With the rising cost of land and construction, and the need to build more densely in order to make building a multifamily community profitable, outdoor spaces become all the more important.
We talked to six veteran landscape architects about how to incorporate gardens and quiet spaces into multifamily communities.
1. Plan your landscape scheme early in the design process.
Don’t think of landscaping as “something you can value engineer to make up for mistakes at the end of the project,” said Craig Karn, ASLA, ULI, NAHB, LEED AP, Founder/Principal, Consilium Design, Denver. “If you’re going to do great, finished outdoor spaces, they need to be central to the design, not leftover space next to the Dumpsters.”
Have your end game in mind at the beginning of the process, he advised: “Your residents want high-quality outdoor spaces, not just sticking a bench along a fence.”
2. Narrow the focus of your plant selection.
Maintenance staffs have a long list of jobs to do every day, and they are not always plant experts. “With any type of fussy landscaping, you have to step up maintenance of the spaces,” said Terry Smith, Associate/Director of Land Planning, BSB Design. “It takes a lot of work to keep them looking good. It might be cool to have the residents involved in the gardens, but management really has to take the lead and be responsible for maintaining it or it becomes an eyesore.”
Regan Pence, PLA, Landscape Architecture Practice Lead, Lamp Rynearson and Associates, Omaha, Neb., advised leaning toward a limited and more formal plant palette. “We try to define the space and make it look architectural and intentional,” he said. “If you leave things as they are, people perceive it as unkempt.” To create a sense of design intent Pence’s firm often adds trellises, walkways, and planters, which are fairly easy for the maintenance staff to take care of.
3. Design small spaces within large spaces.
Even in the midst of busy public areas, landscape designers can carve out small spaces where residents can be on their own. BSB’s Smith compares the experience to hanging out at a coffee shop. “You hear the activity around you, and you can engage if you want to, but you don’t have to. You’re in a quiet space within a noisy environment.”
Creating smaller spaces where your residents can be on their own “is where the creative aspect comes into play,” Smith said. His firm uses plant materials, fencing, landscape walls, and assorted hardscape materials to mold and shape these quiet spots.
He said a dog park is an example of a highly active space that could have a contemplative garden space off to the side “to serve as a quiet space”—possibly with a hammock or two for added relaxation.
4. Use curves and corners in pathways to create quiet spots within a larger open space.
Encountering a small seating area after a sudden change in direction can be a delightfully unexpected experience for your residents. “People love finding these little out of the way spaces,” said Karn. “They become their favorite places to hang out.”
Fireplaces can be used to create multiple intimate seating areas. Karn recommends putting the fireplace in the middle of the space and grouping seating on the various faces.
5. Fire pits and outdoor kitchens are hot-hot-hot.
“Fire pits are really big,” said BSB Design’s Smith. They can be used at night and over an extended period of the year. “They are such a nice gathering area, and they don’t take up much space,” he said.
Fire pits come in all kinds of configurations, he noted. “They’re gas-powered, so they’re acceptable to most fire departments. They’re small, manageable elements where people get a lot of good use out of them.”
Outdoor kitchens are also in demand as social gathering places connected to landscape features. See “Grilled to order: The art of outdoor kitchens,” BDCnetwork.com/OutdoorKitchens2019.
6. Create implied walls and canopies.
Even within large open lawns, intimate spaces can be carved out through what Julie Brinkerhoff-Jacobs, President of Lifescapes International, Newport Beach, Calif., calls “implied walls.”
Shrubbery can frame an open or covered seating area, whether planted at ground level, in raised beds, or in pots that complement the design aesthetic. Or put vines on a fence.
“Create destinations within destinations,” places that are “verdant and intimate,” said Brinkerhoff-Jacobs. “It’s a great way to direct traffic and guide people along a path.” She likes doing a “living, breathing wall or fence,” but warned that they can be expensive unless you have plant material that is very fast-growing.
7. Use lighting to expand garden usage.
The best landscape designs shouldn’t go dark when the sun goes down. “These spaces should have life beyond dusk,” said Scott Baker, PLA, ASLA, President, RELM, Los Angeles.
“People are entertaining in the evening,” said Baker. “These are spaces you come home to at night, grab a bottle of wine, take it downstairs, and hang out with friends.”
Baker said his philosophy is that lights should not be seen; their effect should be perceived. “We work very closely with lighting designers to get a mood and environment,” he said.
You can create the desired effect by underlighting benches and seating and uplighting trees. “It doesn’t have to be big poles with lights that light up an area like a prison yard,” said Baker. “It can be done in a much more subtle way. More successful spaces do everything with a little more intrigue.”
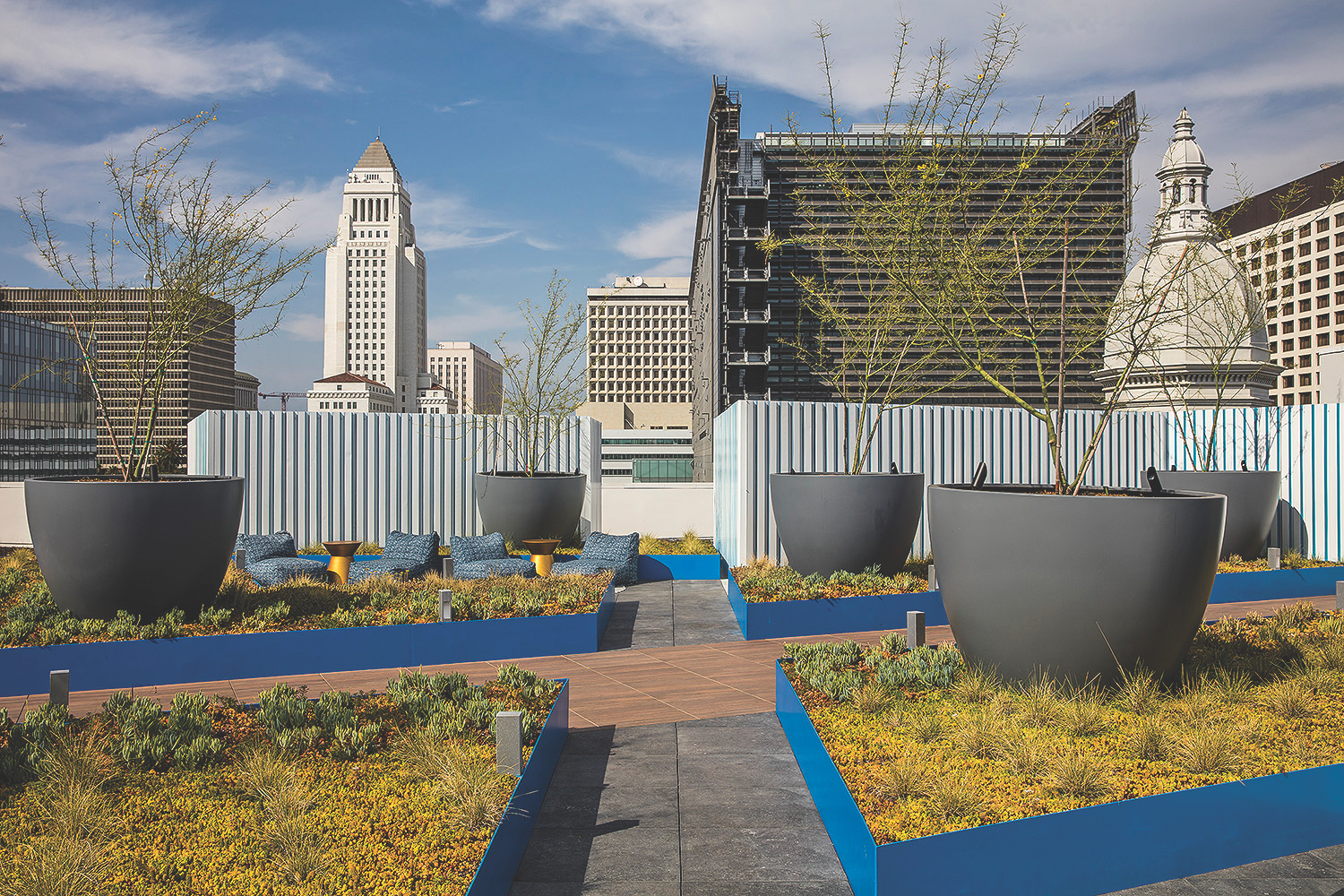 Raised planter beds and stone pavers form the landscaping vocabulary of the 20,000-sf roof garden designed by RELM for STOA, a 224-unit rental high-rise in downtown Los Angeles. The dome of the Cathedral of St. Vibiana (1876), which was damaged in the 1994 Northridge earthquake and later deconsecrated (it’s now an events venue), is at right. Holland Partners was the developer. Togawa Smith Martin was the architect. Photo: Manolo Langis
Raised planter beds and stone pavers form the landscaping vocabulary of the 20,000-sf roof garden designed by RELM for STOA, a 224-unit rental high-rise in downtown Los Angeles. The dome of the Cathedral of St. Vibiana (1876), which was damaged in the 1994 Northridge earthquake and later deconsecrated (it’s now an events venue), is at right. Holland Partners was the developer. Togawa Smith Martin was the architect. Photo: Manolo Langis
8. Make the roof part of your landscape plan.
Ziv Lavi, Founder/Managing Partner of Turf Landscape Design, in New York City, remembers when multifamily developers didn’t think much at all about the rooftop spaces on their buildings. “Today, it’s understood the roof will be activated,” said Lavi, a former urban designer at the New York City Department of City Planning. “It’s what people expect when they come to rent or buy in a building.”
Project teams need to think about how the rooftop can become an amenity, not just a holding space for the mechanical systems. “There’s an opportunity to move those mechanical areas around and craft in cozy, intimate spaces,” he said.
Lavi said roof spaces should embrace a city’s energy, not mask it. Using sound barriers to ward off city noise sends a message that “city noise is bad and nature noise is better,” said Lavi. “You don’t want to do that. You want to be able to feel you’re within the huge metropolitan area. You’re elevated above it in a nature-like area that filters and incorporates the city into your experience.”
One caution: “If you have to have mature trees on a roof deck, you better plan for it, because plant materials are heavy,” warned Lifescapes International’s Brinkerhoff-Jacobs. “The roof is one area where early involvement in the design process is essential.”
9. Don’t overdo the size of the pool.
Does your multifamily community really need a huge pool? According to Consilium Design’s Craig Karn, today’s apartment and condo residents go to the pool primarily to meet people, not to swim. “Make the pool small and the deck big,” he said. “People-watching is a big deal. But people want to be the watcher, not the watched.”
One way to make that happen is by placing several smaller seating areas around the lawn or deck where residents can sit with a few friends. “It creates intimacy where they feel comfortable,” Karn said.
Lifescapes International’s Julie Brinkerhoff-Jacobs recommends adding nearby water features, such as fountains or water walls, to make a small pool area feel larger. She also suggests installing cabanas to make it possible for residents to define their own more private space within the larger, more public pool area.
GARDENS ADD TANGIBLE VALUE TO YOUR PROJECT
“Human beings enjoy being in gardens,” said Brinkerhoff-Jacobs. “Life is hectic. When you have places of repose where you can recharge your batteries and reconnect with a small group of friends, that’s important. If you live in an area with dense population and have a place to have alone time, that will be a very rewarding experience.”
Related Stories
| Nov 25, 2013
Building Teams need to help owners avoid 'operational stray'
"Operational stray" occurs when a building’s MEP systems don’t work the way they should. Even the most well-designed and constructed building can stray from perfection—and that can cost the owner a ton in unnecessary utility costs. But help is on the way.
| Nov 19, 2013
Top 10 green building products for 2014
Assa Abloy's power-over-ethernet access-control locks and Schüco's retrofit façade system are among the products to make BuildingGreen Inc.'s annual Top-10 Green Building Products list.
| Nov 15, 2013
Greenbuild 2013 Report - BD+C Exclusive
The BD+C editorial team brings you this special report on the latest green building trends across nine key market sectors.
| Nov 15, 2013
Metal makes its mark on interior spaces
Beyond its long-standing role as a preferred material for a building’s structure and roof, metal is making its mark on interior spaces as well.
| Nov 13, 2013
Installed capacity of geothermal heat pumps to grow by 150% by 2020, says study
The worldwide installed capacity of GHP systems will reach 127.4 gigawatts-thermal over the next seven years, growth of nearly 150%, according to a recent report from Navigant Research.
| Nov 8, 2013
Net-zero bellwether demonstrates extreme green, multifamily style
The 10-unit zHome in Issaquah Highlands, Wash., is the nation’s first net-zero multifamily project, as certified this year by the International Living Future Institute.
| Nov 6, 2013
Dallas’s goal of carbon neutrality by 2030 advances with second phase of green codes
Dallas stands out as one of the few large cities that is enforcing a green building code, with the city aiming to be carbon neutral by 2030.
| Oct 30, 2013
15 stellar historic preservation, adaptive reuse, and renovation projects
The winners of the 2013 Reconstruction Awards showcase the best work of distinguished Building Teams, encompassing historic preservation, adaptive reuse, and renovations and additions.
| Oct 30, 2013
11 hot BIM/VDC topics for 2013
If you like to geek out on building information modeling and virtual design and construction, you should enjoy this overview of the top BIM/VDC topics.
| Oct 28, 2013
Urban growth doesn’t have to destroy nature—it can work with it
Our collective desire to live in cities has never been stronger. According to the World Health Organization, 60% of the world’s population will live in a city by 2030. As urban populations swell, what people demand from their cities is evolving.