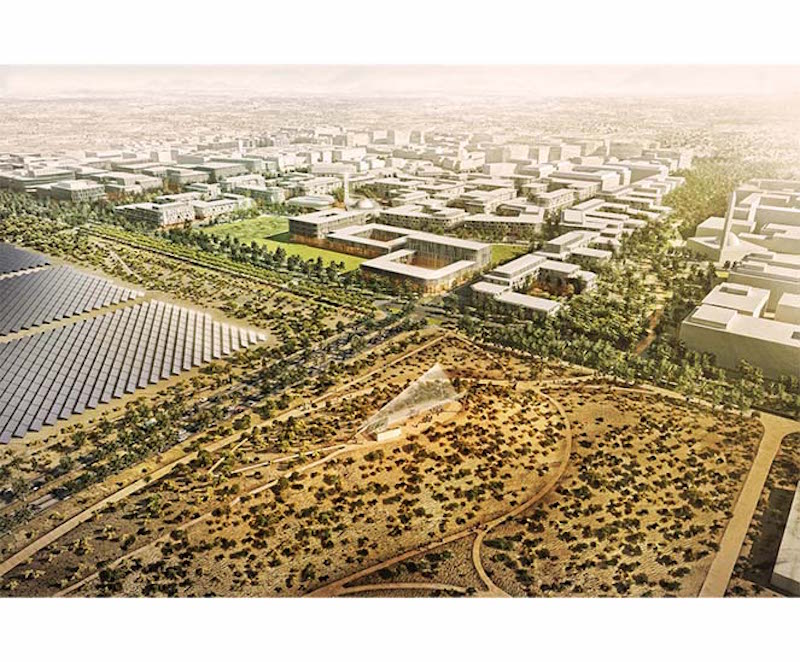
Utopia. A word used to describe a place where everything is perfect. And, from an environmental standpoint, Masdar City, located just outside of the United Arab Emirates’ capital city of Abu Dhabi, was billed as a futuristic, green city that was supposed to be an environmentalist’s utopia.
Ten years ago, Masdar City was the model for a green city, one that would reach net-zero standards, not just for a few of its major buildings, but for the city as a whole. But, as the Scottish poet Robert Burns wrote, "the best laid schemes of mice and men often go awry." Now, Masdar City looks more like a movie set after filming has wrapped or an abandoned Olympic venue of the past than a Jetsons-esque city of the future.
In short, as The Guardian’s Suzanne Goldenberg reports, Masdar City is closer to becoming the world’s first green ghost town than it is to becoming the world’s first net-zero city. The city's completion date was 2016, but that goal is no longer attainable (the new completion date has been pushed back to 2030). Neither is the goal of becoming a net-zero city. Even though, as it currently stands, only about 5% of the original six square kilometer building area has been developed, the city is already unable to keep up with the demand of being truly net-zero. In fact, it’s at about 50% of that.
In 2006, before the hype surrounding Masdar City plummeted back to earth, the project was heralded as a future global hub for the cleantech industry. Developers expected 50,000 permanent residents and 40,000 commuters zipping around the futuristic city via driverless electric cars from one efficient and green building to the next.
In 2016, there are only 300 permanent residents of Masdar City, all of whom are graduate students at the Masdar Institute of Science and Technology and, according to tour guides, fewer than 2,000 people work on campus.
There are around 300 firms with an official presence in Masdar City, but the buildings still, for the most part, remain empty. For example, the International Renewable Energy Agency is headquartered in a state-of-the-art six-story building that manages to use only one-third of the energy as compared to other buildings in Abu Dhabi. But the majority of this six-story structure remains vacant; only around 90 employees actually work in the building.
Other parts of the city act as a museum of half-baked ideas; a 100-station-long autonomous transport system was halted after the first two stops, due in large part to the speedy rise of the electric car. A bike sharing station is in place and ready to use, but it's 10 miles away from Abu Dhabi, which would feel like an even longer trek thanks to the complete lack of bike paths.
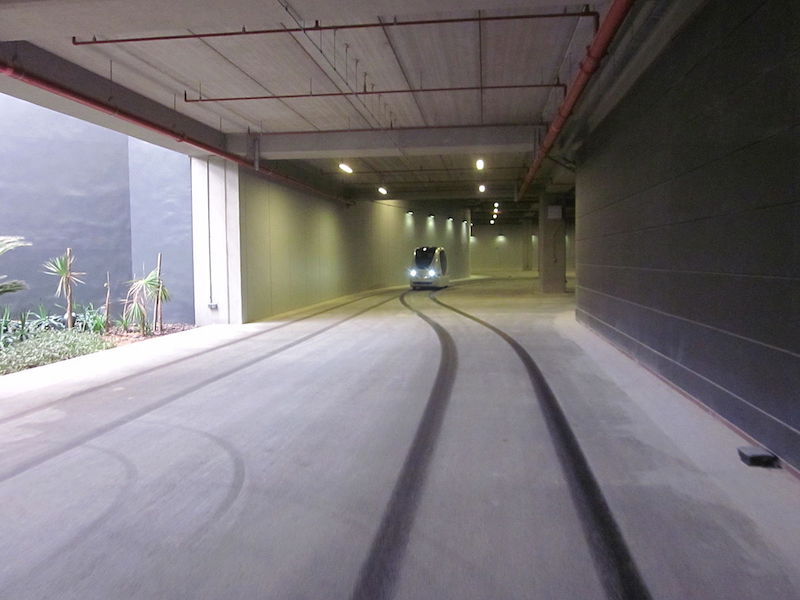 Masdar City's initial design called for automobiles to be banned. Instead, a public transport system using Personal Rapid Transit pods (pictured) would shuttle people around the city. The rise of the electric car made this system an unnecessary expense. Photo: Jan Seifert, Wikimedia Commons
Masdar City's initial design called for automobiles to be banned. Instead, a public transport system using Personal Rapid Transit pods (pictured) would shuttle people around the city. The rise of the electric car made this system an unnecessary expense. Photo: Jan Seifert, Wikimedia Commons
It certainly didn’t help matters that crews broke ground on Masdar City in 2008, just as the global recession was about to kick into high gear. According to Chris Wan, the Design Manager for Masdar City, the recession made the decision of whether or not to invest in Masdar City much easier for many who were contemplating the idea. Ultimately, they decided to just play it safe and watch from the sidelines.
However, Masdar isn’t a complete failure. Sure, it will not reach its goals of being net-zero, but that doesn’t mean the city isn’t much more efficient than a typical city. Airtight insulation, high-efficiency elevators, designs that prefer natural lighting to artificial lighting, and solar water heaters on the roofs of many buildings all optimize energy use and make these buildings more efficient.
The city is still evolving and still has some lofty goals for what it can become upon completion. Until then, it can only be judged on what it currently is: a city of ideas.
 Image Credit: GDS Infographics, Flickr Creative Commons
Image Credit: GDS Infographics, Flickr Creative Commons
Related Stories
Hotel Facilities | Feb 12, 2018
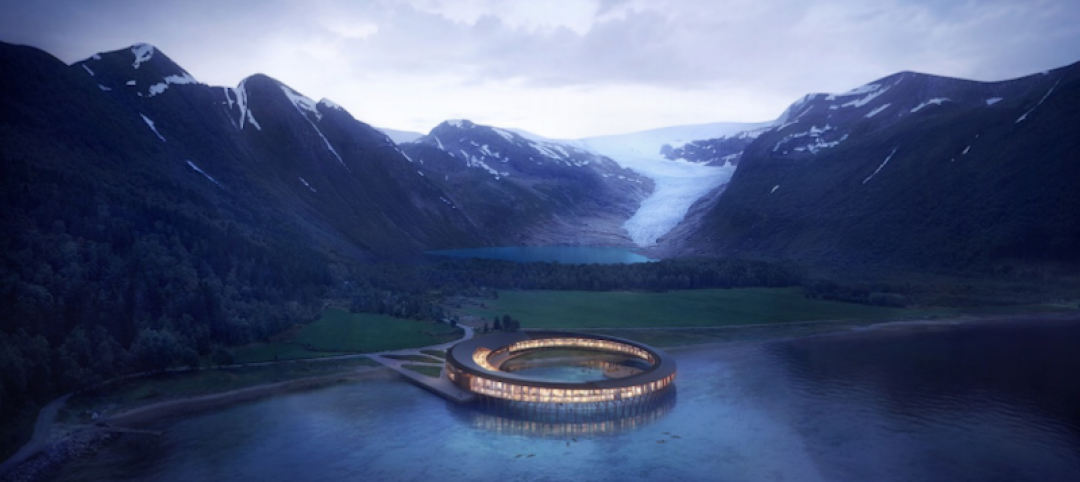
Circular hotel will be world’s first energy positive hotel concept above the Arctic Circle
The hotel will provide 360-degree views of the Svartisen glacier and the surrounding arctic nature.
Green | Feb 5, 2018
Does nature have a lasting positive effect on the mind?
What types of nature-inspired design elements are most effective?
Green | Jan 31, 2018
U.S. Green Building Council releases annual top 10 states for LEED green building per capita
Massachusetts tops the list for the second year; New York, Hawaii and Illinois showcase leadership in geographically diverse locations.
Green | Jan 30, 2018
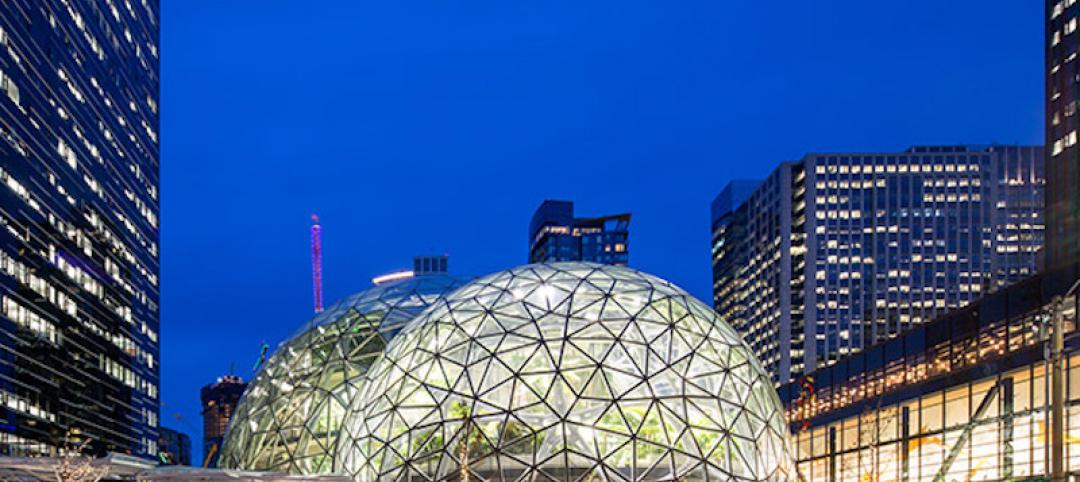
Welcome to the Jungle: Amazon’s Spheres have opened to employees and the public
The Spheres provide the most unique aspect of Amazon’s downtown Seattle headquarters.
Green | Jan 15, 2018
Revolutionizing the standard green lease
The DOE Better Buildings Initiative has made a bold statement calling 2018 the “Year of the Lease”.
Green | Dec 22, 2017
Green builders can use ‘big data’ to make design decisions
More and more, green project teams are relying on publicly available “external datasets” to prioritize sustainable design decisions, says sustainability consultant Adele Houghton.
Giants 400 | Oct 31, 2017
A more intense shade of green
Zero-net energy, sustainability, and wellness are goals more developers and AEC teams strive for.
Giants 400 | Oct 30, 2017
Top 85 green construction firms
Turner Construction Co., Clark Group, and AECOM top BD+C’s ranking of the nation’s largest green sector contractors and construction management firms, as reported in the 2017 Giants 300 Report.
Giants 400 | Oct 30, 2017
Top 45 green engineering firms
WSP, AECOM, and Arup top BD+C’s ranking of the nation’s largest green sector engineering and EA firms, as reported in the 2017 Giants 300 Report.
Giants 400 | Oct 30, 2017
Top 130 green architecture firms
Gensler, Stantec, and HOK top BD+C’s ranking of the nation’s largest green sector architecture and AE firms, as reported in the 2017 Giants 300 Report.