000-sf school (whose alumni include the impresario Quincy Jones) was so functionally inadequate that officials briefly considered razing it.
| Aug 11, 2010
Managing the K-12 Portfolio
In 1995, the city of New Haven, Conn., launched a program to build five new schools and renovate and upgrade seven others. At the time, city officials could not have envisioned their program morphing into a 17-year, 44-school, $1.5 billion project to completely overhaul its entire portfolio of K-12 facilities for nearly 23,000 students.
| Aug 11, 2010
Financial Wizardry Builds a Community
At 69 square miles, Vineland is New Jersey's largest city, at least in geographic area, and it has a rich history. It was established in 1861 as a planned community (well before there were such things) by the utopian Charles Landis. It was in Vineland that Dr. Thomas Welch found a way to preserve grape juice without fermenting it, creating a wine substitute for church use (the town was dry).
| Aug 11, 2010
School Project Offers Lessons in Construction Realities
Imagine this scenario: You're planning a $32.9 million project involving 112,000 sf of new construction and renovation work, and your job site is an active 32-acre junior-K-to-12 school campus bordered by well-heeled neighbors who are extremely concerned about construction noise and traffic. Add to that the fact that within 30 days of groundbreaking, the general contractor gets canned.







