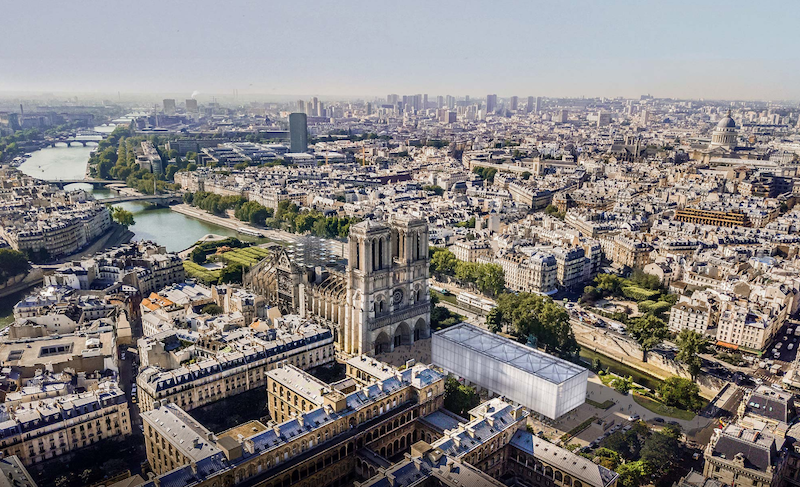
Gensler has recently unveiled the design for the Pavillon Notre-Dame, which will provide a temporary place of worship in Parvis Square while the Notre-Dame Cathedral is being restored from the fire that nearly destroyed it just over 100 days ago.
The pavilion’s primary building material is charred timber. Not only will the charred timber provide the structure with added strength and durability, but it also symbolizes that what once destroyed Notre-Dame will now serve to make it stronger, according to Duncan Swinhoe, Regional Managing Principal, Gensler.
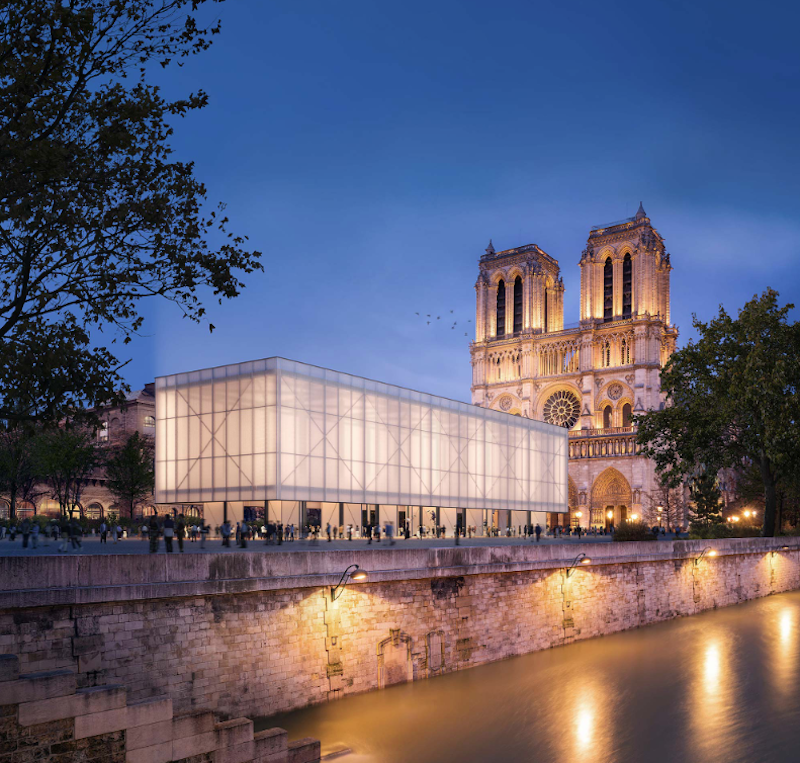

The pavilion acts as a sheltered nave and is reminiscent of the structural rhythms and forms of the Gothic cathedral. The roof is built of ETFE cushions and walls made of translucent polycarbonate, meaning the structure will be flooded with natural light.
Movable panels behind the altar allow for a full view of Notre-Dame. Rotating panels at the ground floor can be positioned to open or close the edge of the structure to mirror the configuration of the cathedral for mass services, or they can be moved to open up the space for its other potential uses as a marketplace or for performances.
“It is important that the design is true to, but doesn’t upstage, the cathedral,” Swinhoe said. “We wanted to strike a balance between a structure that invites the community yet can be transformed to become a reflective and spiritual haven when mass is celebrated.”

Related Stories
| Jun 12, 2014
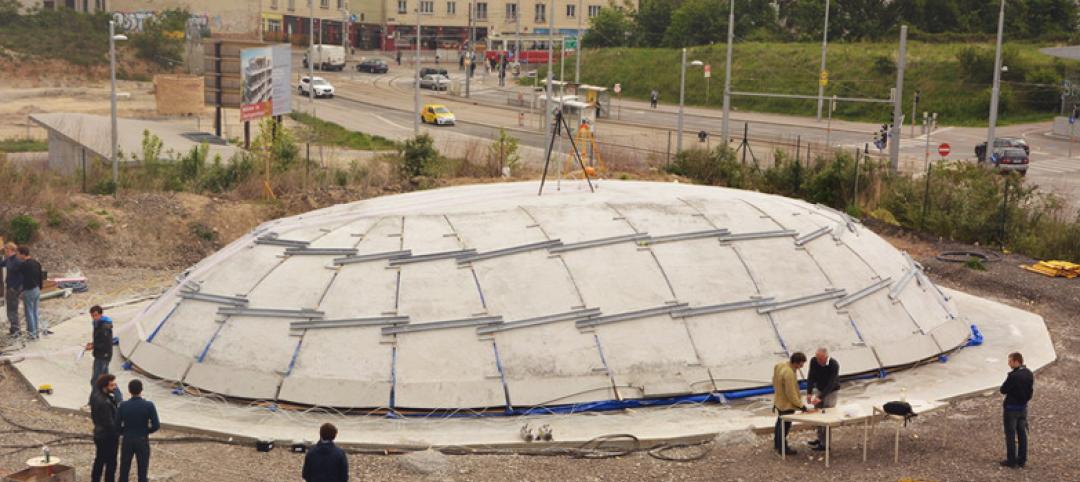
Austrian university develops 'inflatable' concrete dome method
Constructing a concrete dome is a costly process, but this may change soon. A team from the Vienna University of Technology has developed a method that allows concrete domes to form with the use of air and steel cables instead of expensive, timber supporting structures.
| Jun 10, 2014
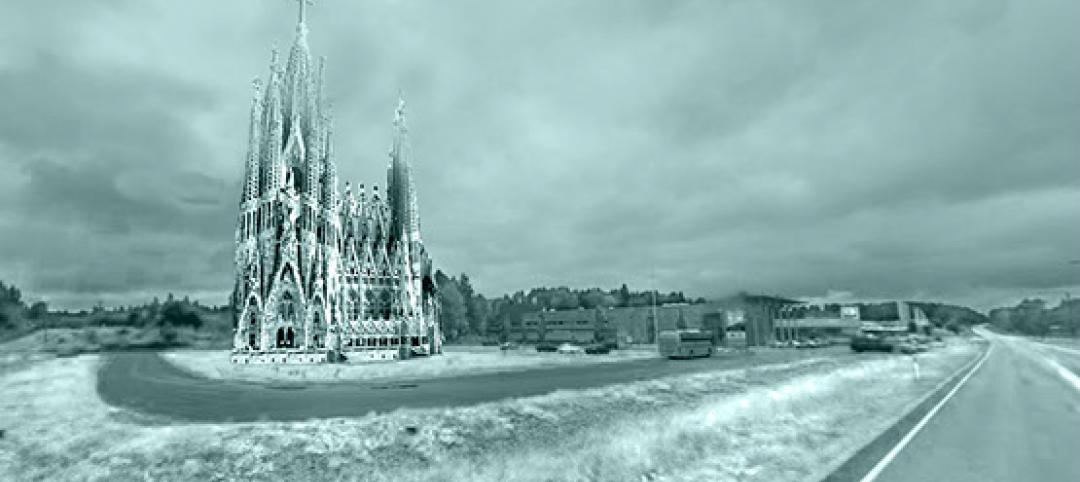
Gaudi’s famed cathedral on ice: Dutch students to construct 132-foot ice replica of Sagrada Familia
"Sagrada Familia in Ice" will be built with a mixture of wooden fibers and plain ice that is three times stronger than ice.
| May 29, 2014
7 cost-effective ways to make U.S. infrastructure more resilient
Moving critical elements to higher ground and designing for longer lifespans are just some of the ways cities and governments can make infrastructure more resilient to natural disasters and climate change, writes Richard Cavallaro, President of Skanska USA Civil.
| May 20, 2014
Kinetic Architecture: New book explores innovations in active façades
The book, co-authored by Arup's Russell Fortmeyer, illustrates the various ways architects, consultants, and engineers approach energy and comfort by manipulating air, water, and light through the layers of passive and active building envelope systems.
| May 19, 2014
What can architects learn from nature’s 3.8 billion years of experience?
In a new report, HOK and Biomimicry 3.8 partnered to study how lessons from the temperate broadleaf forest biome, which houses many of the world’s largest population centers, can inform the design of the built environment.
| May 13, 2014
19 industry groups team to promote resilient planning and building materials
The industry associations, with more than 700,000 members generating almost $1 trillion in GDP, have issued a joint statement on resilience, pushing design and building solutions for disaster mitigation.
| May 12, 2014
Lubbock, Texas, to build modern 'tent city' as shelter for homeless
On the five-acre site of a former cotton gin, the High Cotton program provides temporary shelter for Lubbock's homeless population. The facility needs to expand due to increased need, and new plans have been drawn up.
| May 11, 2014
Final call for entries: 2014 Giants 300 survey
BD+C's 2014 Giants 300 survey forms are due Wednesday, May 21. Survey results will be published in our July 2014 issue. The annual Giants 300 Report ranks the top AEC firms in commercial construction, by revenue.
| Apr 29, 2014
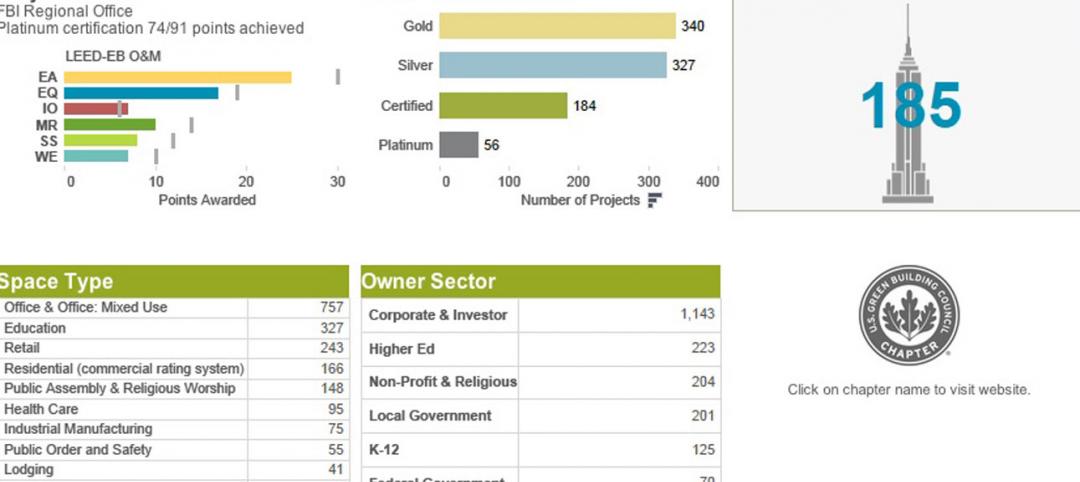
USGBC launches real-time green building data dashboard
The online data visualization resource highlights green building data for each state and Washington, D.C.
| Apr 16, 2014
Upgrading windows: repair, refurbish, or retrofit [AIA course]
Building Teams must focus on a number of key decisions in order to arrive at the optimal solution: repair the windows in place, remove and refurbish them, or opt for full replacement.