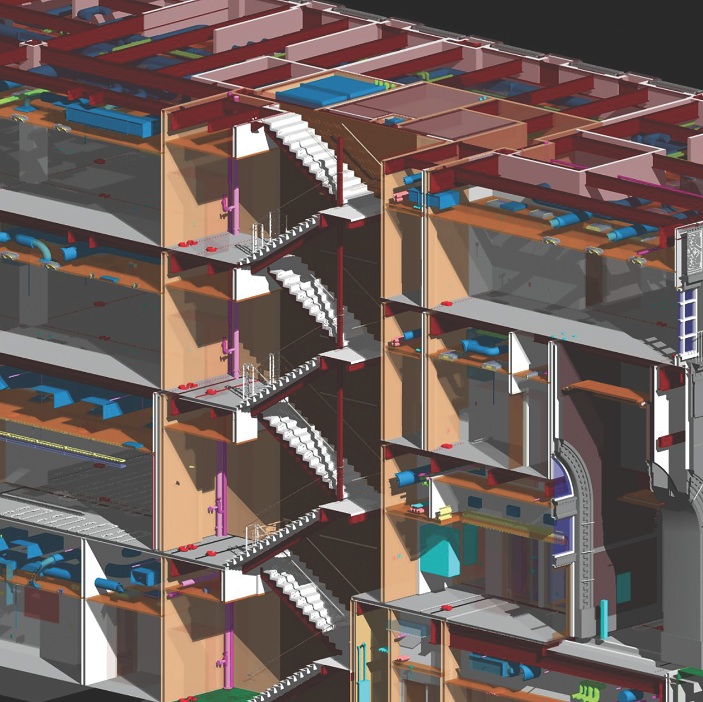
More than two decades into the building information modeling movement, AEC firms are still discovering ways to utilize BIM/VDC tools more effectively. One major current area of focus is how to cut waste in the BIM implementation process.
Inefficient virtual coordination meetings, cumbersome BIM files, and a “rush to model” mentality are just some of the profit-eating miscues that are commonplace in the AEC industry.
We reached out to several BIM/VDC power users for their top tips for eliminating waste in BIM/VDC workflows. Here’s what they said:
1. Recognize the importance of ‘tribal knowledge’
Many large, corporate AEC firms operate their BIM-driven projects like a manufacturing production line, with staff assigned to specific roles—design specialists, production experts, and construction administration specialists, all of whom move from project to project as they finish their piece of the BIM puzzle.
While efficient in theory, this Henry Fordish workflow model ultimately leads to waste and added costs, says Thom Chuparkoff, AIA, LEED AP, Associate with Populous. The problem, he says, lies in the turnover of staff during the transitions from design to documentation. At each transition, as certain staff members exit the project and others enter, the design team loses a bit of its “tribal knowledge”—its sense of knowing where a project came from and where it’s going, says Chuparkoff. Consistency of the team throughout the design and documentation phases is absolutely critical, he adds.
By employing basic process-mapping techniques at the outset of projects, Building Teams can reduce the amount of BIM modeling required on a project and develop models that offer increased value for the team and the client, says John Haymaker, PhD, AIA, LEED AP, Director of Research with Perkins+Will. Illustration: John Haymaker, Georgia Institute of Technology
“It’s troublesome to have, say, five people on the production team, none of whom had anything to do with the design,” says Chuparkoff. “They’re scratching their heads wondering why something was done the way it was. With construction schedules getting shorter, design teams don’t have time to go back and try to figure out what another team member was thinking.”
2. Master the art of the BIM coordination meeting
BIM/VDC tools are great, but if you can’t run efficient, productive coordination meetings, the Building Team will never realize the benefits of true BIM coordination. Gensler Project Architect and BIM/VDC expert Jared Krieger, AIA, LEED AP, recommends the following tips for making the most of virtual coordination meetings:
Practice and prepare. It takes skill to be able to navigate the project model and have the correct model views loaded and visibility settings adjusted for a meeting. Make the most of everyone’s time by allocating at least 15 minutes prior to each coordination meeting for one team member to load the model and specific views.
Assign a “designated driver,” someone who knows the model and is savvy about the software platform. Models can be cumbersome to navigate. Suffering through an inexperienced person trying desperately to steer the model will absolutely kill the momentum and productivity of the meeting.
“We often bypass conceptual 3D modeling software by encouraging the use of other mediums, such as clay and digital sketch models.”
—Thom Chuparkoff, AIA, LEED AP
Consider splitting meetings. Keep meetings focused on small components of the project, and include only the team members directly involved. Consider splitting meetings by profession. For example, meet with the structural engineer first to review structural-specific coordination. Then, have some overlap time with MEP and structural for common coordination. Finish the meeting with MEP coordination.
Use meeting notes to stay focused. Open action items and homework from the previous meeting should be the basis for discussion in your next meeting. Use this structure to keep your team on track, and resolve open coordination issues before moving on to new items.
3. Avoid double modeling whenever you can
Even with all the high-tech design and sketching tools available to designers, Chuparkoff advocates for a pen-and-paper approach to working with clients on early design concepts. He argues that firms allocate too much of their precious resources to creating overly complex 3D conceptual models, which then have to be painstakingly re-created in a BIM environment.
“At some firms, people will spend 40 hours or more building three different project models in SketchUp,” he says. “You don’t need three fully baked ideas, fully modeled, to present to the client. You need five or six good ideas, and not necessarily modeled. We often bypass conceptual 3D modeling software by encouraging the use of other mediums, such as clay and digital sketch models, early on to develop and refine ideas to the point where they can be modeled in BIM for the client one time. Before you get into the hard-line modeling, try to vet as much as you can the good old-fashioned way.”
4. Map your processes
AEC professionals have been trained to jump right in and start building the model. But this “rush to model” mentality often leads to inefficiencies, waste, and less-than-ideal models, says John Haymaker, PhD, AIA, LEED AP, Director of Research with Perkins+Will.
Haymaker, Assistant Professor of Architecture and Building Construction at Georgia Tech, recommends the use of process-mapping techniques—including value stream mapping and business process modeling—at the project outset to identify the decisions that need to be made during the design process, as well as the processes required to make those decisions. When done well, process mapping can help reduce the amount of BIM modeling required on a project and also lead to models that offer increased value for the team and the client, says Haymaker.
“For example, if an architect, mechanical engineer, and contractor can get together to map out their process for performing preliminary energy and cost analysis, the architect may realize that they only need to model spaces and exterior surfaces,” says Haymaker. “This would greatly simplify their modeling effort, and potentially eliminate useless or inaccurate data.”
5. Divvy up the model to avoid unwieldy file sizes
Four years into the Tysons Tower project in Tysons Corner, Va., Gensler’s Krieger has just one minor regret: not managing the size of the BIM file more effectively. “Our model is pretty big, and even with great computers, it can become a bit of a bear at times when all the pieces are loaded in,” he says.
Working with a central BIM model has its benefits—notably, having a single repository for all project information. But on large, complex projects, BIM files can become ponderous, resulting in longer load times during virtual coordination meetings.
Splitting the model into chunks is one approach to managing the file size. “We try to think of logical pieces to keep as separate models,” says Krieger. “For example, if you have a tall building with a podium, you can keep the tower and podium as separate models and reference them into each other as needed. Or, on a building project with a complicated skin, you can keep the curtain wall as a separate model. The earlier you plan the split the better.”
Krieger also advises Building Teams to take note of the file size of BIM object families used on projects. Complicated projects can incorporate more than a thousand families, and some sets can exceed 10 megabytes in size. “We are very careful about how complicated and large the families can get,” he says.
6. Make sure someone ‘owns’ your companywide BIM/VDC standard
Given the rapid pace of change and innovation in the BIM/VDC software industry, it is imperative that AEC firms designate an in-house power user to maintain and update the company BIM/VDC standard.
“These tools are constantly evolving, and the company standard needs to evolve with them,” says Adam Lasota, Junior Architect with Rietveld Architects, New York. “Newer functions and features can make company standards obsolete, so it’s a matter of productivity.”
7. Create a simple BIM execution plan—and stick to it
Setting expectations and staying organized can be addressed through a simple, straightforward BIM execution plan that covers everything from schedule and roles to model sharing and level of development.
“It’s absolutely worth the effort,” says Gensler’s Krieger, referring to the firm’s work setting up an execution plan for Tysons Tower. “All the time we spent setting up views, sheet templates, and detail organization in the beginning is paying off in the construction administration process.”
When in the thick of a large, multi-year project, it’s easy for a team to stray from the original BIM execution plan. Fight that urge, because doing so can save thousands, perhaps millions, of dollars in avoided costs during construction.
“The biggest payoff has come from our team’s early commitment to have weekly BIM coordination sessions throughout the design process,” says Krieger. “It has resulted in a low number of RFIs and very few significant field coordination issues.”
Related Stories
| Aug 11, 2010
New hospital expands Idaho healthcare options
Ascension Group Architects, Arlington, Texas, is designing a $150 million replacement hospital for Portneuf Medical Center in Pocatello, Idaho. An existing facility will be renovated as part of the project. The new six-story, 320-000-sf complex will house 187 beds, along with an intensive care unit, a cardiovascular care unit, pediatrics, psychiatry, surgical suites, rehabilitation clinic, and ...
| Aug 11, 2010
Colonnade fixes setback problem in Brooklyn condo project
The New York firm Scarano Architects was brought in by the developers of Olive Park condominiums in the Williamsburg section of Brooklyn to bring the facility up to code after frame out was completed. The architects designed colonnades along the building's perimeter to create the 15-foot setback required by the New York City Planning Commission.
| Aug 11, 2010
Wisconsin becomes the first state to require BIM on public projects
As of July 1, the Wisconsin Division of State Facilities will require all state projects with a total budget of $5 million or more and all new construction with a budget of $2.5 million or more to have their designs begin with a Building Information Model. The new guidelines and standards require A/E services in a design-bid-build project delivery format to use BIM and 3D software from initial ...
| Aug 11, 2010
Opening night close for Kent State performing arts center
The curtain opens on the Tuscarawas Performing Arts Center at Kent State University in early 2010, giving the New Philadelphia, Ohio, school a 1,100-seat multipurpose theater. The team of Legat & Kingscott of Columbus, Ohio, and Schorr Architects of Dublin, Ohio, designed the 50,000-sf facility with a curving metal and glass façade to create a sense of movement and activity.
| Aug 11, 2010
Residence hall designed specifically for freshman
Hardin Construction Company's Austin, Texas, office is serving as GC for the $50 million freshman housing complex at the University of Houston. Designed by HADP Architecture, Austin, the seven-story, 300,000-sf facility will be located on the university's central campus and have 1,172 beds, residential advisor offices, a social lounge, a computer lab, multipurpose rooms, a fitness center, and a...
| Aug 11, 2010
News Briefs: GBCI begins testing for new LEED professional credentials... Architects rank durability over 'green' in product attributes... ABI falls slightly in April, but shows market improvement
News Briefs: GBCI begins testing for new LEED professional credentials... Architects rank durability over 'green' in product attributes... ABI falls slightly in April, but shows market improvement
| Aug 11, 2010
Luxury Hotel required faceted design
Goettsch Partners, Chicago, designed a new five-star, 214-room hotel for the King Abdullah Financial District (KAFD) in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The design-build project, with Saudi Oger Ltd. as contractor and Rayadah Investment Co. as developer, has a three-story podium supporting a 17-story glass tower with a nine-story opening that allows light to penetrate the mass of the building.
| Aug 11, 2010
Three Schools checking into L.A.'s Ambassador Hotel site
Pasadena-based Gonzalez Goodale Architects is designing three new schools for Los Angeles Unified School District's Central Wilshire District. The $400 million campus, located on the site of the former Ambassador Hotel, will house a K-5 elementary school, a middle school, a high school, a shared recreation facility (including soccer field, 25-meter swimming pool, two gymnasiums), and a new publ...