As a result of the coronavirus pandemic, higher education is confronting its history of questionable facilities investment decisions and an unprecedented transformation on campuses that has made it imperative to reimagine construction, space allocation, and sustainability.
Gordian, a leading provider of facility and construction cost data, software, and services, analyzes the complexities of this transformation in the latest edition of its State of Facilities in Higher Education report, which this year Gordian conducted with APPA, an organization that represents more than 18,000 educational facilities professionals from over 1,300 learning institutions.
The report advocates for the increasing relevance of facilities managers at a time when campuses are building more space (schools in Gordian’s database were up 16% since 2007), but have also ill-advisedly deferred renovation on existing buildings, to the point where their backlog of asset renewal has increased by 35% since 2007, and their investment shortfall grew to 25%.
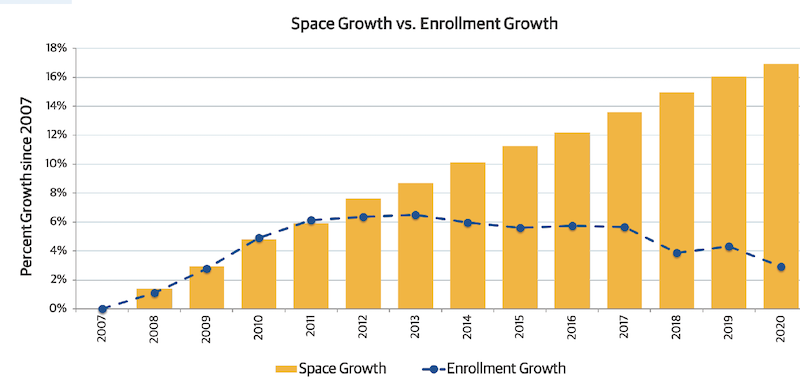
Colleges in Gordian's database have increased their space by 16% since 2007, but their student enrollment has increased only 2%. Images: Gordian and APPA
HOW MUCH SPACE WILL BE REQUIRED?
The pandemic has disrupted institutional improvement budgets by reducing student enrollment and shifting learning to remote and digital platforms that have lessened the need for campus spaces such as offices, dining halls, and residences. Outdoor spaces “were the rare bright spot, when weather has allowed,” the report states.
Consequently, campus planners are raising questions about what kinds of spaces will be needed in the future, and why. But adaptively reusing campus space is easier said than done. “Facilities offices aren’t sized and organized to maintain, clean and renovate according to student and staff activity. Rather, these offices maintain campus buildings independent of activity level,” the report observes.
Finding ways to fund facilities improvements and upgrades won’t be simple, either. The American Council on Education projects that the industry needs at least $180 billion to offset revenue losses and COVID-related expenses to maintain safe operations during the pandemic. But with between 50% and 70% of campus expenditures earmarked for employee compensation, the opportunities for addressing budget shortfalls without touching staffing are limited. For the whole of 2020, the industry lost 650,000 jobs.
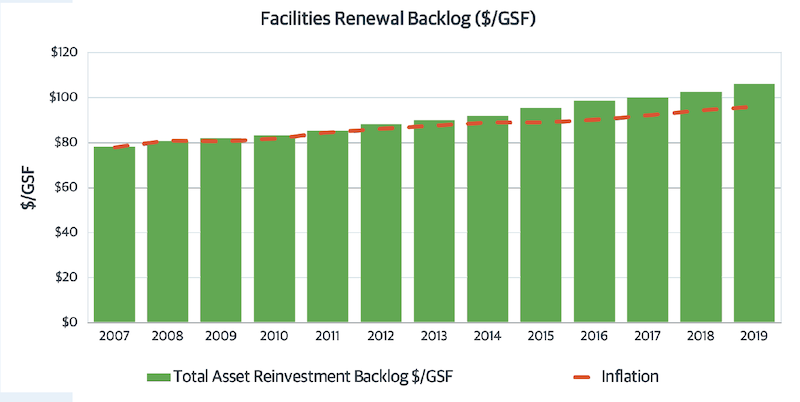
Backlogs of campuses' asset renewal needs have grown to $106 per gross sf, and 35% increase since 2007.
WHAT DOES ‘COMMUNITY’ MEAN TODAY?
The report notes that in the 2020 fall semester, 44% of schools were fully or primarily online, with another 21% operating in hybrid teaching mode. However, Gordian and APPA contend that the virtual world is not yet able to replace the in-person [educational] experience. “Community continues to be reliant on the physical gatherings of people, which will be an expected element of the collegiate experience for some time to come.”
If schools can’t provide this meaningful engagement, as well as some demonstrable evidence of a return on students’ investment, enrollments will continue to drop. The 13% decline in last year’s incoming freshman class “will have a ripple effect across the next three to five years,” the report states.
And schools can no longer rely on international students to help bridge their financial gaps.
The whole concept of campus “community” is changing. And the sudden embrace of digital tools for teaching opens endless interpretations of what an academic community looks like. “An opportunity clearly exists to reimagine campus space. The window is open to embrace digital, distant and trust-based work environments, and [schools] should leap to take advantage of the moment.”
More to the point, “the data say we need to use less space because [schools] simply can’t care for what [they’ve] built,” says the report.
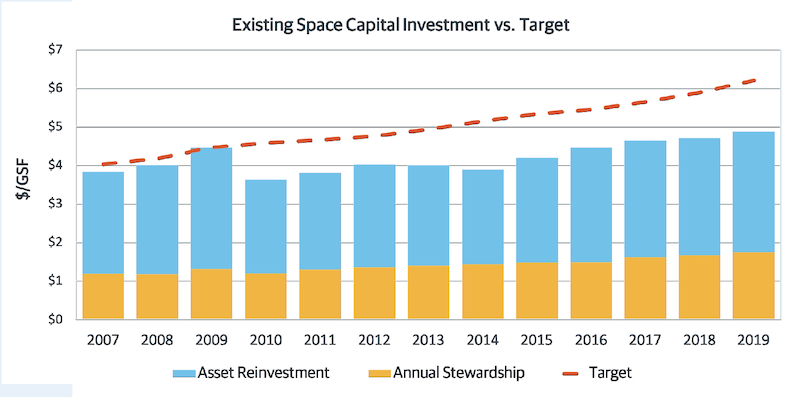
The investment shortfall in existing campus facilities has grown to 25% over the past 13 years.
HARD CHOICES WILL BE NECESSARY
So what are colleges and universities to do?
A start would be to document real operating costs, including the accrual of deferred needs with altered staffing and reduced capital investment. Facilities managers must prioritize space going forward, and clarify how students are likely to be taught. “Create a coherent narrative, incorporating the expectations of the community and the demands of the facilities, that represents a shared agreement for how to best optimize service to academic aspirations and institutional mission.”
Regarding future investments, schools must define their risk tolerances, especially it comes to keeping building systems operable to avoid shutdowns. Finance and facilities leaders must jointly understand how best to invest in a school’s physical plant, and develop a suitable investment strategy based on future need. That strategy, states the report, should have buy-in from the school’s senior leadership as well as stakeholders—students, faculty, workers—who will be affected by those decisions.
To meet the challenges of more dynamic campuses with fluid spaces and use, the report suggests that, at a minimum, institutions need to honestly appraise their facilities management teams, and determine what skills they will need for the next crisis but also routine times.
“Assess the type or work that has been required and is anticipated to be required to match hiring practices with the skills of the future,” the report states.
Related Stories
| Nov 23, 2010
Honeywell's School Energy and Environment Survey: 68% of districts delayed or eliminated improvements because of economy
Results of Honeywell's second annual “School Energy and Environment Survey” reveal that almost 90% of school leaders see a direct link between the quality and performance of school facilities, and student achievement. However, districts face several obstacles when it comes to keeping their buildings up to date and well maintained. For example, 68% of school districts have either delayed or eliminated building improvements in response to the economic downturn.
| Nov 9, 2010
Just how green is that college campus?
The College Sustainability Report Card 2011 evaluated colleges and universities in the U.S. and Canada with the 300 largest endowments—plus 22 others that asked to be included in the GreenReportCard.org study—on nine categories, including climate change, energy use, green building, and investment priorities. More than half (56%) earned a B or better, but 6% got a D. Can you guess which is the greenest of these: UC San Diego, Dickinson College, University of Calgary, and Dartmouth? Hint: The Red Devil has turned green.
| Nov 3, 2010
First of three green labs opens at Iowa State University
Designed by ZGF Architects, in association with OPN Architects, the Biorenewable Research Laboratory on the Ames campus of Iowa State University is the first of three projects completed as part of the school’s Biorenewables Complex. The 71,800-sf LEED Gold project is one of three wings that will make up the 210,000-sf complex.
| Nov 3, 2010
Park’s green education center a lesson in sustainability
The new Cantigny Outdoor Education Center, located within the 500-acre Cantigny Park in Wheaton, Ill., earned LEED Silver. Designed by DLA Architects, the 3,100-sf multipurpose center will serve patrons of the park’s golf courses, museums, and display garden, one of the largest such gardens in the Midwest.
| Nov 3, 2010
Seattle University’s expanded library trying for LEED Gold
Pfeiffer Partners Architects, in collaboration with Mithun Architects, programmed, planned, and designed the $55 million renovation and expansion of Lemieux Library and McGoldrick Learning Commons at Seattle University. The LEED-Gold-designed facility’s green features include daylighting, sustainable and recycled materials, and a rain garden.
| Nov 3, 2010
Recreation center targets student health, earns LEED Platinum
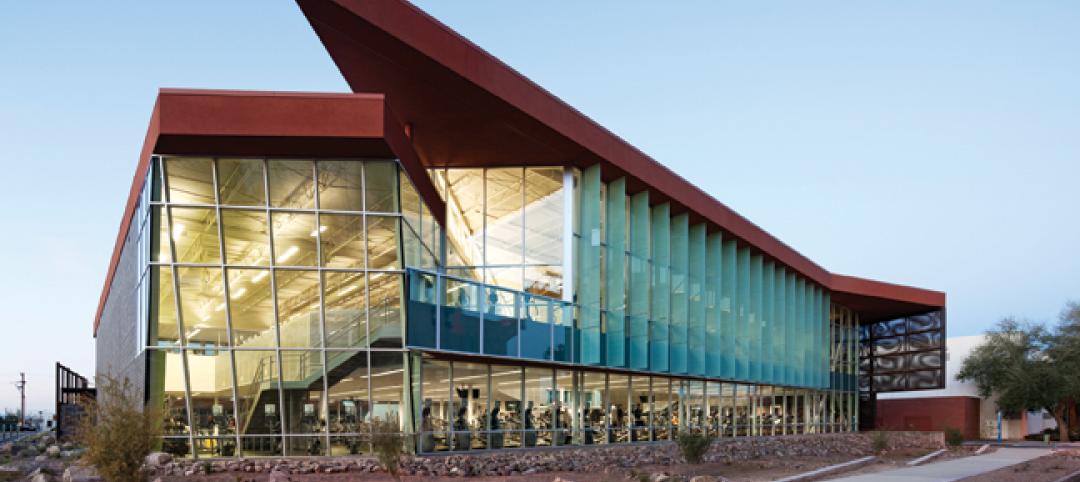
Not only is the student recreation center at the University of Arizona, Tucson, the hub of student life but its new 54,000-sf addition is also super-green, having recently attained LEED Platinum certification.
| Nov 3, 2010
Designs complete for new elementary school
SchenkelShultz has completed design of the new 101,270-sf elementary Highlands Elementary School, as well as designs for three existing buildings that will be renovated, in Kissimmee, Fla. The school will provide 48 classrooms for 920 students, a cafeteria, a media center, and a music/art suite with outdoor patio. Three facilities scheduled for renovations total 19,459 sf and include an eight-classroom building that will be used as an exceptional student education center, a older media center that will be used as a multipurpose building, and another building that will be reworked as a parent center, with two meeting rooms for community use. W.G. Mills/Ranger is serving as CM for the $15.1 million project.
| Nov 3, 2010
Virginia biofuel research center moving along
The Sustainable Energy Technology Center has broken ground in October on the Danville, Va., campus of the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research. The 25,000-sf facility will be used to develop enhanced bio-based fuels, and will house research laboratories, support labs, graduate student research space, and faculty offices. Rainwater harvesting, a vegetated roof, low-VOC and recycled materials, photovoltaic panels, high-efficiency plumbing fixtures and water-saving systems, and LED light fixtures will be deployed. Dewberry served as lead architect, with Lord Aeck & Sargent serving as laboratory designer and sustainability consultant. Perigon Engineering consulted on high-bay process labs. New Atlantic Contracting is building the facility.
| Nov 3, 2010
Dining center cooks up LEED Platinum rating
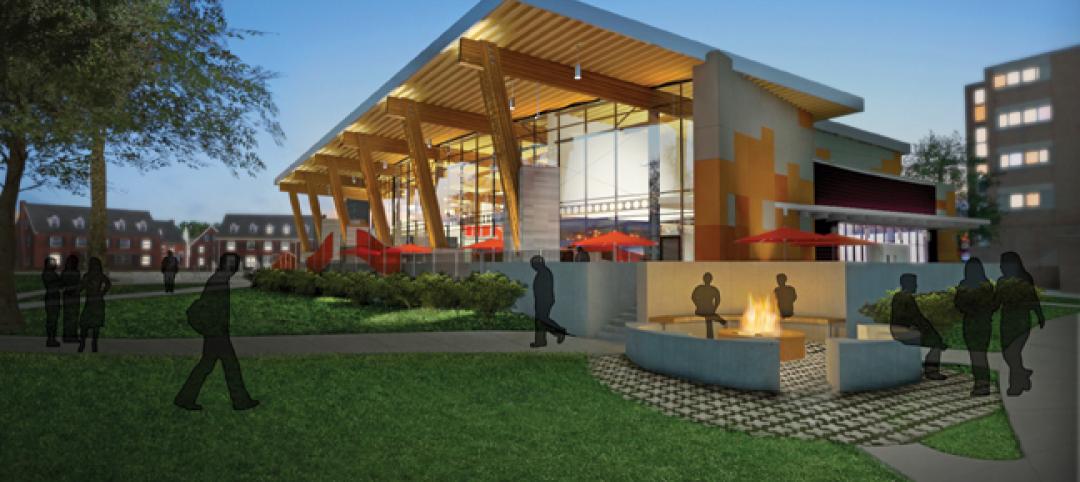
Students at Bowling Green State University in Ohio will be eating in a new LEED Platinum multiuse dining center next fall. The 30,000-sf McDonald Dining Center will have a 700-seat main dining room, a quick-service restaurant, retail space, and multiple areas for students to gather inside and out, including a fire pit and several patios—one of them on the rooftop.
| Nov 2, 2010
Cypress Siding Helps Nature Center Look its Part
The Trinity River Audubon Center, which sits within a 6,000-acre forest just outside Dallas, utilizes sustainable materials that help the $12.5 million nature center fit its wooded setting and put it on a path to earning LEED Gold.















