The American Institute of Architects' Committee on the Environment (COTE) has selected the top ten examples of sustainable architecture and ecological design projects that protect and enhance the environment. The projects will be honored at the AIA 2014 National Convention and Design Exposition in Chicago.
The COTE Top Ten Awards program, now in its 18th year, is the profession's best known recognition program for sustainable design excellence. The program celebrates projects that are the result of a thoroughly integrated approach to architecture, natural systems, and technology.
These projects make a positive contribution to their communities, improve comfort for building occupants, and reduce environmental impacts through strategies such as reuse of existing structures, connection to transit systems, low-impact and regenerative site development, energy and water conservation, use of sustainable or renewable construction materials, and design that improves indoor air quality.
The 2014 COTE Top Ten Green Projects jury included: Frederick Steiner, School of Architecture at the University of Texas at Austin; Catherine Gavin, Texas Architect; Bill Browning, Hon. AIA, Terrapin Bright Green; Thomas E. Simpson, PE, LEED AP, US East Integral Group; and Jennifer Yoos, FAIA, LEED AP, VJAA.
Here's a recap of the 2014 winners:
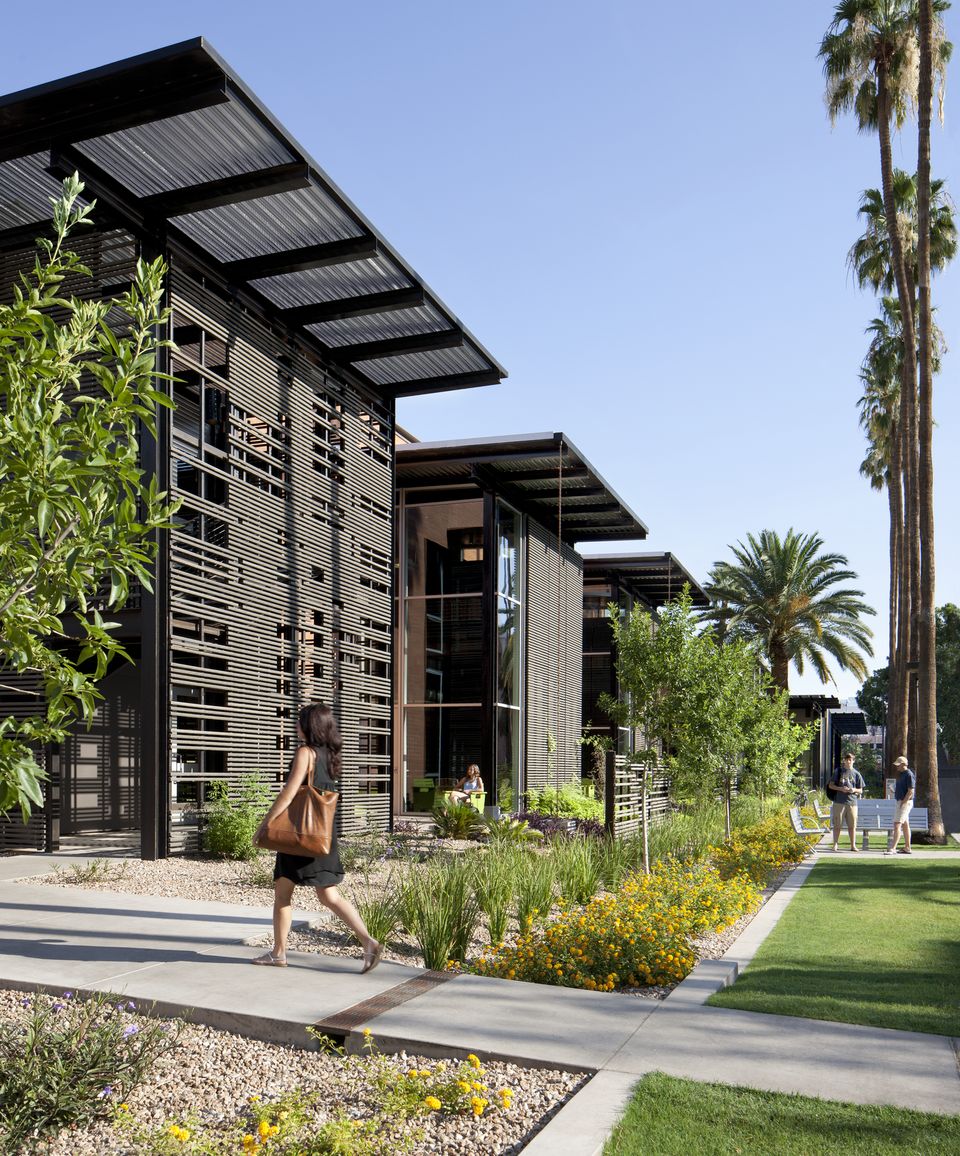
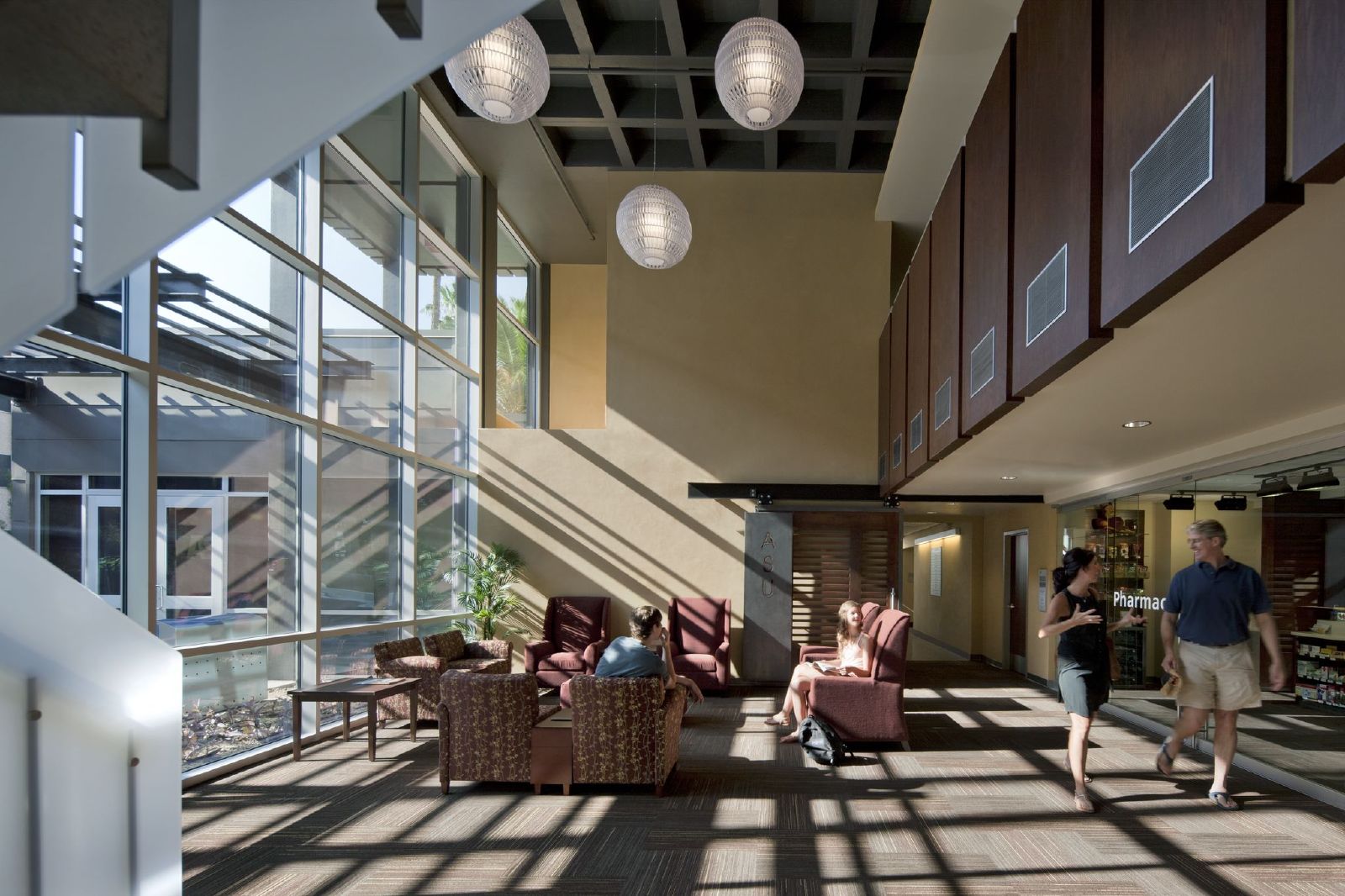
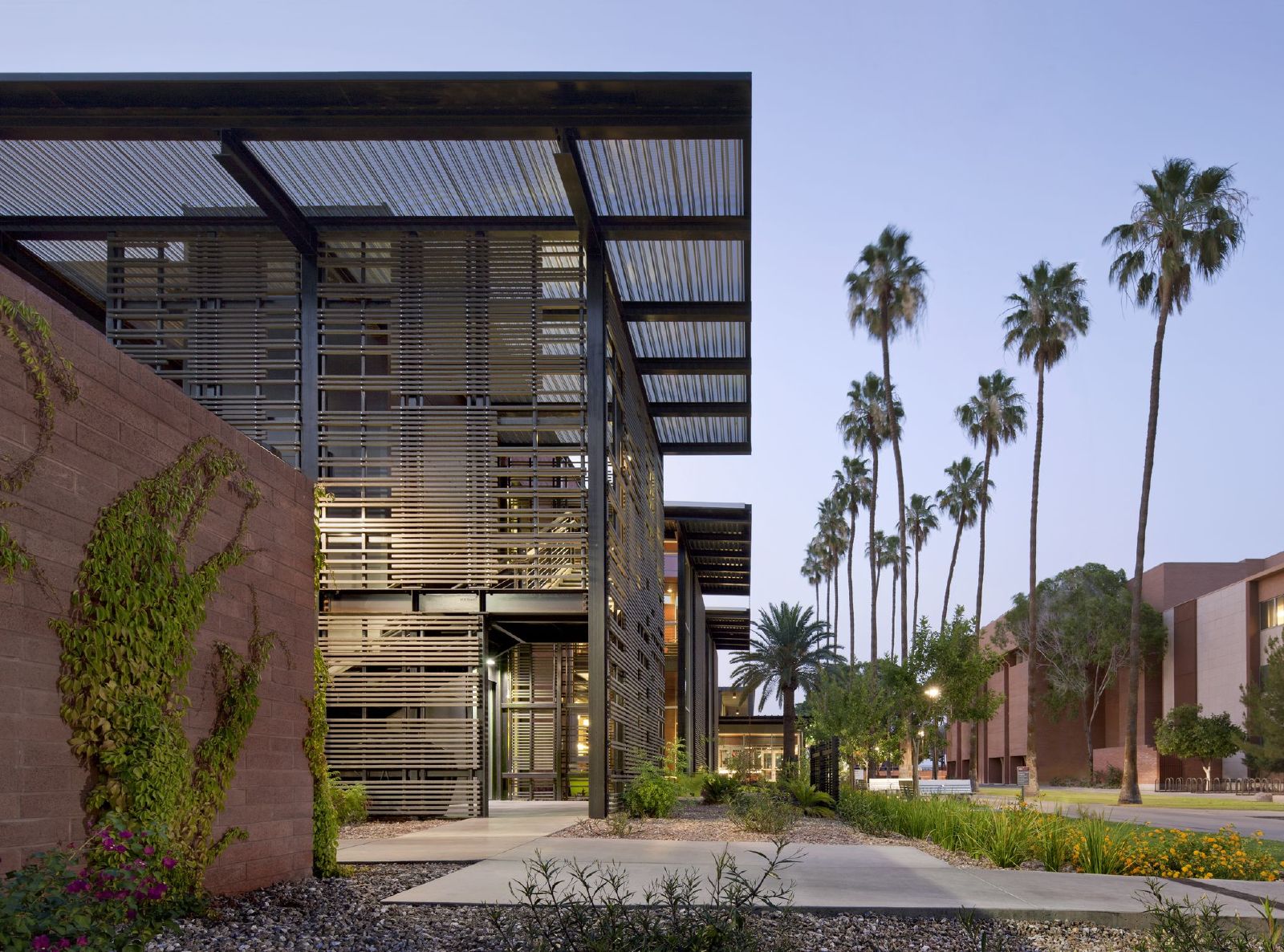
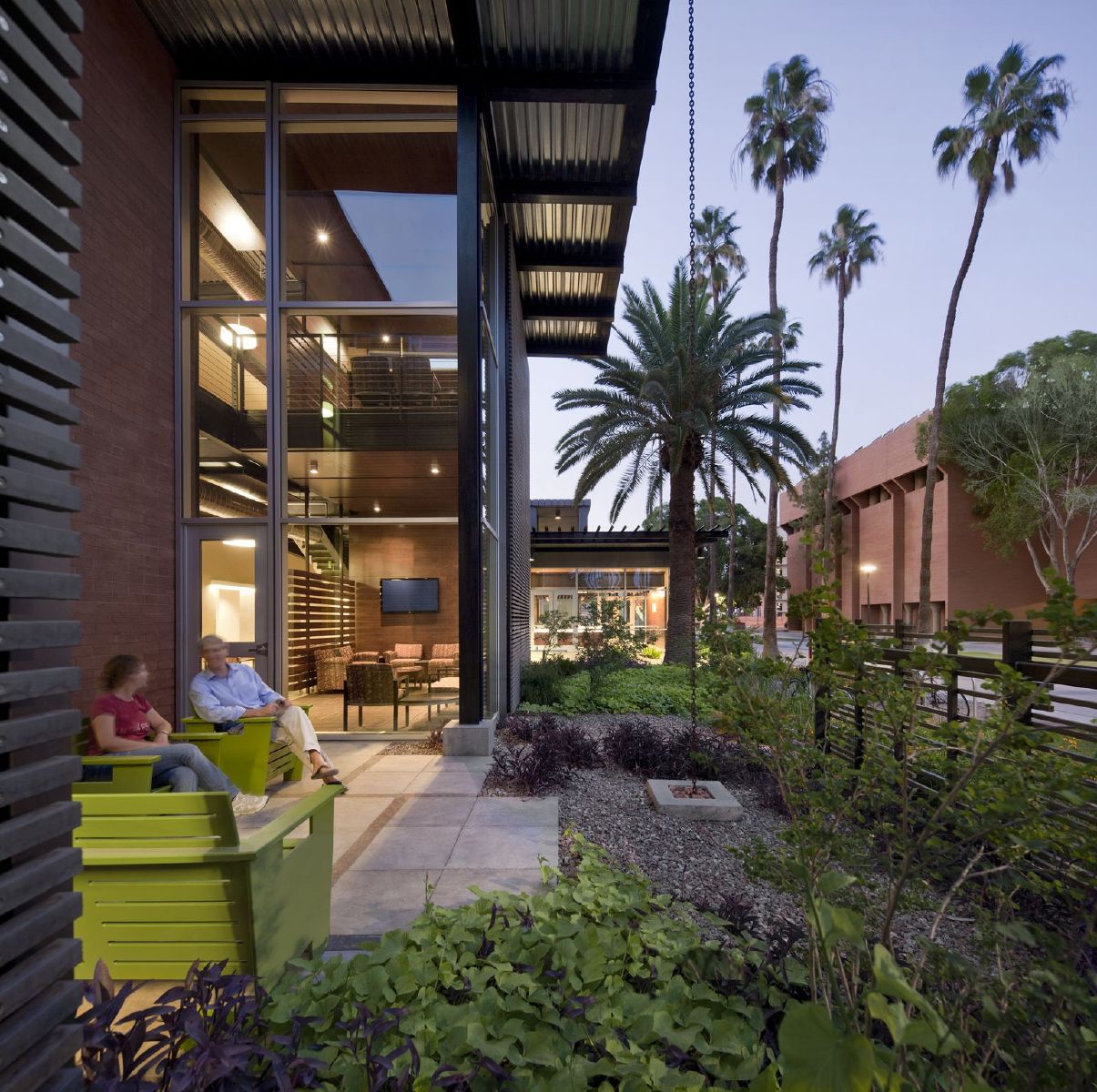
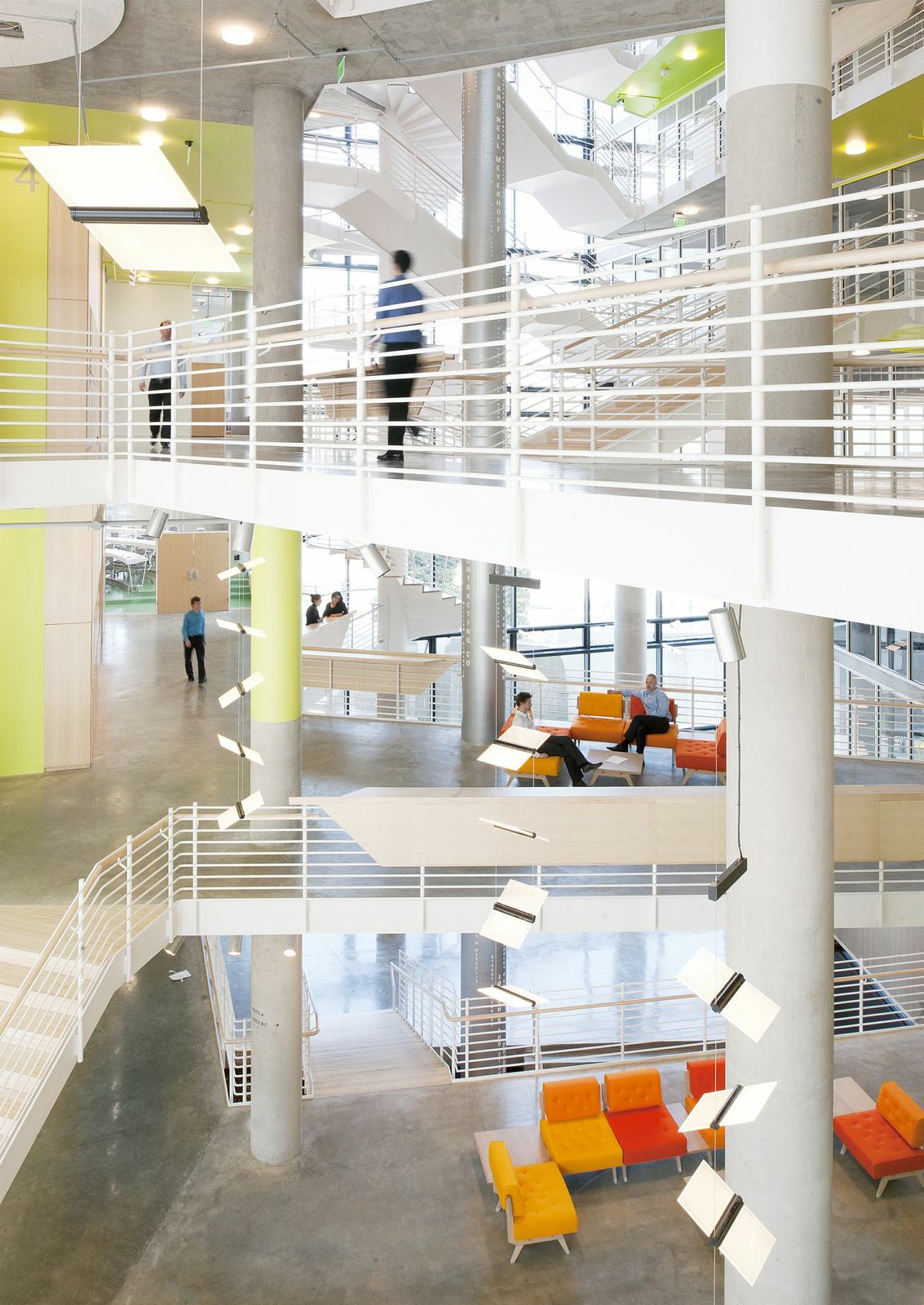
1. Arizona State University Student Health Services, Tempe, Ariz
Lake|Flato Architects + Orcutt|Winslow
Photos: Bill Timmerman
The Arizona State University (ASU) Health Services Building is an adaptive reuse project that transformed the existing sterile and inefficient clinic into a clearly organized, efficient, and welcoming facility. The design imbues the new facility with a sense of health and wellness that leverages Tempe’s natural environment and contributes to a more cohesive pedestrian oriented campus. The building’s energy performance is 49% below ASHRAE 90.1-2007, exceeding the current target of the 2030 Challenge. The facility achieved LEED Platinum certification and is one of the best energy performers on campus as evidenced by ASU’s Campus Metabolism interactive web-tool tracking real-time resource use.
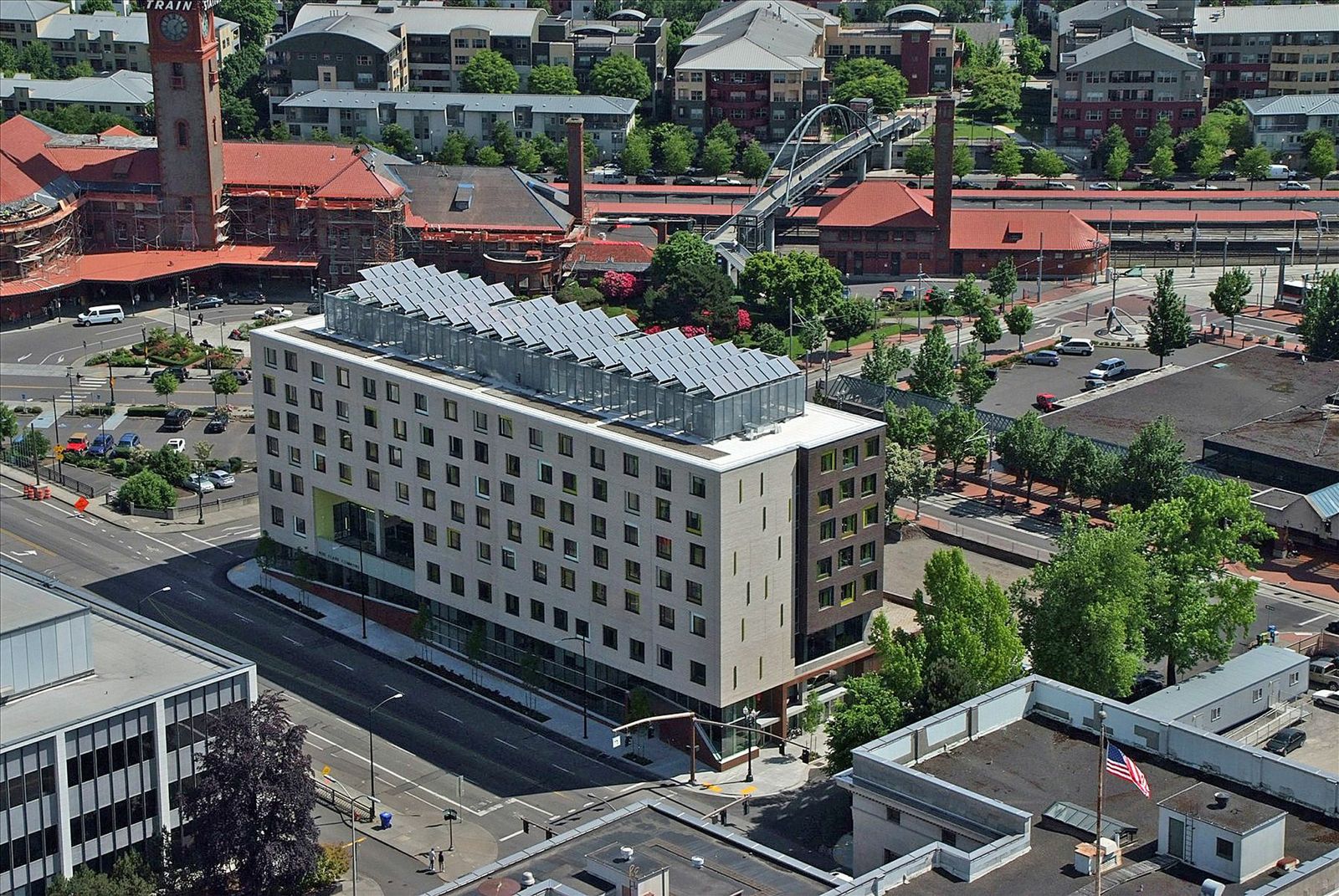
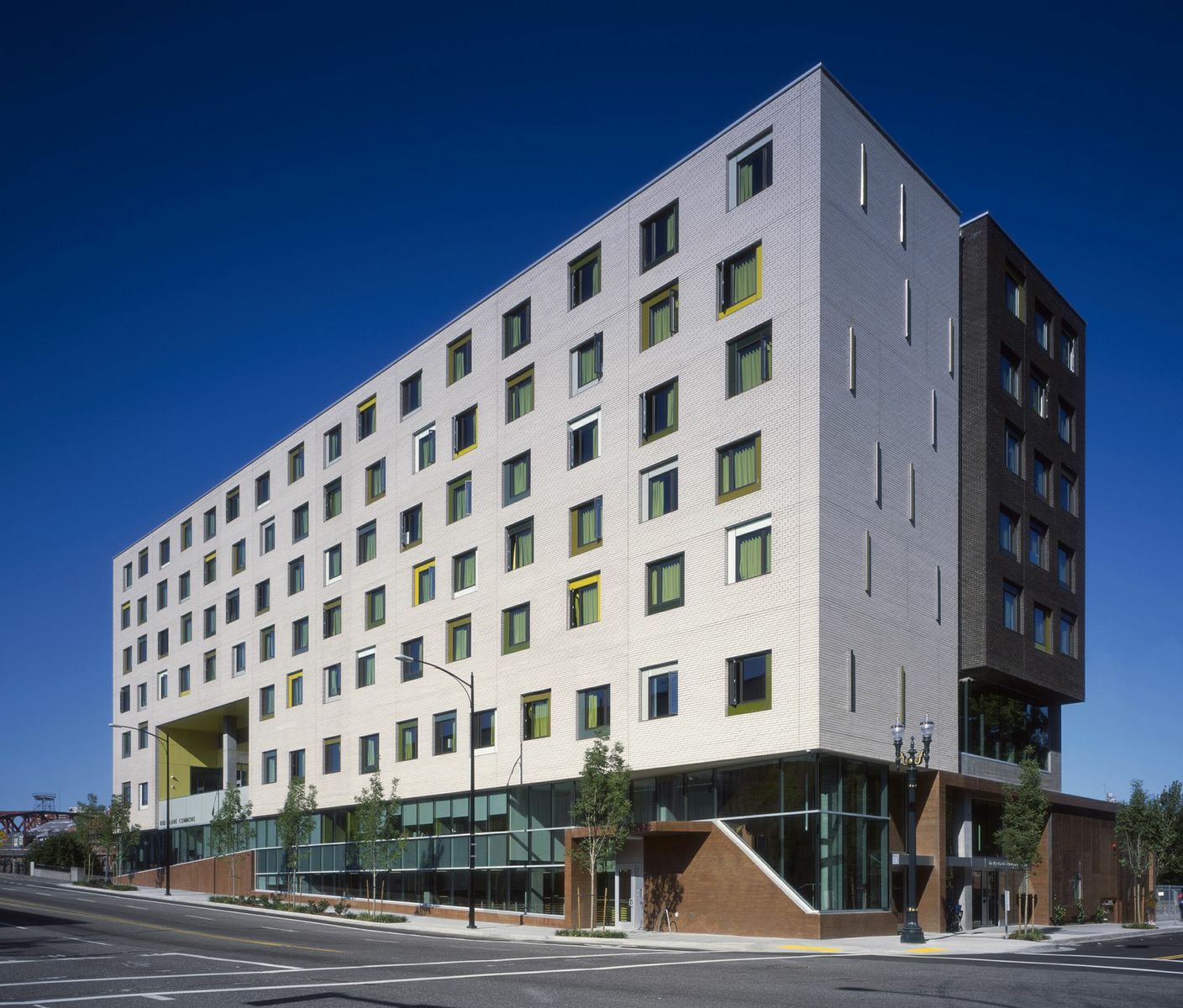
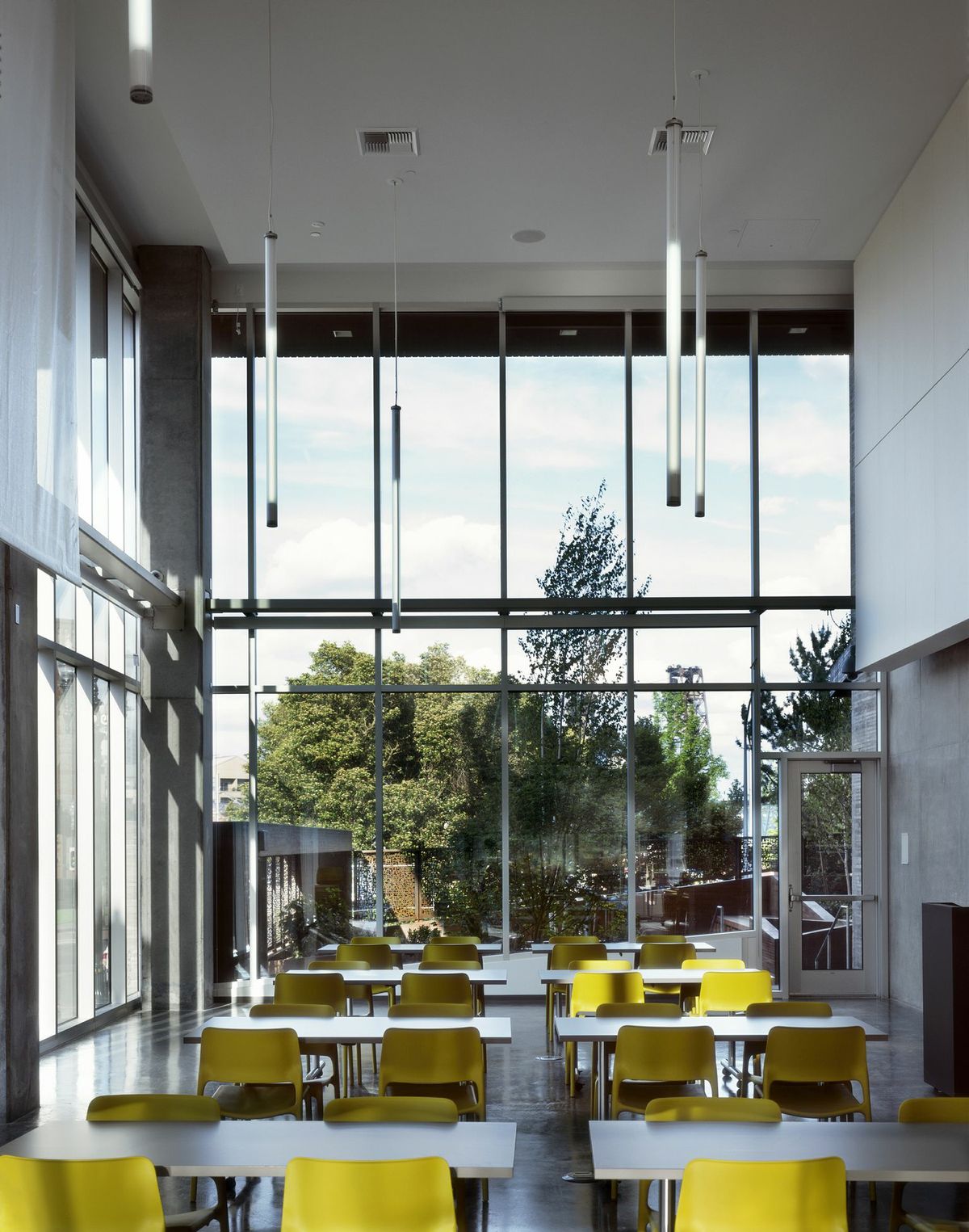
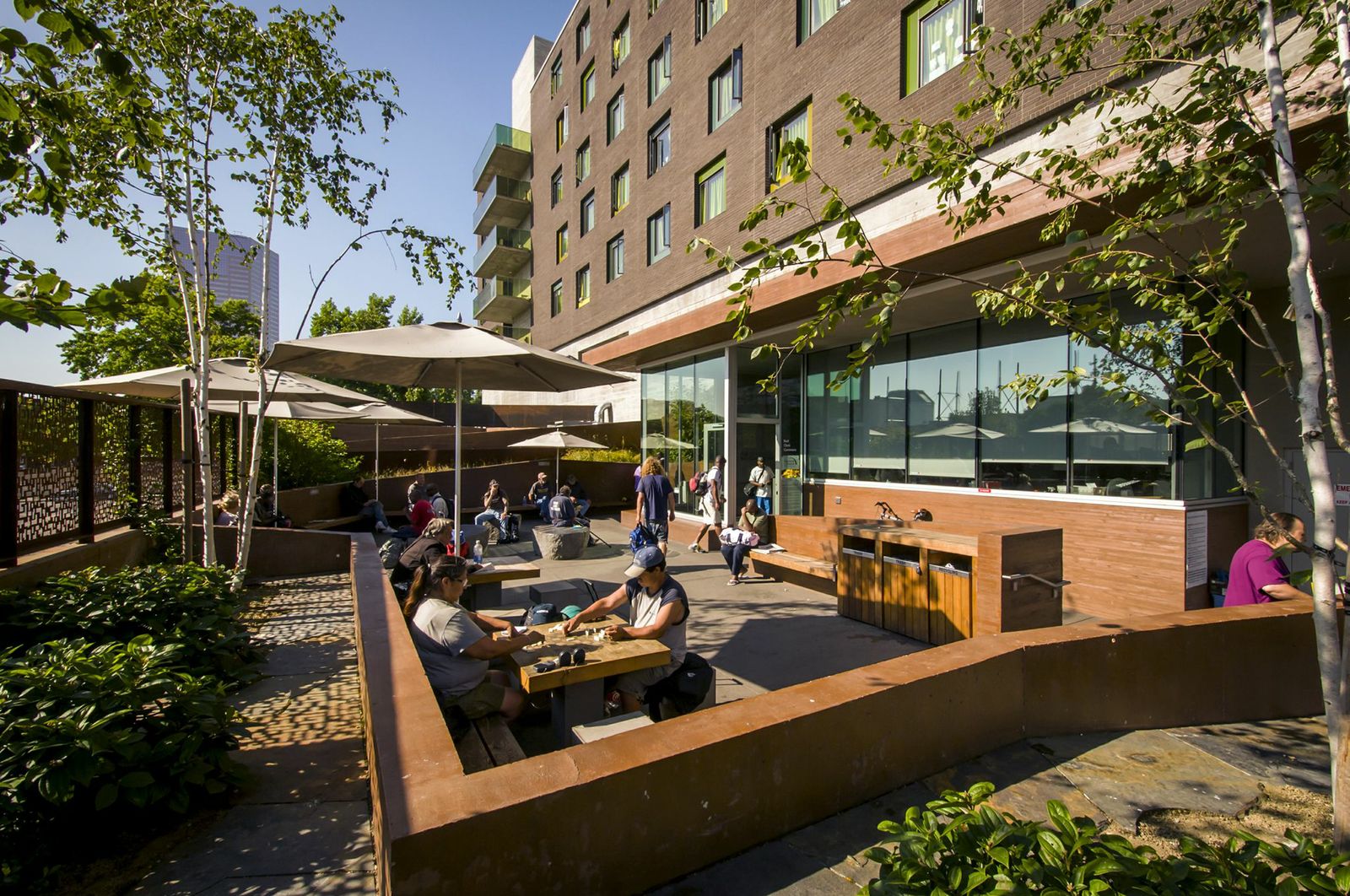
2. Bud Clark Commons, Portland, Ore.
Holst Architecture
Photos: Sally Schoolmaster
As a centerpiece of Portland’s 10-Year Plan to End Homelessness, this LEED Platinum project provides a continuum of services to help transition homeless individuals toward stable, permanent living arrangements. The architecture helps achieve this goal with a walk-in day center with public courtyard and access to support services; a 90-bed temporary shelter; and a separate and secure entrance to 130 efficient, furnished studio apartments for homeless individuals seeking permanent housing.
The building’s design aims to deinstitutionalize services and housing for the most vulnerable in our population. Sustainable features include large-scale graywater recycling, zero stormwater runoff, solar hot water, and a high-performance envelope, resulting in energy savings estimated at $60,000 annually.
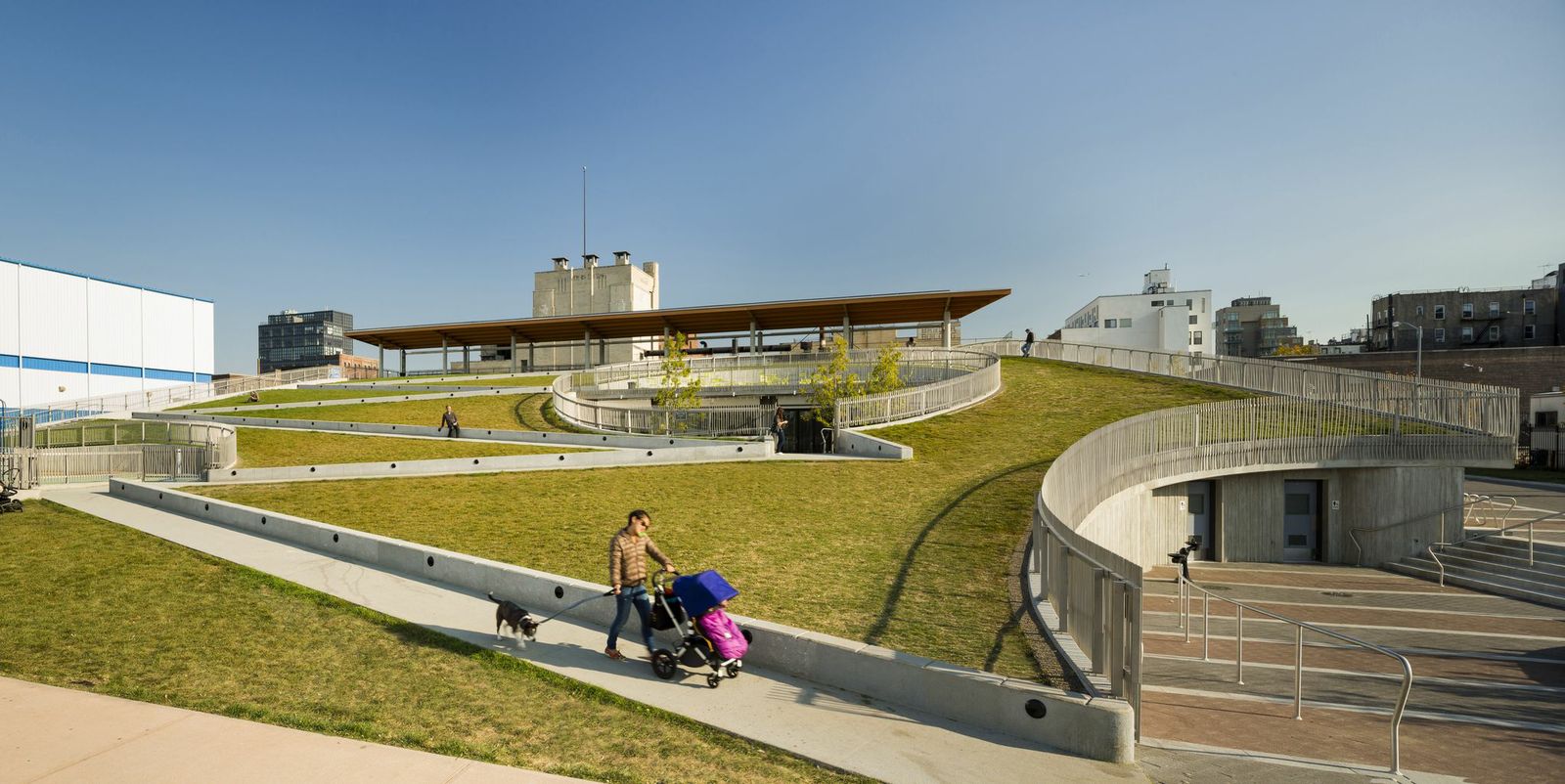
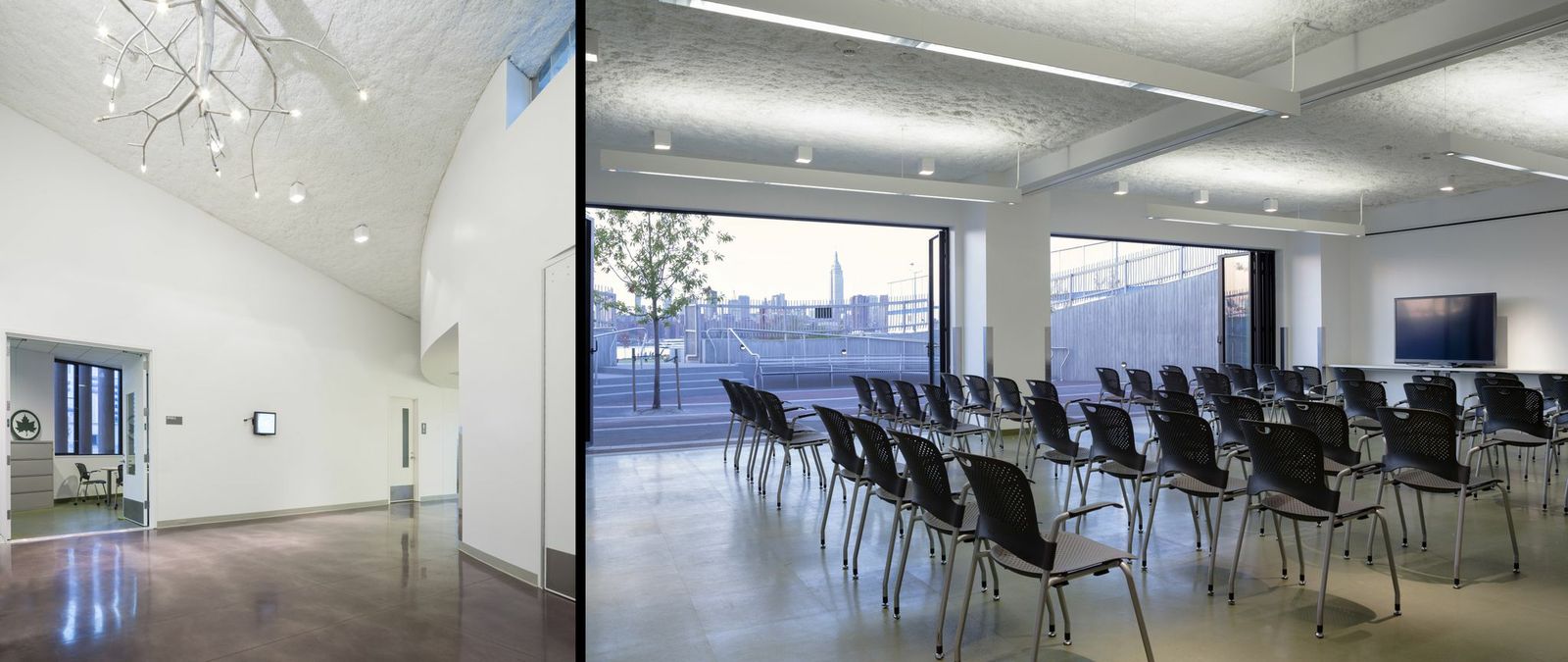
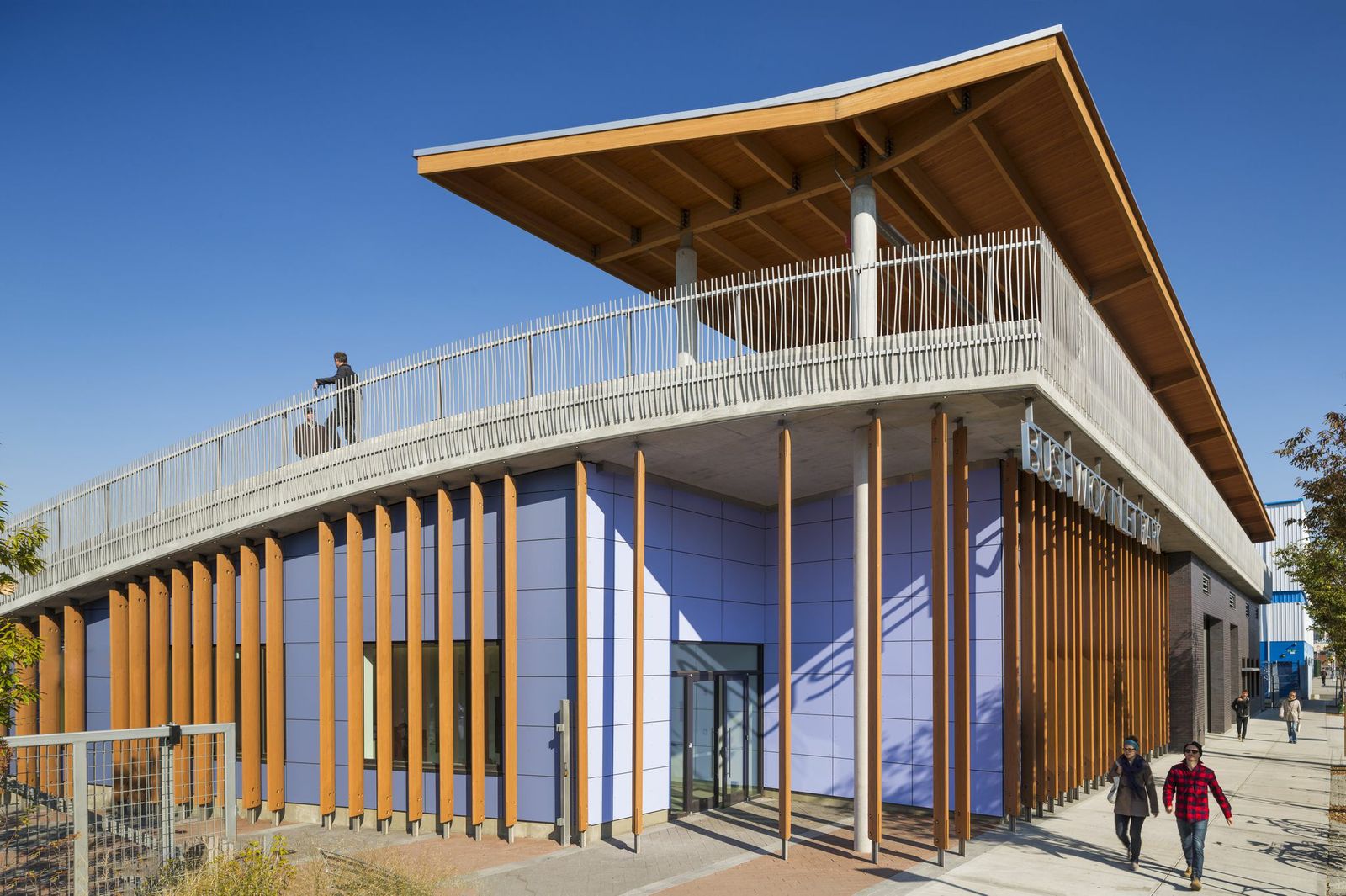
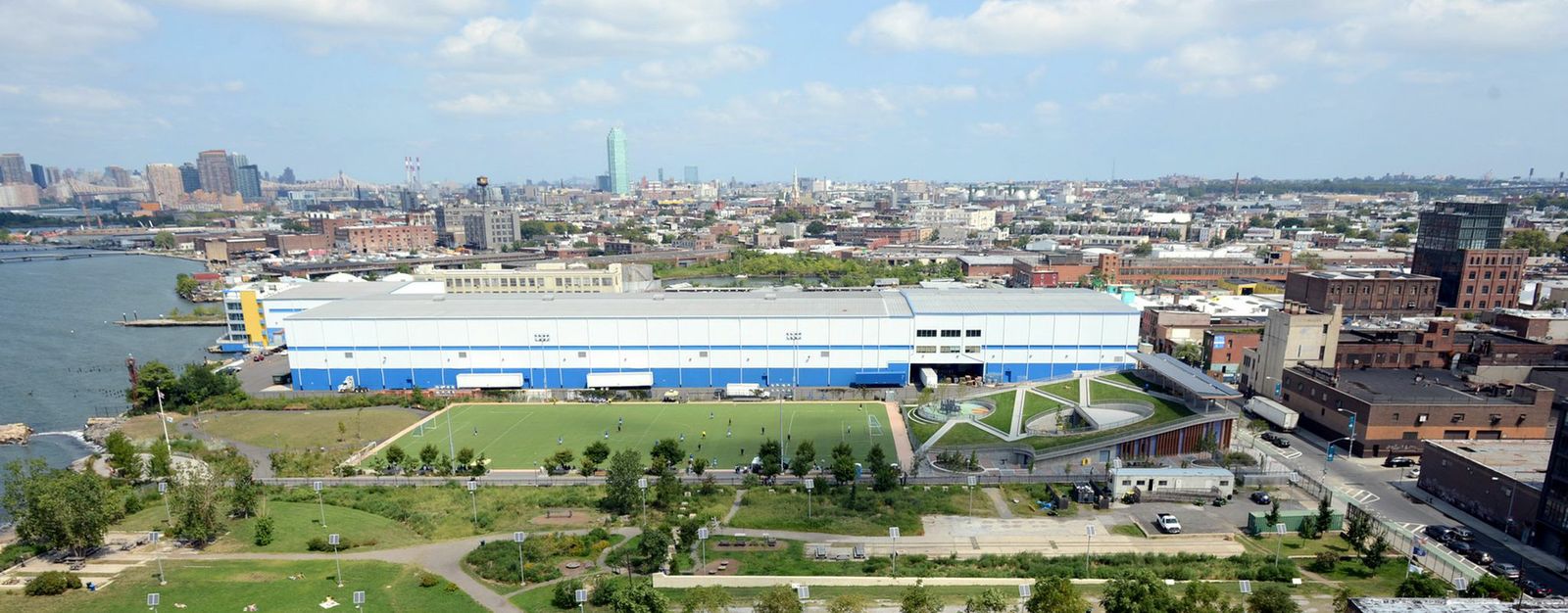
3. Bushwick Inlet Park, Brooklyn, N.Y.
Kiss + Cathcart, Architects
Photos: Paul Warchol
This project is the first phase of the transformation of the Greenpoint–Williamsburg waterfront from a decaying industrial strip to a multifaceted public park. The design team integrated a program of playfields, public meeting rooms, classrooms, and park maintenance facilities, into a city-block sized site. The park building becomes a green hill on the west side, making 100% of the site usable to the public, and offering views to Manhattan. Below the green roof is a complex of building systems – ground source heat pump wells, rainwater harvest and storage, and drip irrigation. A solar trellis produces half the total energy used in the building.
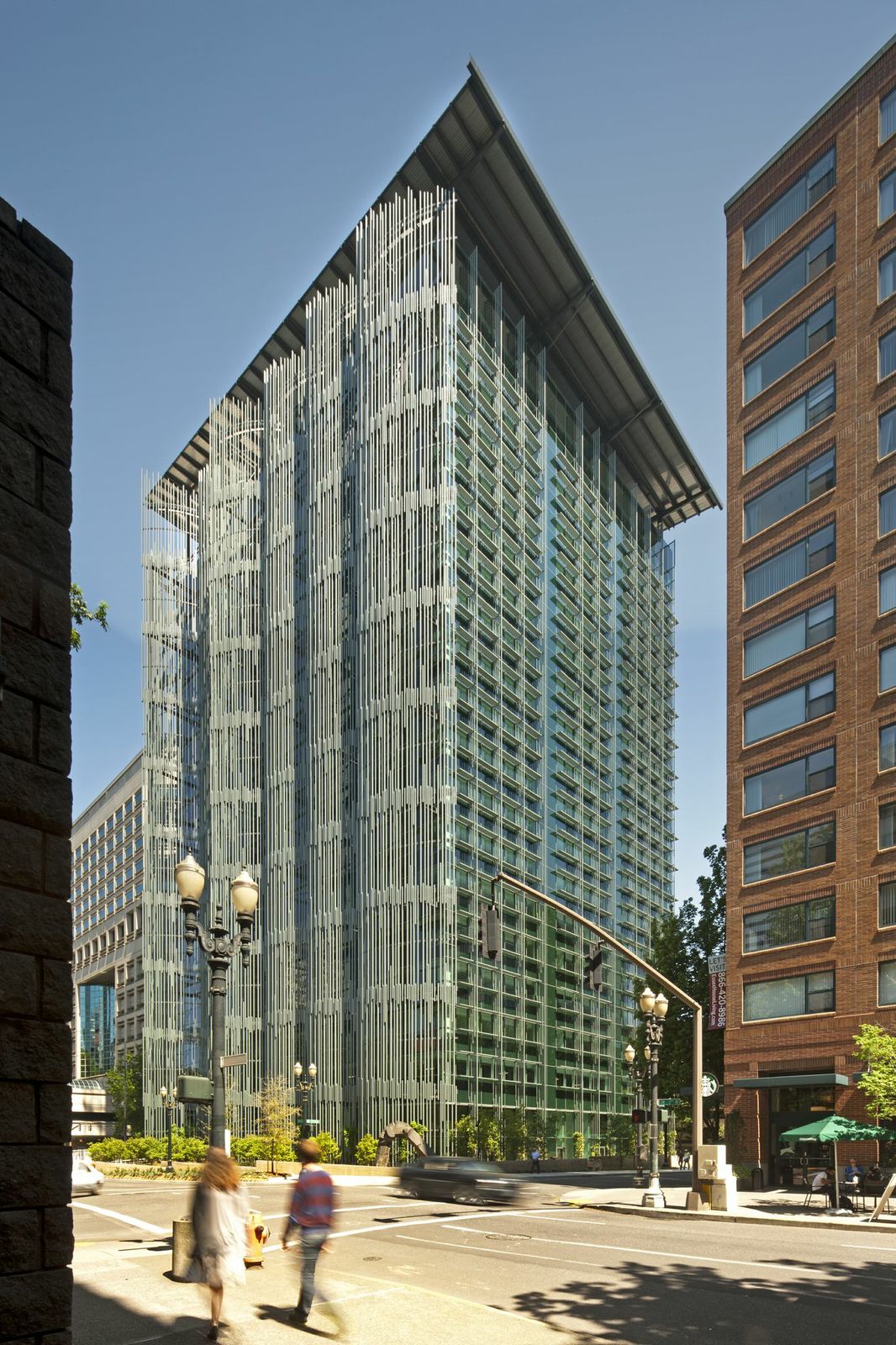
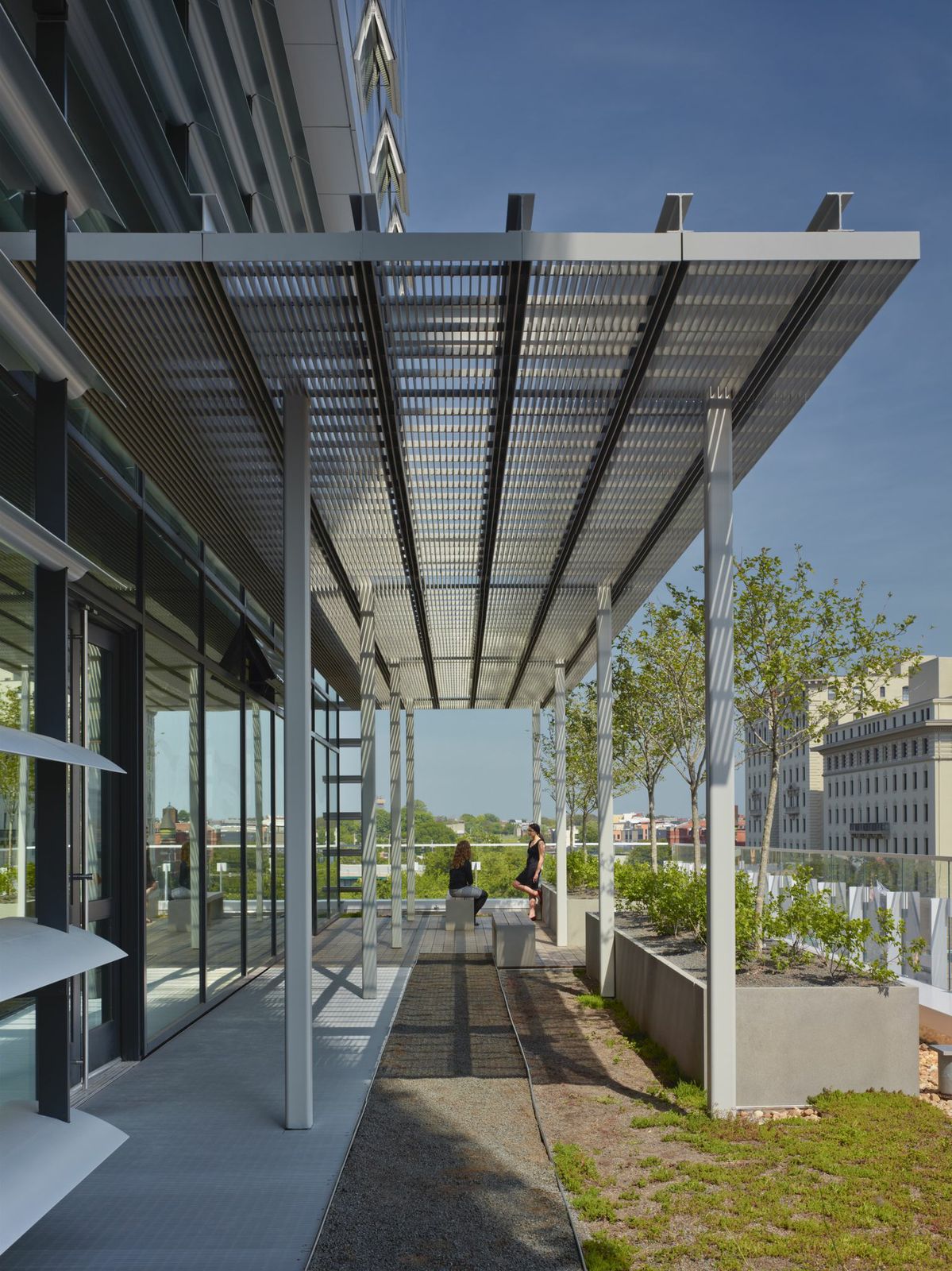
4. Edith Green-Wendell Wyatt Federal Building Modernization, Portland, Ore.
SERA Architects in association with Cutler Anderson Architects
Photo credit: Nic Lehoux
On track to be one of the lowest energy-use buildings in the U.S., EGWW is a model for U.S. General Services Administration nationwide. The project’s goal was to transform the existing building from an aging, energy hog to one of the premiere environmentally-friendly buildings in the nation. With a unique facade of “reeds”, light shelf /sunshades designed by orientation and a roof canopy that supports a 180 kW photovoltaic array while collecting rainwater, EGWW pushes the boundaries for innovative sustainable deign strategies. In addition to the energy improvements, the design reveals the history of the building, exposing the artifacts of the original builders.
5. Gateway Center - SUNY-ESF College of Environmental Science & Forestry, Syracuse, N.Y.
Architerra
Photos: David Lamb Photography
The SUNY-ESF College of Environmental Science & Forestry Gateway Center is a striking symbol of environmental stewardship and climate action leadership. This LEED Platinum campus center meets ESF’s goal of reducing the overall carbon footprint of the campus through net positive renewable energy production, while creating a combined heat and power plant and intensive green roof that serve as hands-on teaching and research tools. The double-ended bioclimatic form exemplifies passive solar design. Net positive energy systems integrated with the design serve four adjacent ESF buildings, providing 60% of annual campus heating needs and 20% of annual power needs.
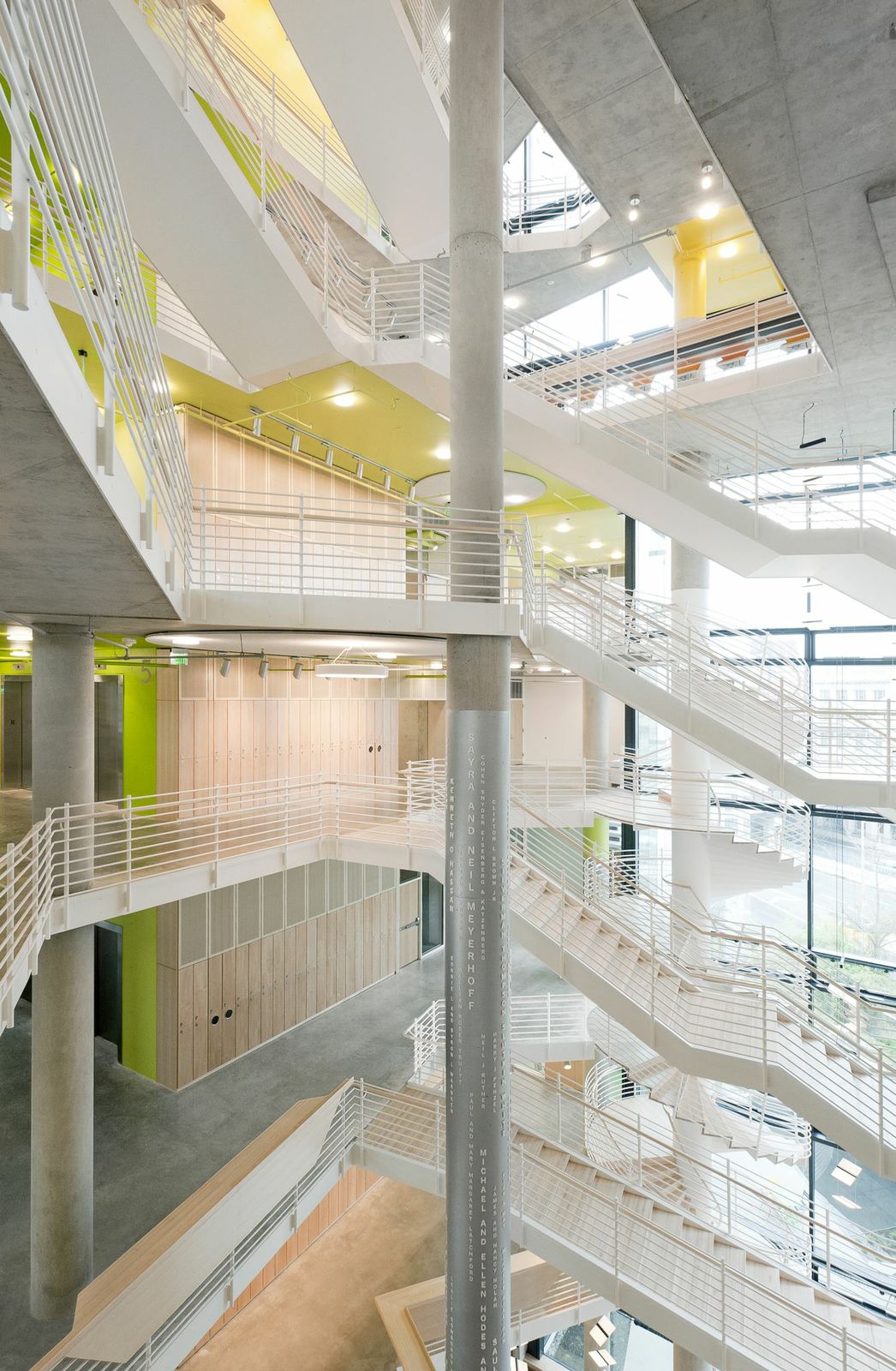
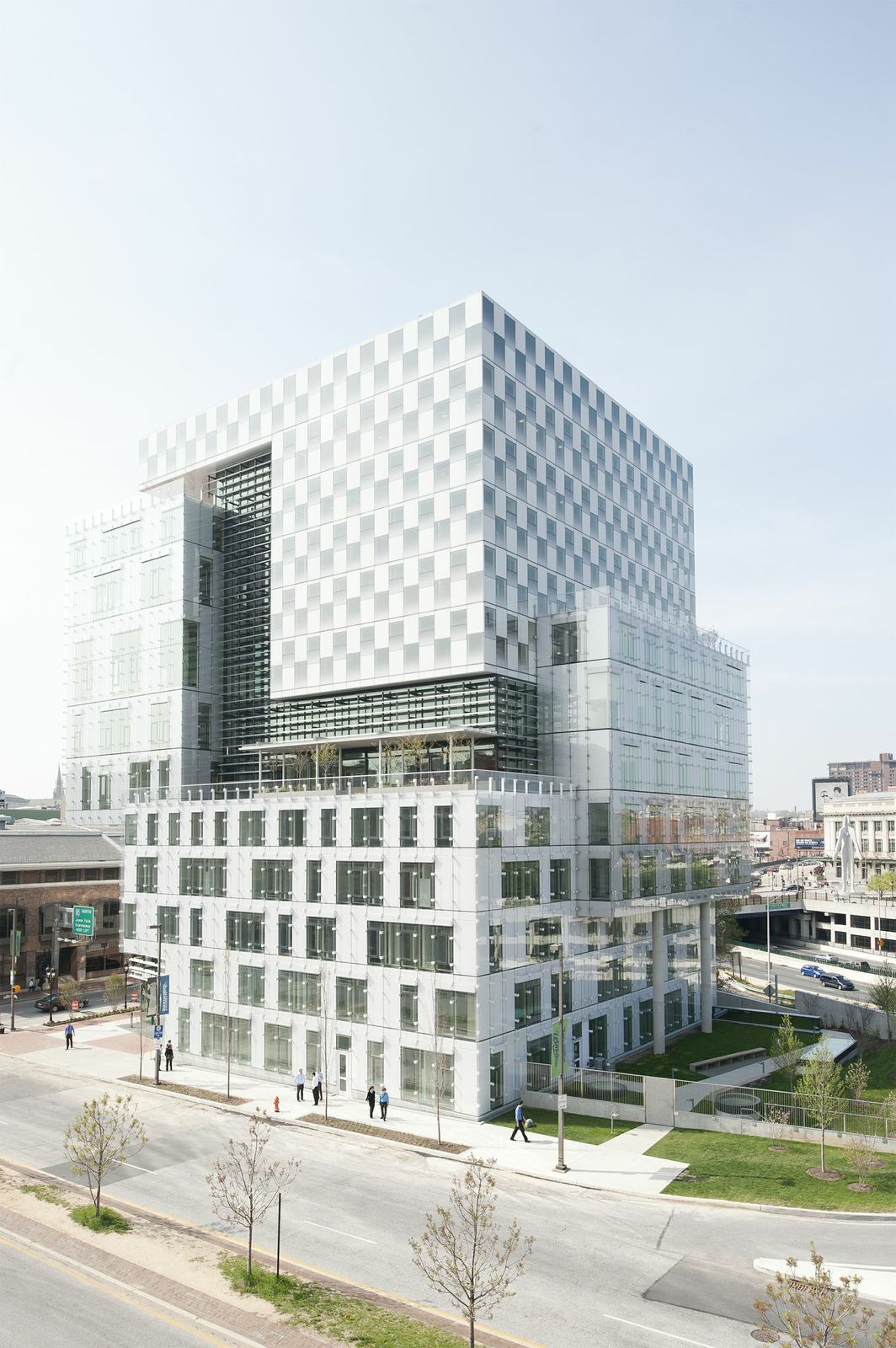
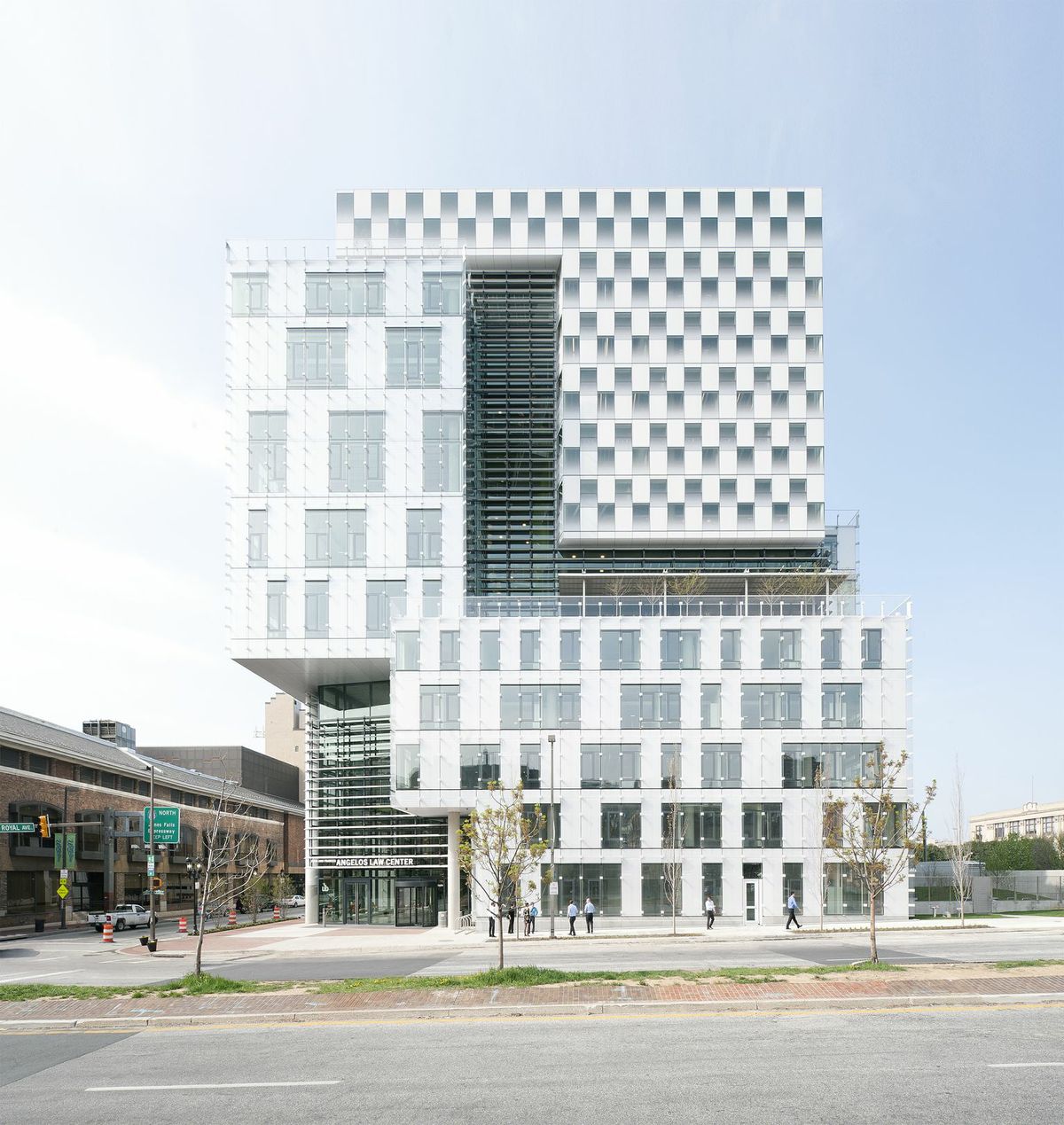
6. John & Frances Angelos Law Center, Baltimore, Md.
Behnisch Architekten and Ayers Saint Gross
Photos: Brad Feinknopf
The John and Frances Angelos Law Center is the first large-scale opportunity for the University of Baltimore to demonstrate its intent to pursue strategies that eliminate global warming emissions and achieve climate neutrality. With this in mind, the Law Center is a highly sustainable and innovative structure that strives to reduce reliance on energy and natural resources, minimizing its dependence on mechanical ventilation and artificial lighting of interiors. This is part of a larger comprehensive effort on the part of the A/E team to approach sustainability from a more holistic vantage point from the outset of the project.
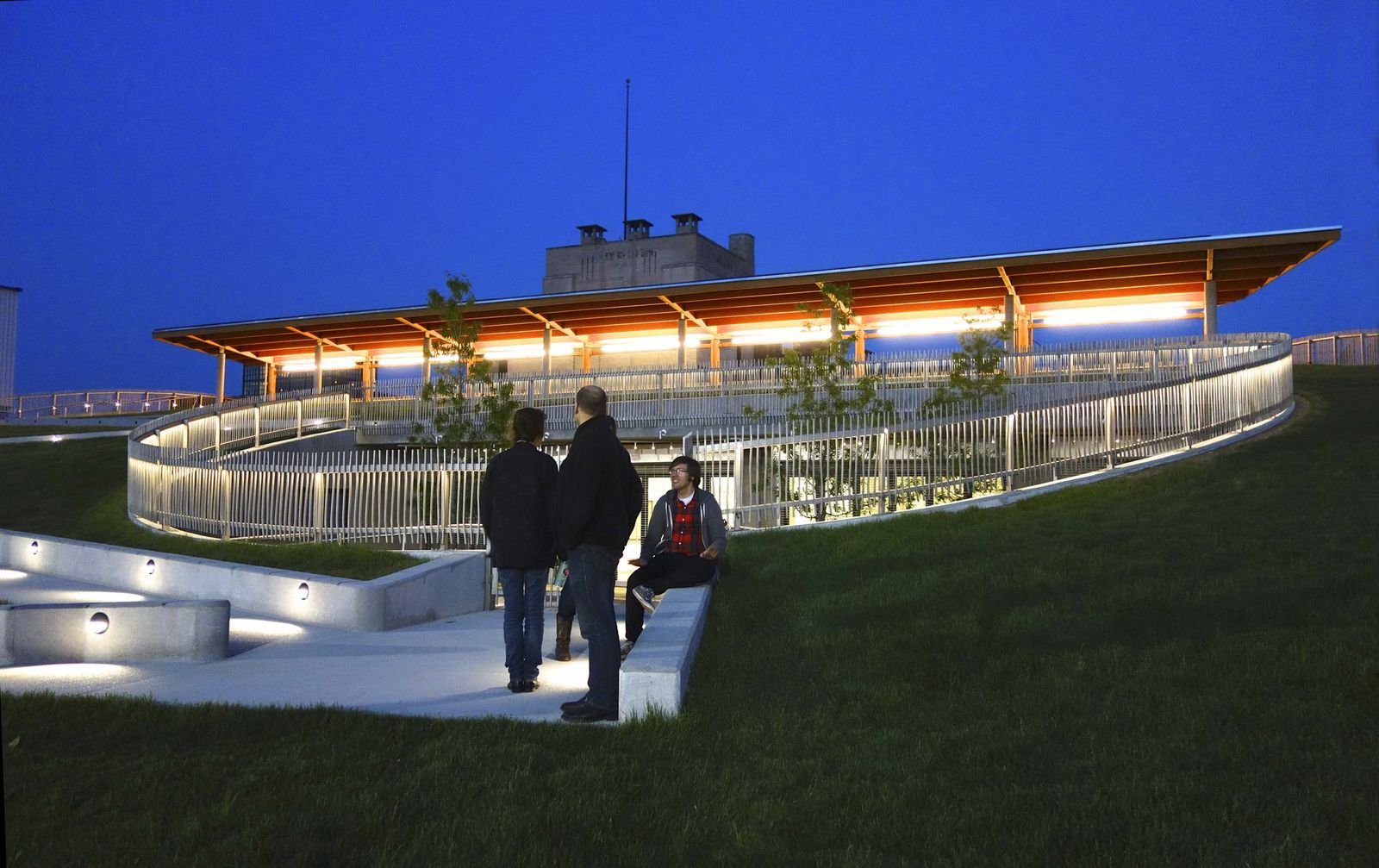
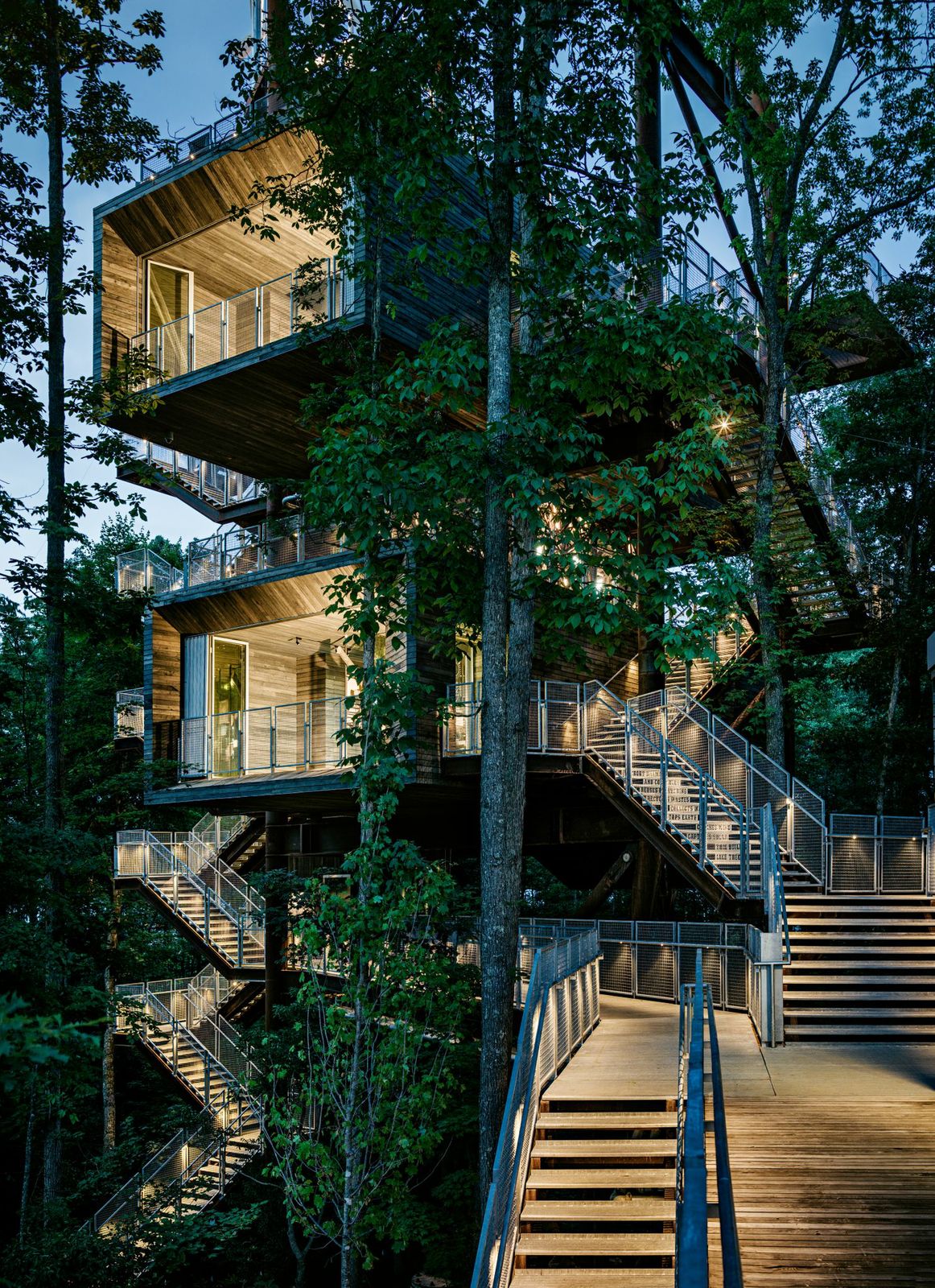
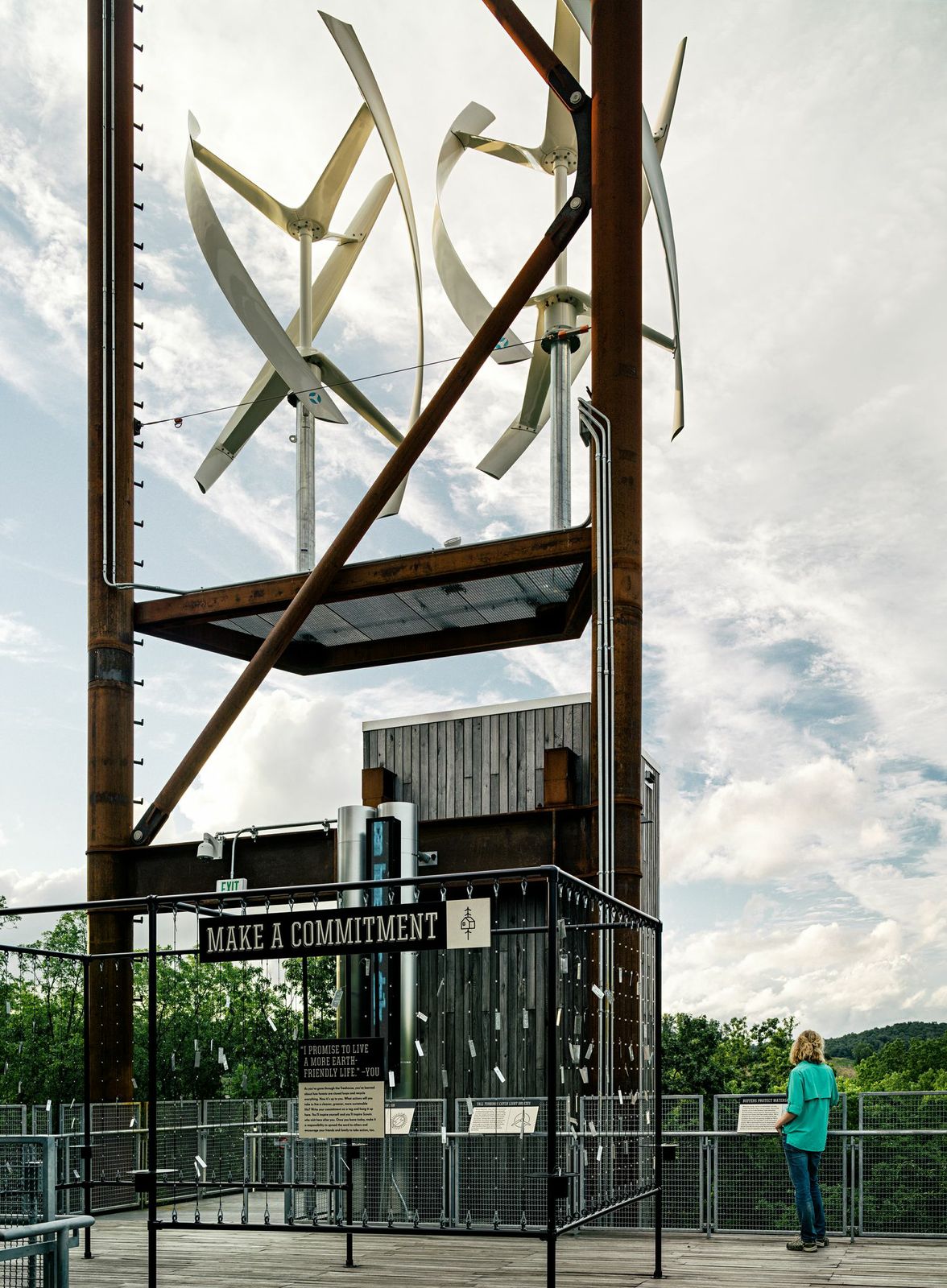
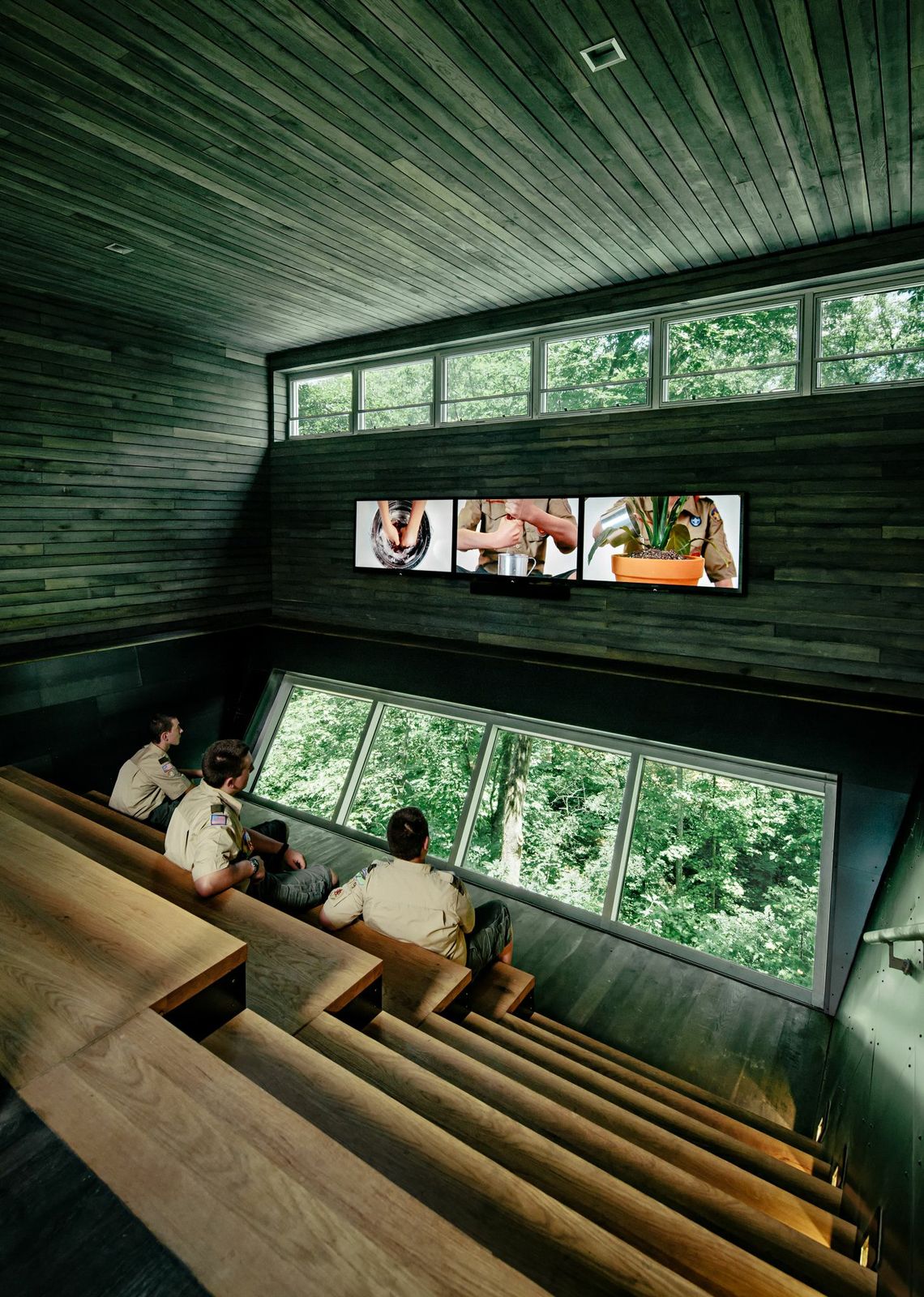
7. Sustainability Treehouse, Glen Jean, W.V.
Design Architect: Mithun; Executive Architect/Architect of Record: BNIM
Photos: Joe Fletcher
Situated in the forest at the Summit Bechtel Reserve, this interactive, interpretive and gathering facility serves as a unique icon of scouting adventure, environmental stewardship and high performance building design. Visitors ascend indoor and outdoor platforms to experience the forest from multiple vantages and engage with educational exhibits that explore the site and ecosystem at the levels of ground, tree canopy and sky. Innovative green building systems—including a 6,450-watt photovoltaic array output, two 4,000-watt wind turbines, and a 1,000-gallon cistern and water cleansing system—combine to yield a net-zero energy and net-zero water facility that touches its site lightly.
Photos: Jeremy Bitterman
The David and Lucile Packard Foundation headquarters acts as a catalyst for broad organizational sustainability and brings staff, grantees and partners together to solve the world’s most intractable problems. The Foundation's connection to the Los Altos community dates back to its inception in 1964. For the last two decades, as its grant making programs expanded locally and worldwide, staff and operations have been scattered in buildings throughout the city. This project enhances proximity and collaboration while renewing the Foundation’s commitment to the local community by investing in a downtown project intended to last through the end of 21st century.
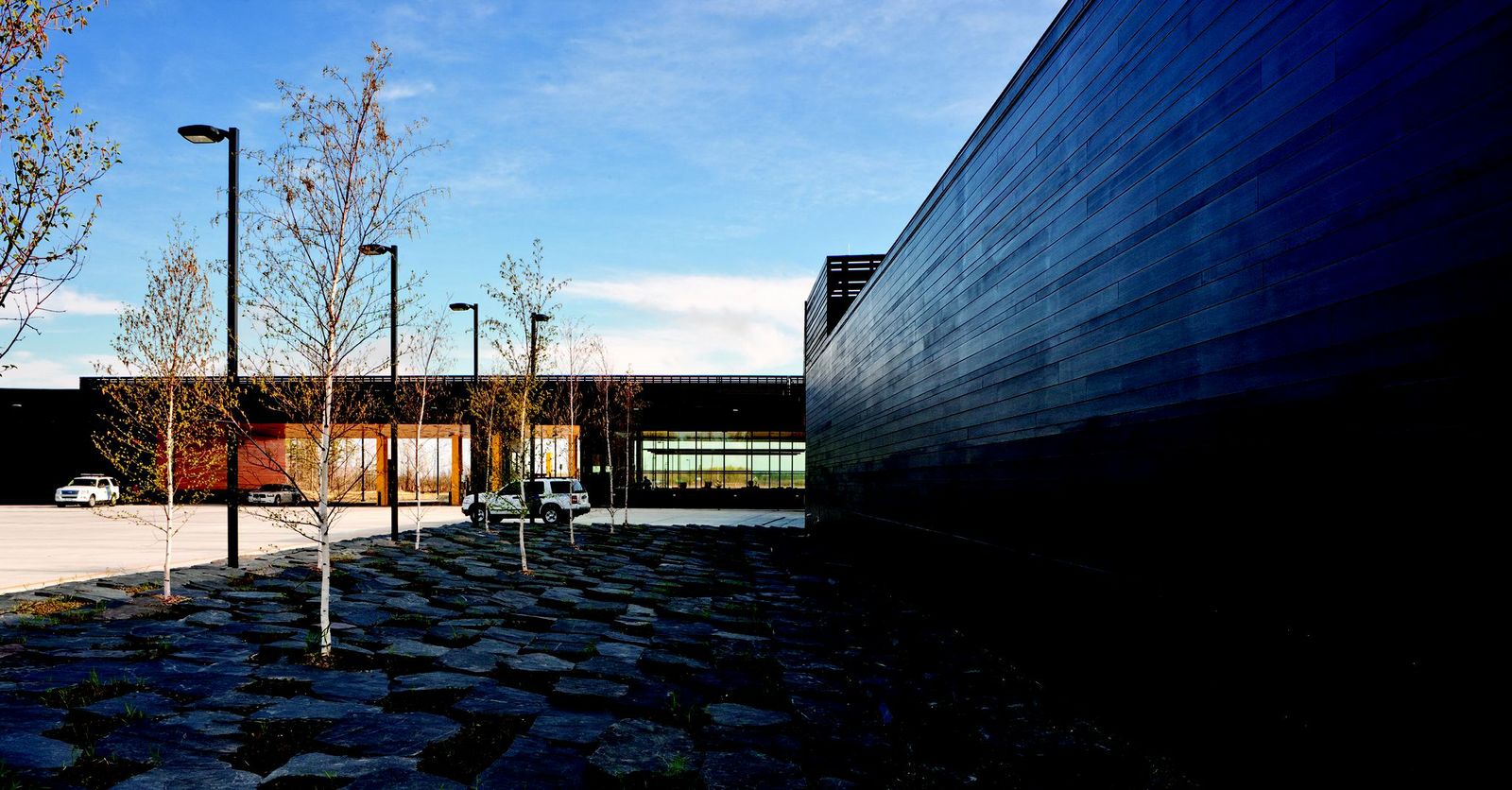
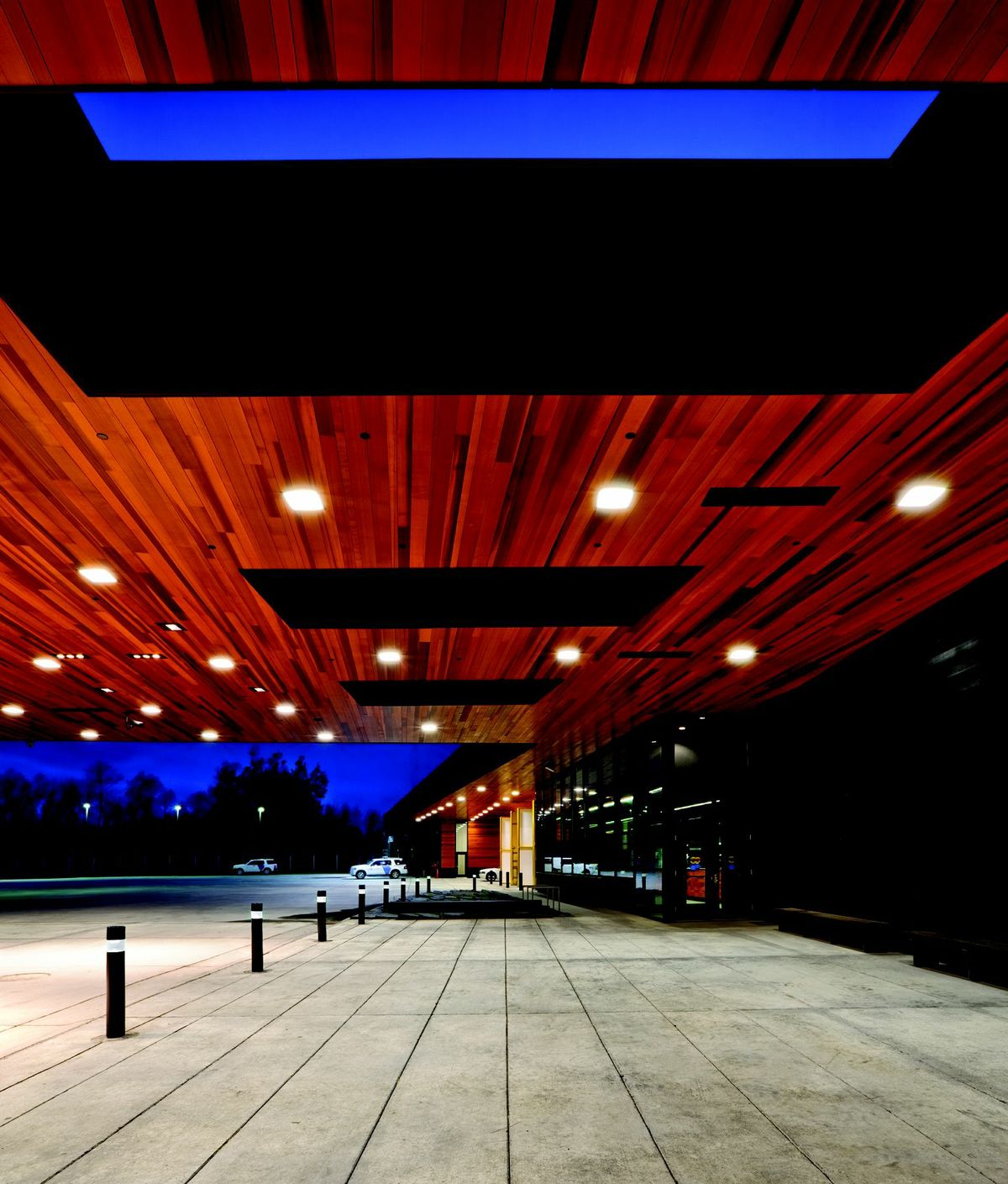
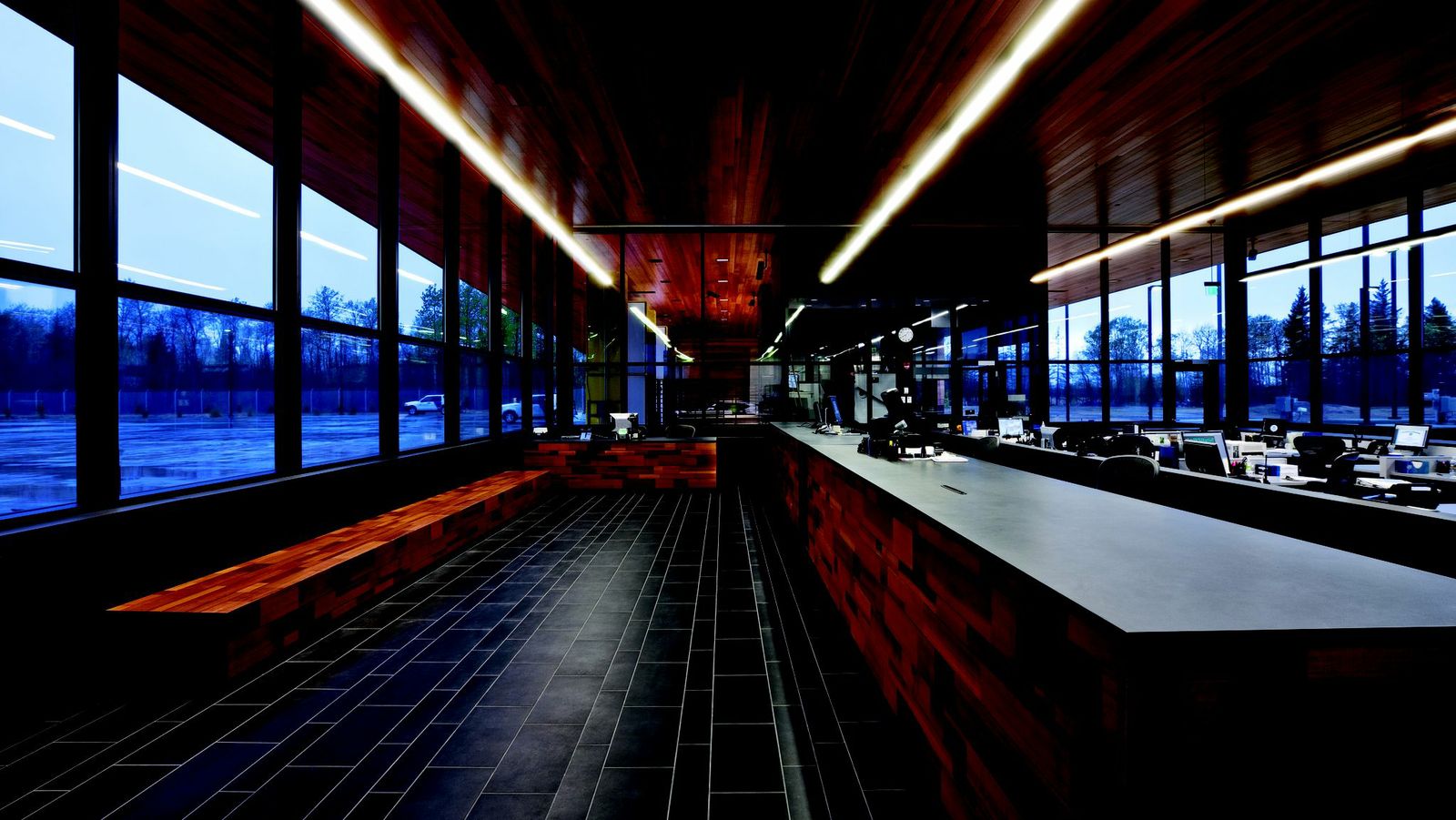
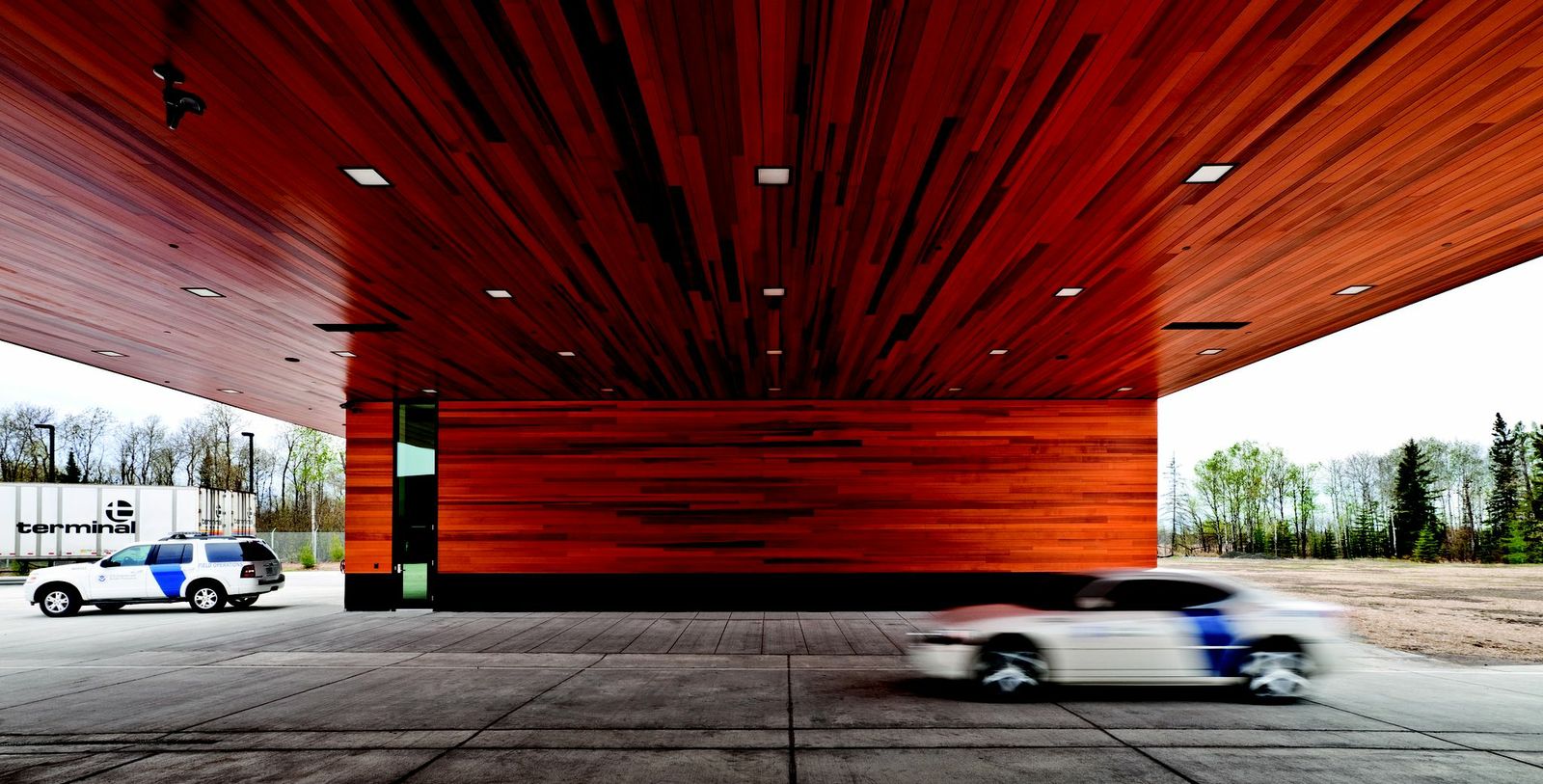
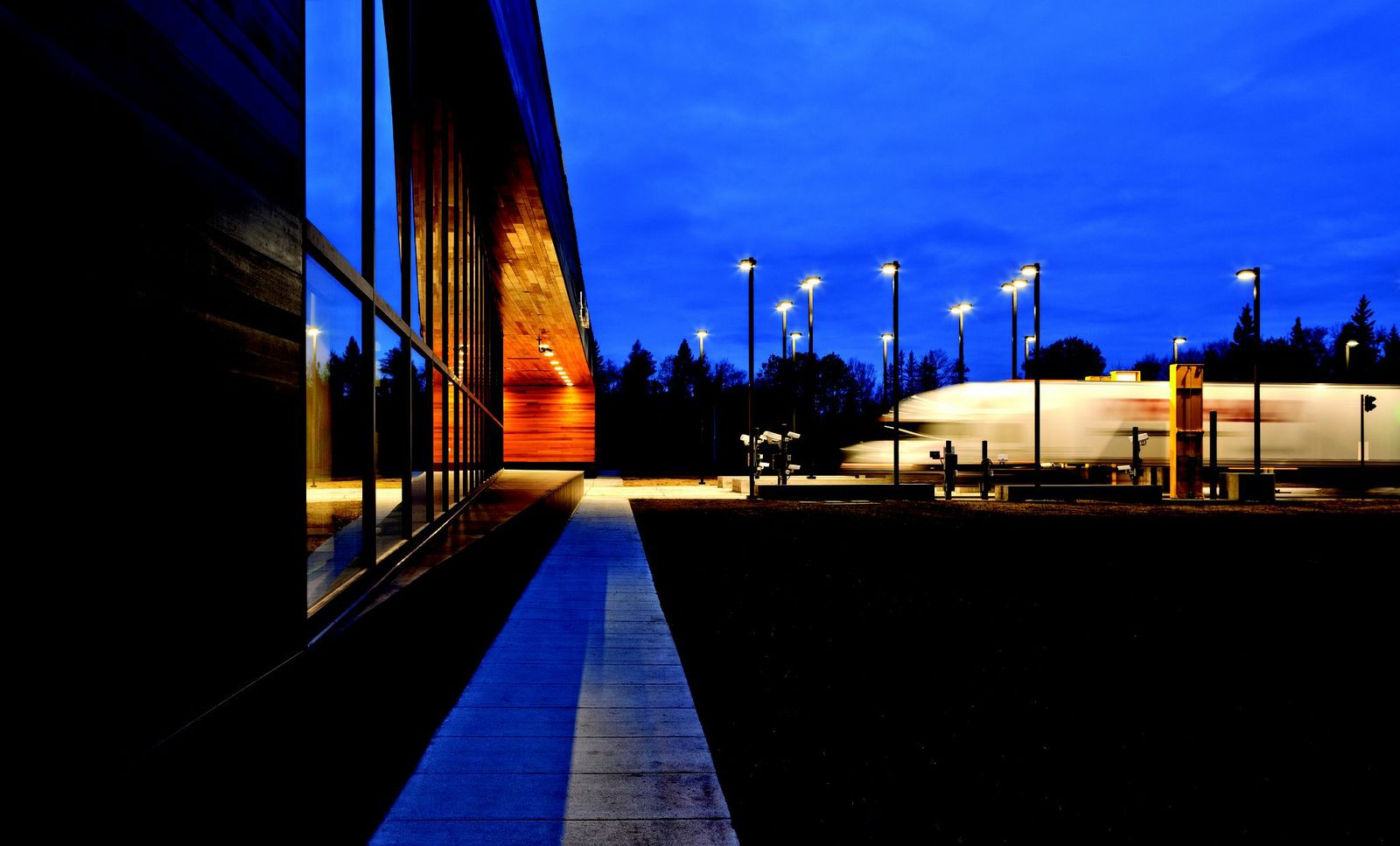
9. U.S. Land Port of Entry, Warroad, Minn.
Snow Kreilich Architects, Inc.
Photos: Paul Crosby
This LEED Gold certified Land Port of Entry is the first to employ a ground source heat pump system. Sustainably harvested cedar was used on the entire exterior envelope, canopies and some interior walls and 98% of all wood on the project is FSC certified. Additionally 22% of the material content came from recycled materials and 91% of all work areas have access to daylight. Rainwater collection, reconstructed wetlands and native plantings address resource and site-specific responses. The facility proudly supports the mission-driven demands of US Customs and Border Protection while addressing the sustainable challenges of our future.
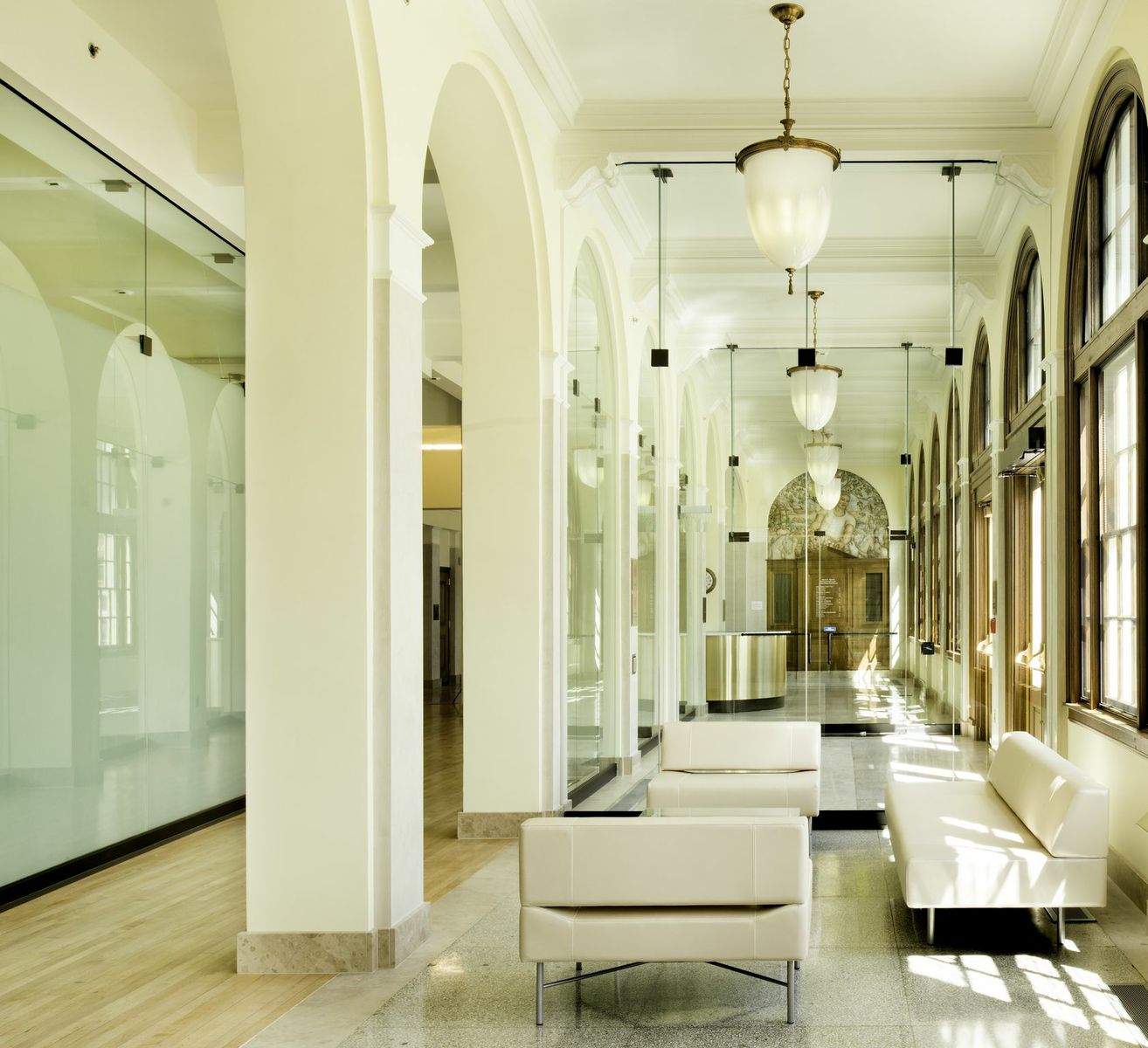
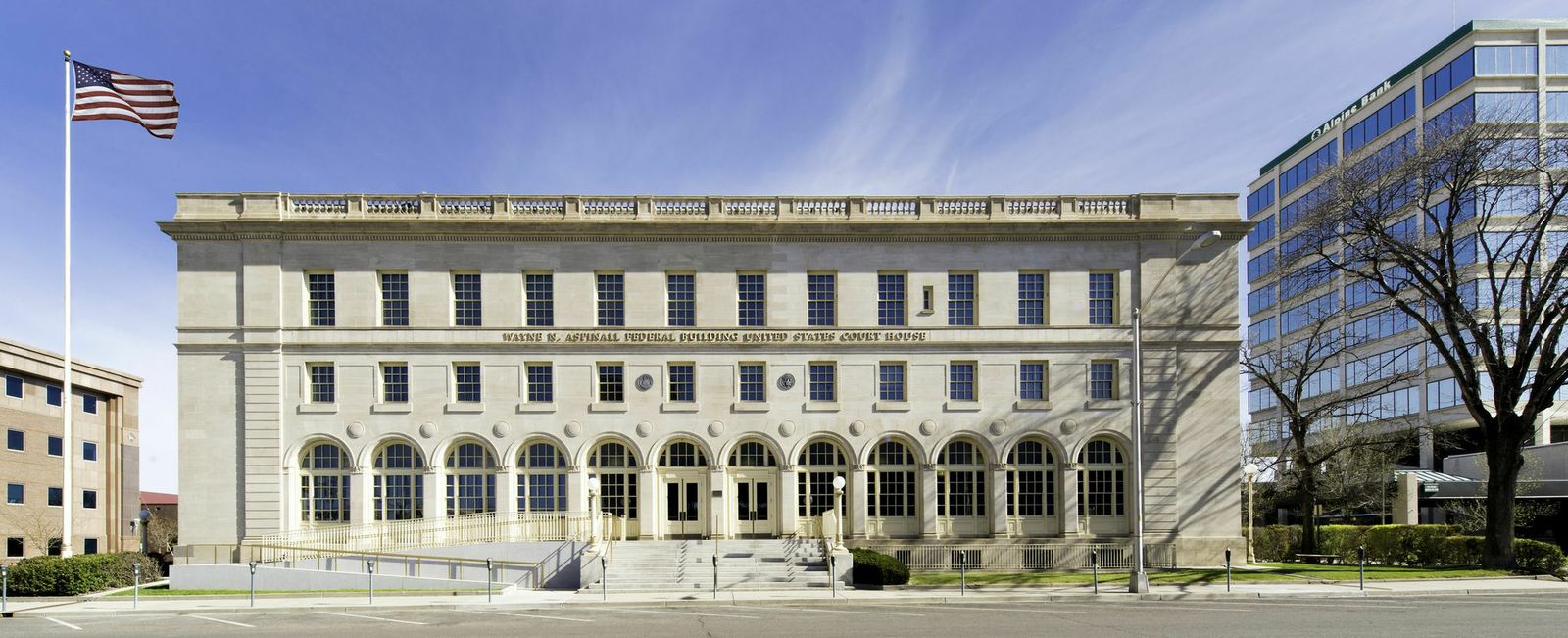
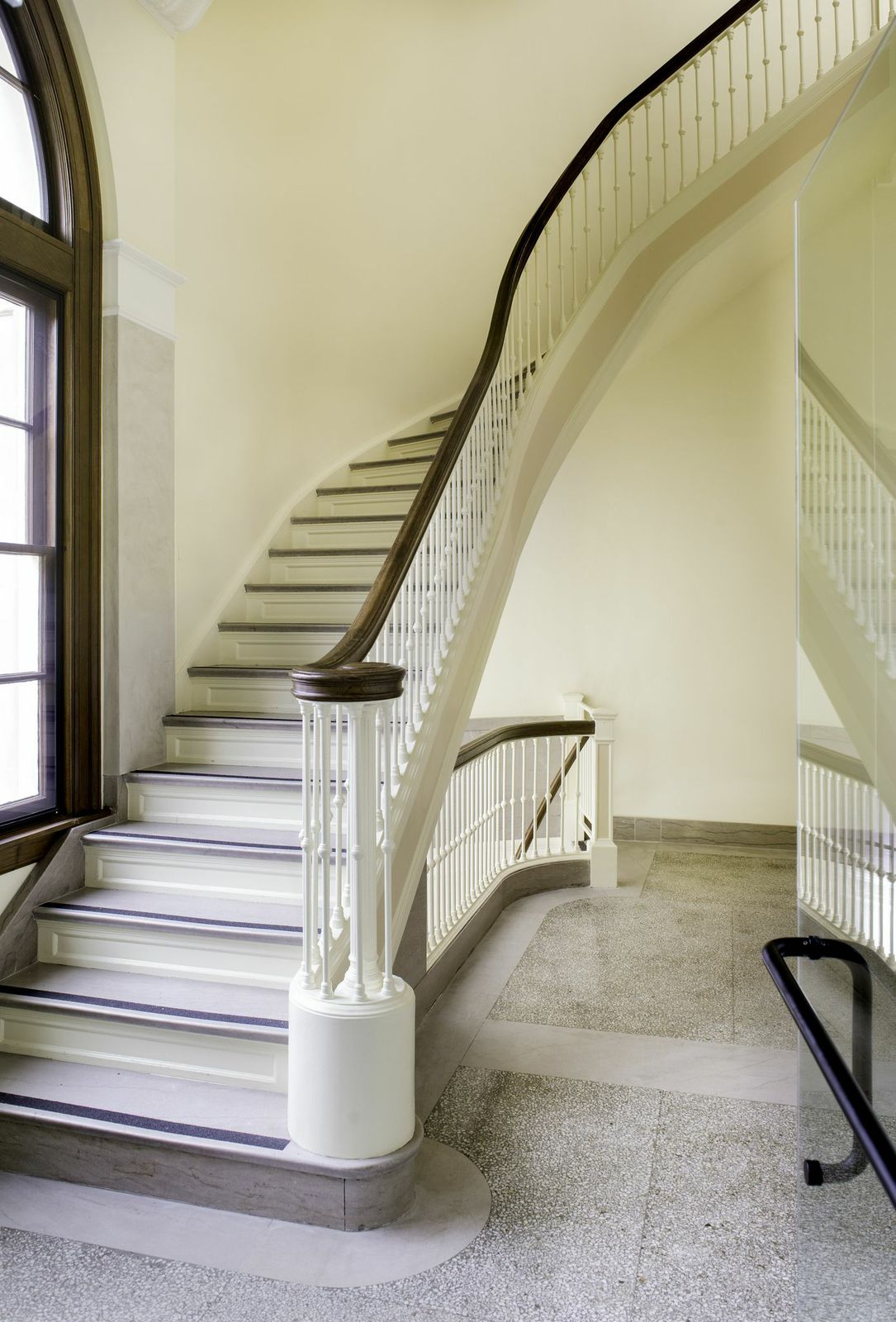
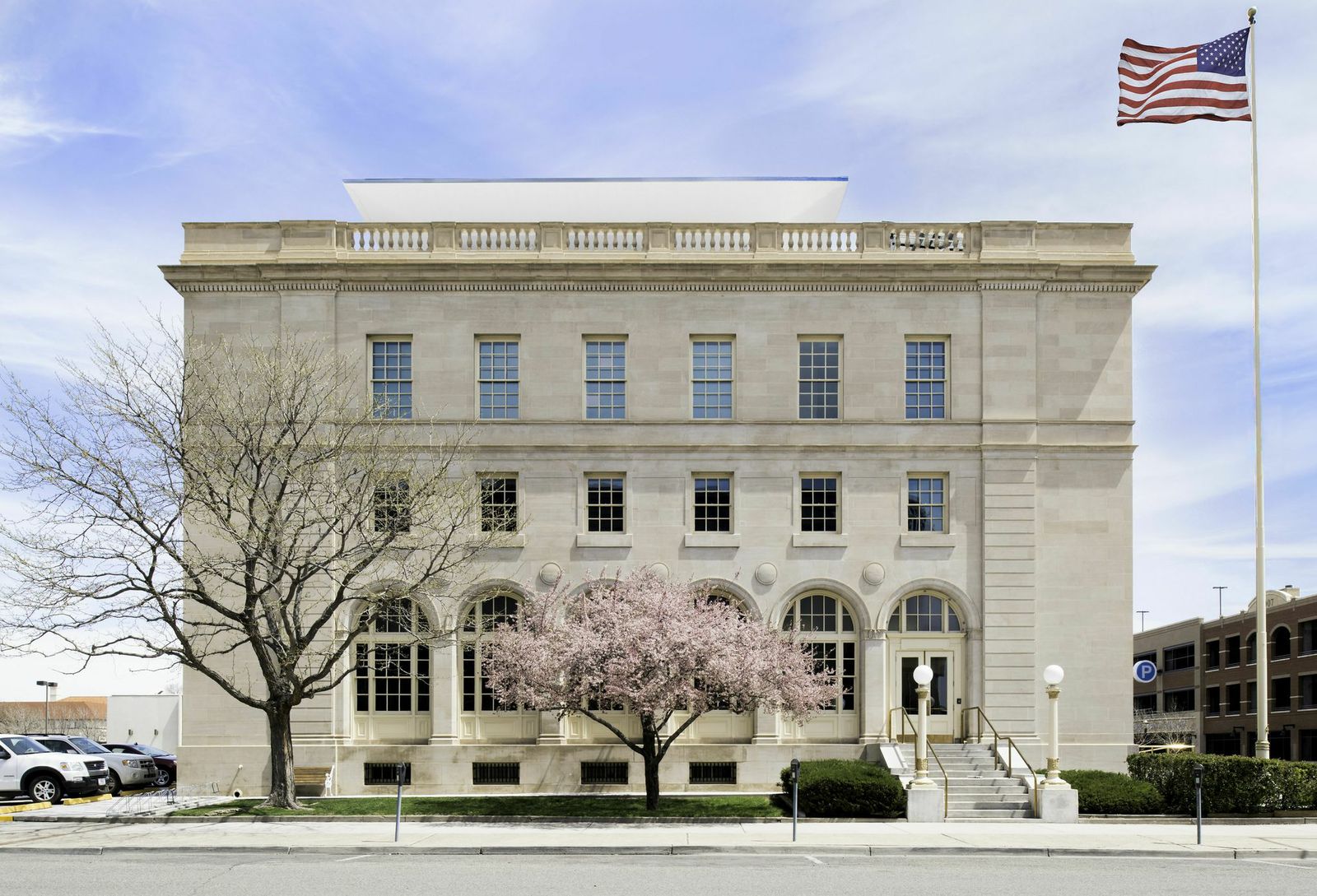
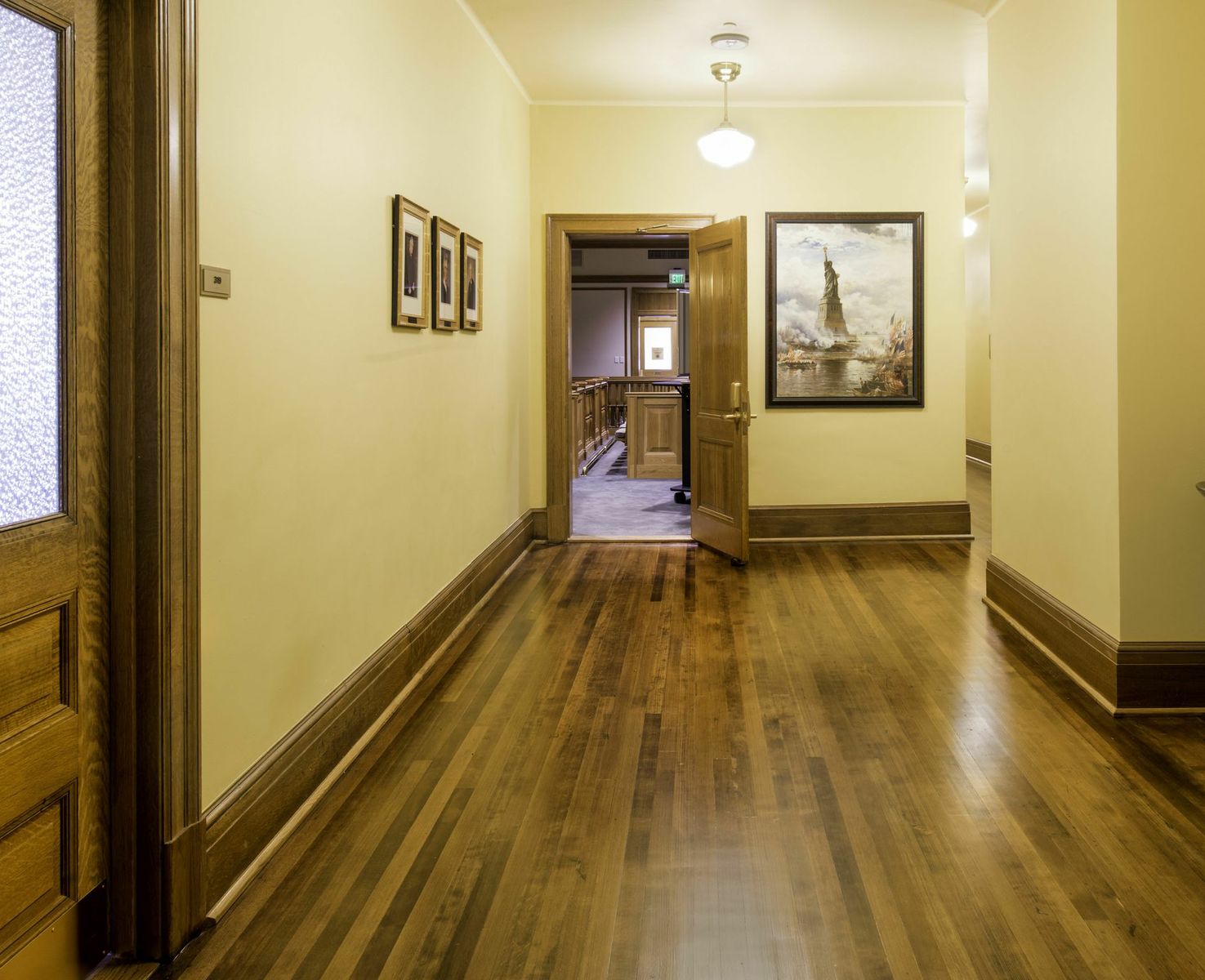
10. Wayne N. Aspinall Federal Building and U.S. Courthouse, Grand Junction, Colo.
Design Architect, Westlake Reed Leskosky and Architect of Record, The Beck Group
Photos: Kevin G. Reeves
The LEED Platinum renovation preserves an anchor in Grand Junction, and converts the 1918 landmark into one of the most energy efficient, sustainable historic buildings in the country. The design aims to be GSA’s first Site Net-Zero Energy facility on the National Register. Exemplifying sustainable preservation, it restores and showcases historic volumes and finishes, while sensitively incorporating innovative systems and drastically reducing energy consumption. Features include a roof canopy-mounted 123 kW photovoltaic array, variable-refrigerant flow heating and cooling systems, 32-well passive Geo-Exchange system, a thermally upgraded enclosure, energy recovery, wireless controls, fluorescent and LED lighting, and post-occupancy monitoring.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Burt Hill, HOK top BD+C's ranking of the nation's 100 largest university design firms
A ranking of the Top 100 University Design Firms based on Building Design+Construction's 2009 Giants 300 survey. For more Giants 300 rankings, visit http://www.BDCnetwork.com/Giants
| Aug 11, 2010
PBK, DLR Group among nation's largest K-12 school design firms, according to BD+C's Giants 300 report
A ranking of the Top 75 K-12 School Design Firms based on Building Design+Construction's 2009 Giants 300 survey. For more Giants 300 rankings, visit http://www.BDCnetwork.com/Giants
| Aug 11, 2010
Turner Building Cost Index dips nearly 4% in second quarter 2009
Turner Construction Company announced that the second quarter 2009 Turner Building Cost Index, which measures nonresidential building construction costs in the U.S., has decreased 3.35% from the first quarter 2009 and is 8.92% lower than its peak in the second quarter of 2008. The Turner Building Cost Index number for second quarter 2009 is 837.
| Aug 11, 2010
AGC unveils comprehensive plan to revive the construction industry
The Associated General Contractors of America unveiled a new plan today designed to revive the nation’s construction industry. The plan, “Build Now for the Future: A Blueprint for Economic Growth,” is designed to reverse predictions that construction activity will continue to shrink through 2010, crippling broader economic growth.
| Aug 11, 2010
New AIA report on embassies: integrate security and design excellence
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) released a new report to help the State Department design and build 21st Century embassies.
| Aug 11, 2010
Section Eight Design wins 2009 Open Architecture Challenge for classroom design
Victor, Idaho-based Section Eight Design beat out seven other finalists to win the 2009 Open Architecture Challenge: Classroom, spearheaded by the Open Architecture Network. Section Eight partnered with Teton Valley Community School (TVCS) in Victor to design the classroom of the future. Currently based out of a remodeled house, students at Teton Valley Community School are now one step closer to getting a real classroom.