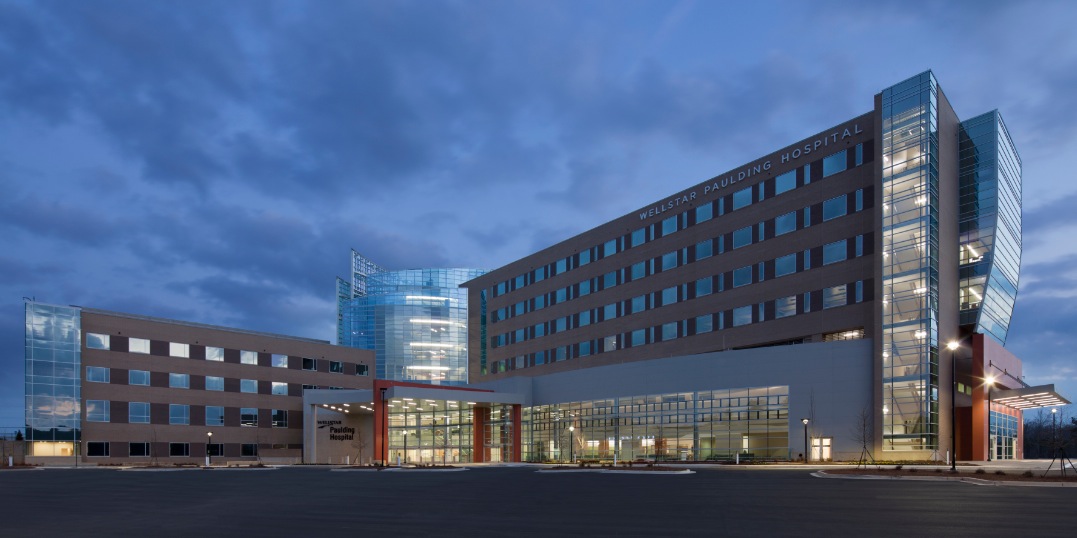
For years we have been told that the benefits of prefabrication often parallel those of building information modeling: increased safety and efficiency, higher quality, and reduced labor and material costs. Contractor Brasfield & Gorrie’s use of BIM and prefabrication on the $94 million WellStar Paulding Hospital in Hiram, Ga., is an excellent case study of how digital tools can inform prefabrication and lead to project savings, a safer work environment, and better-delivered construction.
The 100-bed Wellstar Paulding Hospital is one of the first hospitals in the U.S. to rely almost entirely on geothermal energy. The scope of the 24-month project took in 33 acres of site work, including a one-level, 120,000-sf precast parking deck; site utilities; modular block and concrete retaining walls; an eight-story, 295,700-sf hospital; a four-story, 82,220-sf medical office building; and a seven-story atrium that links the site’s two medical office buildings to the new hospital.
The design of the geothermal system called for 35,000 sf of radiant floor piping to heat and cool the atrium and high-ceiling areas. The ground-source heat pump system utilizes 209 wells, each 400 feet deep, with a total of about 38 miles of piping. The GSHP equipment included six chiller/heat pump modules, each with capacity for 110 tons of cooling and 2,038 MBH of heating.
The system has three sets of pumps: one for hot water, one for chilled water, and one for ground-loop circulation. More than half of the facility’s 700-ton total building cooling load is handled by the GSHP system. The remainder is managed by the air-cooled chillers. The GSHP system also handles the building heating and domestic hot water load of approximately 5,000 MBH.
With such complexity involved, both in the construction of the new hospital and connecting it with the medical office buildings, Brasfield & Gorrie turned to laser scanning and a sophisticated BIM program to inform its construction decisions.
VDC Modeling Starts the Process
Brasfield & Gorrie’s Virtual Design and Construction group created BIM models and collaborated in real time with the design team (including architect CPH Partners and engineering firm PerryCrabb) through more than 23 revision packages. Models were created in Autodesk Revit and reviewed in Autodesk Navisworks.
The BIM process correlated with the construction schedule, and was carefully planned as part of the overall project schedule. Each floor was modeled; each model included every trade and discipline.
The first step was to model everything under the basement slab, such as underground plumbing and electrical conduit. This model alone resolved 50 conflicts, including invert tie-in elevations with building and site storm systems and sloping grade beams with underground conduit.
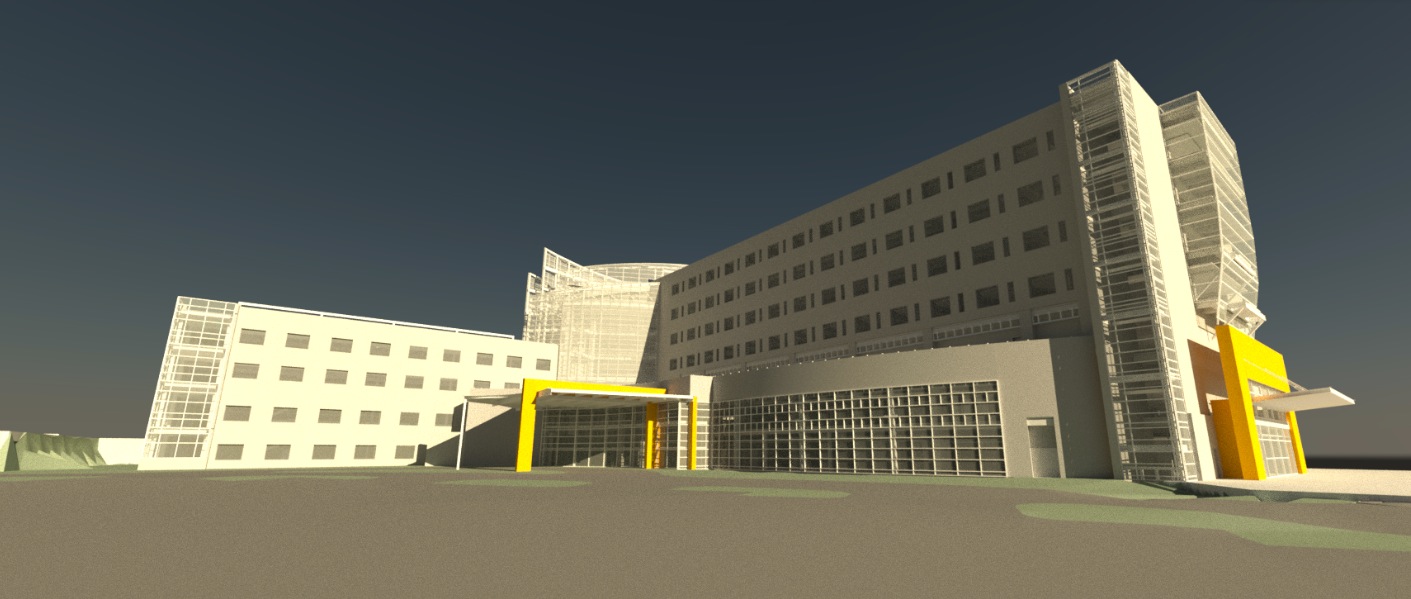 The $94 million WellStar Paulding Hospital in Hiram, Ga., is one of the first hospitals in the U.S. to rely almost entirely on geothermal energy. General contractor Brasfield & Gorrie worked with key subcontractors to create a comprehensive VDC model of the hospital’s systems.
The $94 million WellStar Paulding Hospital in Hiram, Ga., is one of the first hospitals in the U.S. to rely almost entirely on geothermal energy. General contractor Brasfield & Gorrie worked with key subcontractors to create a comprehensive VDC model of the hospital’s systems.
Utilizing existing conditions data imported from Trimble scans, the team was able to streamline the placement and installation of the hangers. “The efficiency in layout for hanger locations was achieved through the use of detailed models showing all locations, or insert points, where the hangers were needed,” says Scott Cloud, Brasfield & Gorrie’s Director of VDC.
The Building Team was able to coordinate the hanger locations within the model. Robotic total stations were utilized once formwork was completed and prior to concrete pours. Because the team was able to locate inserts within the concrete slabs as the structure was completed, it eliminated the need to drill/epoxy hangers in the concrete deck, post-shore removal. Not only did this allow for gains in schedule, it supported Brasfield & Gorrie’s ability to prefabricate larger assemblies for MEP overhead utilities and improved overall safety on the job by eliminating extra stockpiles of materials.
Electrical contractor Inglett & Stubbs exported data from the construction model to the company’s prefabrication department so that boxes and conduit could be built and delivered to the site already connected and ready for placement. All prefabricated units—junction boxes, conduit assemblies—and trapeze hanger assemblies were completed off site within Inglett & Stubbs’s shop.
Sheet metal contractor R.F. Knox Co. used the construction model for accurate prefabrication of ductwork and other metal components. The detailed development of the models fully supported material procurement for ductwork, piping, conduit, and even some equipment.
Because the BIM coordination process began nearly four months prior to the start of the elevated structure, the team was able to approve the fabrication design shop drawings and release material fabrication much earlier in the process than usual. As owner changes in the design occurred throughout construction, the detailed models aided in quicker and more accurate response times to pricing changes.
“When one section of the hospital originally designated as clinical office space changed to surgery recovery, we were able to quickly adapt to help complete a design that met design intent,” says Cloud, “but accurately relayed routing paths for utilities that would impact MEP material quantities.”
Sure Shoring with Shotcrete
Brasfield & Gorrie specified a shotcrete wall to hold up the foundation, and used a field survey to model the shotcrete wall virtually and coordinate the material for the slab rebar and penetrations.
A Brasfield & Gorrie field crew surveyed a series of points along the wall. This information was used to develop a 3D model of the wall, which was then incorporated within the composite model to coordinate MEP penetrations and structural dimensions, based on the actual dimensional survey information taken from the field.
Once coordinated in the model, this information was shared with the formwork, rebar, and MEP contractors to support material fabrication, release, deliveries, and installation in the field.
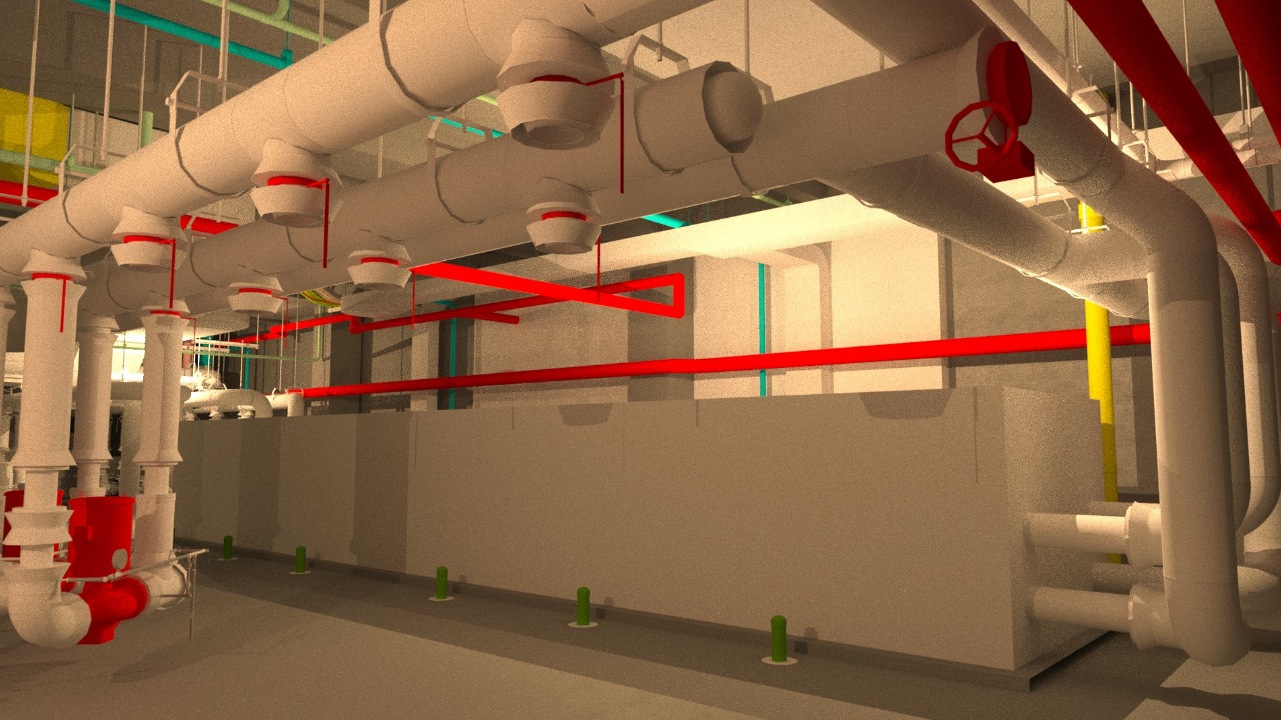 Using existing conditions data collected through laser scanning, the Building Team was able to coordinate the MEP systems hanger locations within the model. Robotic total stations were utilized to locate each hanger insert point within the concrete slabs as the structure was completed.
Using existing conditions data collected through laser scanning, the Building Team was able to coordinate the MEP systems hanger locations within the model. Robotic total stations were utilized to locate each hanger insert point within the concrete slabs as the structure was completed.
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
Luxury Hotel required faceted design
Goettsch Partners, Chicago, designed a new five-star, 214-room hotel for the King Abdullah Financial District (KAFD) in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The design-build project, with Saudi Oger Ltd. as contractor and Rayadah Investment Co. as developer, has a three-story podium supporting a 17-story glass tower with a nine-story opening that allows light to penetrate the mass of the building.
| Aug 11, 2010
Architectural Visualization Rendering the Future
Three-dimensional design tools have revolutionized the way architects and engineers design buildings; in recent years, parametric modeling has enabled Building Teams to impart weight tolerances and other intelligent information to a finished design. Yet many designers say they use 3D most in the conceptual design stage, when detailed building information is not necessary and can actually encumb...
| Aug 11, 2010
Big-time BIM
As the need for new state, county, and municipal facilities keeps growing and funding for public building construction continues to shrink, state and local officials are left with two basic options: renovate dilapidated older buildings and hope for the best, or build new facilities on anemic budgets.
| Aug 11, 2010
Dotting the I in IPD
Collaboration software is going beyond just sharing files. It is being used to enable full building information modeling early in design. Two programs are enabling Building Teams to more easily share the information in BIM and use it for integrated project delivery: Bluebeam Software, which just released the newest version of its AEC-specific PDF collaboration tool; and eBuilder Enterprise, a W...
| Aug 11, 2010
Great Solutions: Business Management
22. Commercial Properties Repositioned for University USE Tocci Building Companies is finding success in repositioning commercial properties for university use, and it expects the trend to continue. The firm's Capital Cove project in Providence, R.I., for instance, was originally designed by Elkus Manfredi (with design continued by HDS Architects) to be a mixed-use complex with private, market-...
| Aug 11, 2010
BIM adoption tops 80% among the nation's largest AEC firms, according to BD+C's Giants 300 survey
The nation's largest architecture, engineering, and construction companies are on the BIM bandwagon in a big way, according to Building Design+Construction's premier Top 50 BIM Adopters ranking, published as part of the 2009 Giants 300 survey. Of the 320 AEC firms that participated in Giants survey, 83% report having at least one BIM seat license in house, half have more than 30 seats, and near...
| Aug 11, 2010
Thrown For a Loop in China
While the Bird's Nest and Water Cube captured all the TV coverage during the Beijing Olympics in August, the Rem Koolhaas-designed CCTV Headquarters in Beijing—known as the “Drunken Towers” or “Big Shorts,” for its unusual shape—is certain to steal the show when it opens next year.
| Aug 11, 2010
Great Solutions: BIM/Information Technology
4. Architectural Visualization through Gaming Technology Before 3D walkthroughs for client presentations were popular, HKS manager of Advanced Technologies Pat Carmichael and his team were working to marry gaming engines with 3D building models. "What's being tasked to us more and more is not just to show design, but to show function," Carmichael said.
| Aug 11, 2010
Great Solutions: Collaboration
9. HOK Takes Videoconferencing to A New Level with its Advanced Collaboration Rooms To help foster collaboration among its 2,212 employees while cutting travel time, expenses, and carbon emissions traveling between its 24 office locations, HOK is fitting out its major offices with prototype videoconferencing rooms that are like no other in the U.
| Aug 11, 2010
BIM school, green school: California's newest high-performance school
Nestled deep in the Napa Valley, the city of American Canyon is one of a number of new communities in Northern California that have experienced tremendous growth in the last five years. Located 42 miles northeast of San Francisco, American Canyon had a population of just over 9,000 in 2000; by 2008, that figure stood at 15,276, with 28% of the population under age 18.







