As a result of the coronavirus pandemic, higher education is confronting its history of questionable facilities investment decisions and an unprecedented transformation on campuses that has made it imperative to reimagine construction, space allocation, and sustainability.
Gordian, a leading provider of facility and construction cost data, software, and services, analyzes the complexities of this transformation in the latest edition of its State of Facilities in Higher Education report, which this year Gordian conducted with APPA, an organization that represents more than 18,000 educational facilities professionals from over 1,300 learning institutions.
The report advocates for the increasing relevance of facilities managers at a time when campuses are building more space (schools in Gordian’s database were up 16% since 2007), but have also ill-advisedly deferred renovation on existing buildings, to the point where their backlog of asset renewal has increased by 35% since 2007, and their investment shortfall grew to 25%.
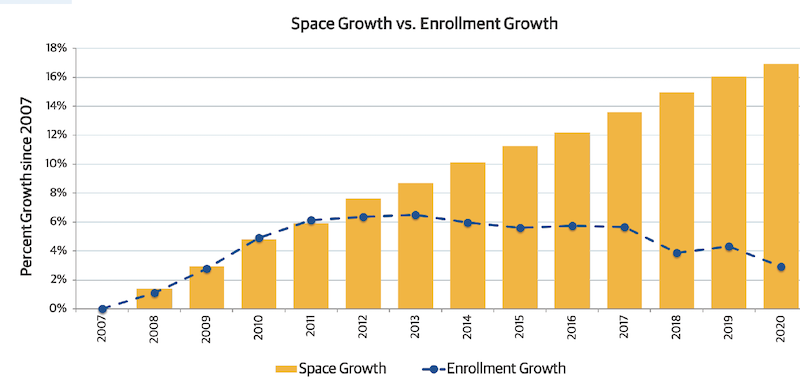
Colleges in Gordian's database have increased their space by 16% since 2007, but their student enrollment has increased only 2%. Images: Gordian and APPA
HOW MUCH SPACE WILL BE REQUIRED?
The pandemic has disrupted institutional improvement budgets by reducing student enrollment and shifting learning to remote and digital platforms that have lessened the need for campus spaces such as offices, dining halls, and residences. Outdoor spaces “were the rare bright spot, when weather has allowed,” the report states.
Consequently, campus planners are raising questions about what kinds of spaces will be needed in the future, and why. But adaptively reusing campus space is easier said than done. “Facilities offices aren’t sized and organized to maintain, clean and renovate according to student and staff activity. Rather, these offices maintain campus buildings independent of activity level,” the report observes.
Finding ways to fund facilities improvements and upgrades won’t be simple, either. The American Council on Education projects that the industry needs at least $180 billion to offset revenue losses and COVID-related expenses to maintain safe operations during the pandemic. But with between 50% and 70% of campus expenditures earmarked for employee compensation, the opportunities for addressing budget shortfalls without touching staffing are limited. For the whole of 2020, the industry lost 650,000 jobs.
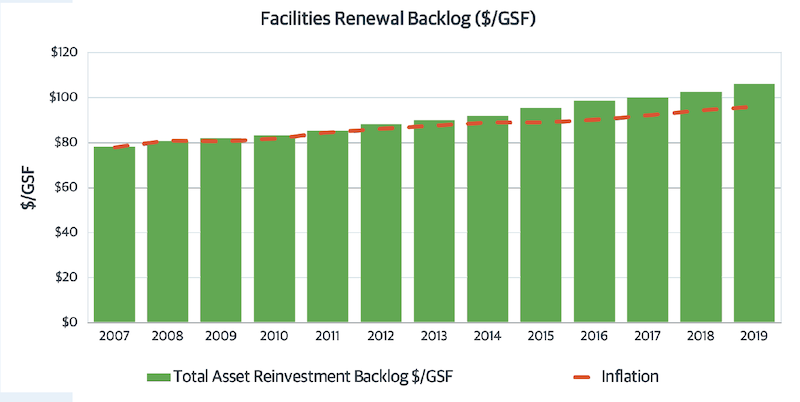
Backlogs of campuses' asset renewal needs have grown to $106 per gross sf, and 35% increase since 2007.
WHAT DOES ‘COMMUNITY’ MEAN TODAY?
The report notes that in the 2020 fall semester, 44% of schools were fully or primarily online, with another 21% operating in hybrid teaching mode. However, Gordian and APPA contend that the virtual world is not yet able to replace the in-person [educational] experience. “Community continues to be reliant on the physical gatherings of people, which will be an expected element of the collegiate experience for some time to come.”
If schools can’t provide this meaningful engagement, as well as some demonstrable evidence of a return on students’ investment, enrollments will continue to drop. The 13% decline in last year’s incoming freshman class “will have a ripple effect across the next three to five years,” the report states.
And schools can no longer rely on international students to help bridge their financial gaps.
The whole concept of campus “community” is changing. And the sudden embrace of digital tools for teaching opens endless interpretations of what an academic community looks like. “An opportunity clearly exists to reimagine campus space. The window is open to embrace digital, distant and trust-based work environments, and [schools] should leap to take advantage of the moment.”
More to the point, “the data say we need to use less space because [schools] simply can’t care for what [they’ve] built,” says the report.
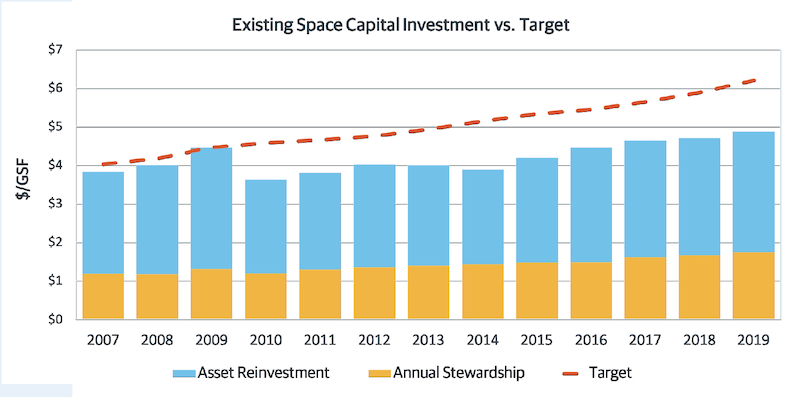
The investment shortfall in existing campus facilities has grown to 25% over the past 13 years.
HARD CHOICES WILL BE NECESSARY
So what are colleges and universities to do?
A start would be to document real operating costs, including the accrual of deferred needs with altered staffing and reduced capital investment. Facilities managers must prioritize space going forward, and clarify how students are likely to be taught. “Create a coherent narrative, incorporating the expectations of the community and the demands of the facilities, that represents a shared agreement for how to best optimize service to academic aspirations and institutional mission.”
Regarding future investments, schools must define their risk tolerances, especially it comes to keeping building systems operable to avoid shutdowns. Finance and facilities leaders must jointly understand how best to invest in a school’s physical plant, and develop a suitable investment strategy based on future need. That strategy, states the report, should have buy-in from the school’s senior leadership as well as stakeholders—students, faculty, workers—who will be affected by those decisions.
To meet the challenges of more dynamic campuses with fluid spaces and use, the report suggests that, at a minimum, institutions need to honestly appraise their facilities management teams, and determine what skills they will need for the next crisis but also routine times.
“Assess the type or work that has been required and is anticipated to be required to match hiring practices with the skills of the future,” the report states.
Related Stories
| Jul 20, 2012
2012 Giants 300 Special Report
Ranking the leading firms in Architecture, Engineering, and Construction.
| Jul 16, 2012
Business school goes for maximum vision, transparency, and safety with fire rated glass
Architects were able to create a 2-hour exit enclosure/stairwell that provided vision and maximum fire safety using fire rated glazing that seamlessly matched the look of other non-rated glazing systems.
| Jun 1, 2012
New BD+C University Course on Insulated Metal Panels available
By completing this course, you earn 1.0 HSW/SD AIA Learning Units.
| May 31, 2012
2011 Reconstruction Award Profile: Seegers Student Union at Muhlenberg College
Seegers Student Union at Muhlenberg College has been reconstructed to serve as the core of social life on campus.
| May 29, 2012
Reconstruction Awards Entry Information
Download a PDF of the Entry Information at the bottom of this page.
| May 24, 2012
2012 Reconstruction Awards Entry Form
Download a PDF of the Entry Form at the bottom of this page.
| May 1, 2012
White paper discusses benefits of diaphragm and piston flushometer valves
The white paper highlights considerations that impact which type of technology is most appropriate for various restroom environments.
| Apr 13, 2012
Goettsch Partners designs new music building for Northwestern
The showcase facility is the recital hall, an intimate, two-level space with undulating walls of wood that provide optimal acoustics and lead to the stage, as well as a 50-foot-high wall of cable-supported, double-skin glass
| Apr 13, 2012
Best Commercial Modular Buildings Recognized
Judges scored building entries on a number of criteria including architectural excellence, technical innovation, cost effectiveness, energy efficiency, and calendar days to complete, while marketing pieces were judged on strategy, implementation, and quantifiable results. Read More
| Mar 1, 2012
Cornell shortlists six architectural firms for first building on tech campus
Each of the firms will be asked to assemble a team of consultants and prepare for an interview to discuss their team’s capabilities to successfully design the university’s project.















