Last month, I wrote about how automation and AI are dramatically changing all four fundamental relationships between buildings and machines. For example, nanotechnology, which manipulates individual atoms and molecules to assemble things, could make the modernist metaphor of a “machine for living in” into reality, since the building would actually be composed of many tiny machines.
In fact, that’s not quite accurate. The definition of “machine” is “an apparatus using or applying mechanical power and having several parts, each with a definite function and together performing a particular task.”
So machines are made of distinct parts, cobbled together to fulfill a function. They are characterized by their composition, as assemblages of singular bits and pieces in which the whole is greater than the sum.
SEE ALSO: Assessing AI's impact on the AEC profession and the built environment
But nanotech will completely change this. When entire buildings can be shaped from microscopic components, the visible distinction between the individual parts will evaporate. A structure built from invisible machines will not appear to be a machine at all, since it no longer will be perceived as an assembly of parts. An edifice made of congealed cybernetic butter will look to be all whole, no parts. The very concept of a “building” could become meaningless, since it will no longer be “built” in any traditional way.
Remember “Terminator 2”? Arnold Schwarzenegger’s T-800 is a machine: steel and servos wrapped in human skin. Robert Patrick’s T-1000 is made of liquid metal (“mimetic polyalloy”). He’s like sentient mercury, morphing into any shape he needs. A nanotech building (“nanotecture”?) would make conventional structures seem like Robby the Robot (of “Forbidden Planet” fame).
Buttery buildings could change everything we think and know about architecture. Frank Lloyd Wright felt that architectural form should stem from the inherent “nature” of its materials: “Each material speaks a language of its own.” In his mind, the proportions, heft, and texture of brick logically translated into structures such as the Robie House, which extends horizontally and hugs the land. But when the constituent parts of a building are too small to be seen with the naked eye, the relationships between form and materials will change. What is the “language” of a nanobot?
Because the character of a building could vary upon command—hard and opaque one minute, soft and transparent the next—the fabric of buildings could become fluid, fluctuating states from solid to liquid to gas and back. The notion of truth in materials will become irrelevant. In fact, the word material could go away. When the basic building blocks of architecture have no strict definition, structure and substance could separate. Matter may not matter.
Could there come a time when buildings will become less about bricks and mortar and feel more like mists or fogs, vaguely enveloping space in ways we can barely picture now? What will it be like to live in a cloud?
Lance Hosey, FAIA, LEED Fellow, is a Design Director with Gensler. His book, The Shape of Green: Aesthetics, Ecology, and Design, has been an Amazon #1 bestseller in the Sustainability & Green Design category.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | May 9, 2023
4 insights on building product manufacturers getting ‘smart’
Overall, half of building product manufacturers plan to invest in one or more areas of technology in the next three years.
Sustainability | May 1, 2023
Increased focus on sustainability is good for business and attracting employees
A recent study, 2023 State of Design & Make by software developer Autodesk, contains some interesting takeaways for the design and construction industry. Respondents to a survey of industry leaders from the architecture, engineering, construction, product design, manufacturing, and entertainment spheres strongly support the idea that improving their organization’s sustainability practices is good for business.
AEC Tech | May 1, 2023
Utilizing computer vision, AI technology for visual jobsite tasks
Burns & McDonnell breaks down three ways computer vision can effectively assist workers on the job site, from project progress to safety measures.
AEC Tech Innovation | Apr 27, 2023
Does your firm use ChatGPT?
Is your firm having success utilizing ChatGPT (or other AI chat tools) on your building projects or as part of your business operations? If so, we want to hear from you.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Resiliency | Apr 18, 2023
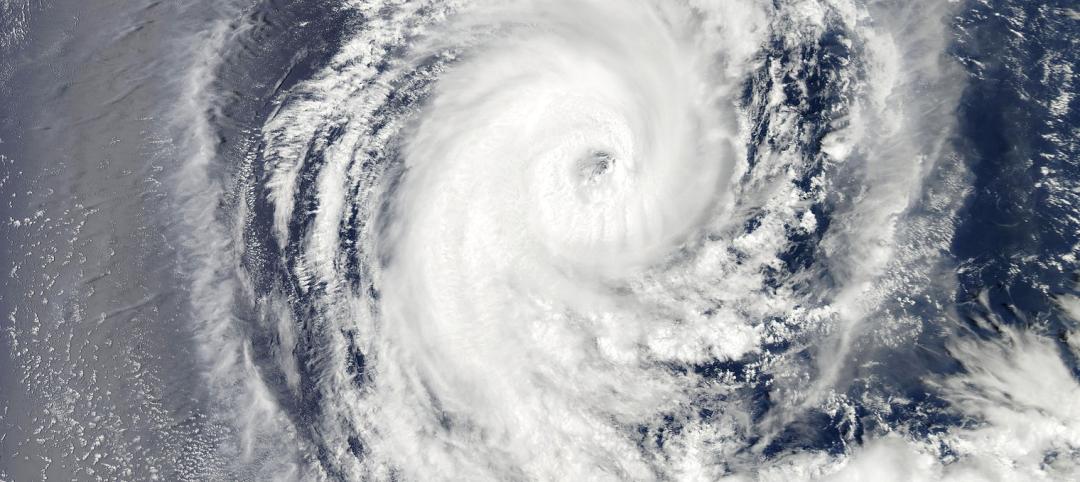
AI-simulated hurricanes could aid in designing more resilient buildings
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have devised a new method of digitally simulating hurricanes in an effort to create more resilient buildings. A recent study asserts that the simulations can accurately represent the trajectory and wind speeds of a collection of actual storms.
3D Printing | Apr 11, 2023
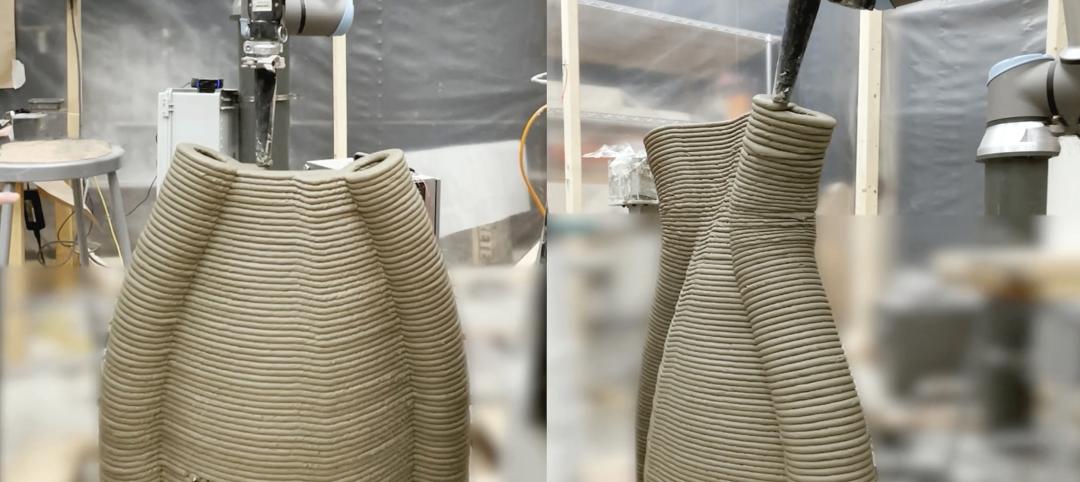
University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory unveils Shell Wall—a concrete wall that’s lightweight and freeform 3D printed
The University of Michigan’s DART Laboratory has unveiled a new product called Shell Wall—which the organization describes as the first lightweight, freeform 3D printed and structurally reinforced concrete wall. The innovative product leverages DART Laboratory’s research and development on the use of 3D-printing technology to build structures that require less concrete.
Smart Buildings | Apr 7, 2023
Carnegie Mellon University's research on advanced building sensors provokes heated controversy
A research project to test next-generation building sensors at Carnegie Mellon University provoked intense debate over the privacy implications of widespread deployment of the devices in a new 90,000-sf building. The light-switch-size devices, capable of measuring 12 types of data including motion and sound, were mounted in more than 300 locations throughout the building.
Architects | Apr 6, 2023
New tool from Perkins&Will will make public health data more accessible to designers and architects
Called PRECEDE, the dashboard is an open-source tool developed by Perkins&Will that draws on federal data to identify and assess community health priorities within the U.S. by location. The firm was recently awarded a $30,000 ASID Foundation Grant to enhance the tool.
AEC Tech | Mar 14, 2023
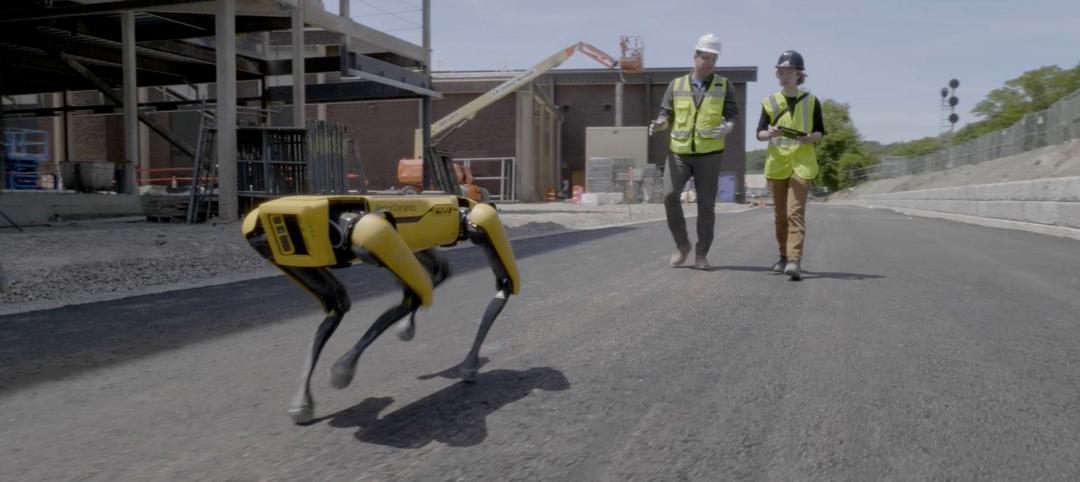
Skanska tests robots to keep construction sites clean
What if we could increase consistency and efficiency with housekeeping by automating this process with a robot? Introducing: Spot.