Planners are often asked to test a facilities concept, define how much space it will take, and determine how much it will cost to complete. These questions are useful in the early concept phase of a project, but the basis for planning is missing; what am I solving for, and how does this potential “bricks and mortar” solution meet a defined service, market, or strategic need of the organization? It’s all about scoping the right concept before getting too far down the facility planning phase.
Defining and documenting project scope (the project intention, goal, or purpose) at the outset and controlling scope throughout the planning and delivery process is essential to ensuring the project vision becomes reality.
Ask yourself:
● What strategies and goals are we trying to achieve?
● What is the scope of the envisioned project and how was it defined?
Clearly defining the project, then articulating the scope and rationale to the team is paramount prior to launch. Scope typically relates to:
● Meeting the demands of the organization’s patients (service area)
● Cultivating a new or expanded service line opportunity
● Helping to improve throughput and operations
● Fixing an infrastructure or standard-of-care issue
● Scope control/communicating clear scope of work
● Attaining successful project definition
Rushing into design and construction without clearly defining the project scope can lead to project delay and frustration later in the process. If each team member cannot clearly articulate the scope of the project, you should stop and get everyone on the same page. Establish measurable project goals early to stay on track.
Scope Definition and Documentation
A facility project is a tactical element of a strategic plan or the output of business plan; this plan is built on the mission, vision, and goals of the organization. An organization’s strategic plan should include:
● Mission and vision identification
● SWOT analysis (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats)
● Internal and external environmental analysis
● Identification of gaps between mission/vision and internal/external needs
● Service needs identification
● Market-based needs and capacity analysis
● Strategic financial analysis
● Measurable strategic goals
● Tactics to meet the strategic goals of the organization
The needs identified in a strategic plan or focused business plan drive the tactical need for a project—not the other way around. A well-conceived scope guides facilities master planning and the detailed programming and design phases of a project. The scope of the project also acts as the base to define the project budget. Scope and budget are inextricably linked and need to be constantly checked against each other. It’s imperative that the two balance relative to a complete financial analysis of the project. If the project doesn’t “pencil” from a return-on-investment (ROI) perspective, then you’ll need to adjust scope and budget to get the project in line financially and still meet the market and service delivery goals of the organization.
If you conduct these analyses early, you have a better chance of making less costing changes if needed. As you move through the project delivery process, the ability to easily make changes decreases, and the cost of changes increases. Therefore, it’s important to appropriately define the scope, test it against the budget, and communicate and document it at the project outset.

Scope Control
Once scope is defined and clearly communicated to the project delivery team, it must be managed. Use scope control tools developed during the early planning phases and during each subsequent planning and design phase (master planning, space planning, schematic design, design development, and construction documents) to avoid scope creep. Scope creep refers to uncontrolled changes in a project’s defined scope. Typically, scope increases consist of new services, new features, or additional room elements without corresponding strategic or market demand justification. Avoid scope creep early by:
● Plan based on defined and justified needs rather than articulated wants
● Encourage stakeholder participation and plan based on facts and analysis to ensure buy-in from all parties
● Eliminate “pet” projects or elements with no financial strategic justification; this is “wish-casting” instead of “forecasting” and usually results in wasted finite resources at the expense of needed projects
● Clearly communicate scope to all key constituents and members of the project delivery team before embarking on detailed planning, design, and construction
● Track scope early and continue to track throughout the life of the project
Remember, you don’t need to eliminate scope changes all together. Sound strategic logic and rapidly changing market dynamics may dictate appropriate (controlled) changes to scope that are justified. Strong scope controls will identify acceptable variances and appropriately jump-start conversations as to the “why” for the changes.
Scope increases may require additional resources (e.g. staffing, space, equipment, capital costs, time, and operational costs) which must be justified or they could potentially put the project at risk. A few thousand square feet of scope creep could add millions to your total project cost, create delays if changed late in the design process, and cause a few headaches along the way. Allowing scope creep without correlating demand and revenue may require additional staffing resources, equipment, and furnishings, and carries the long-term operational cost without the requisite return on investment.
Interestingly scope can shrink too. Cutting revenue producing scope to make budget will have downward impact on potential ROI, the ability to meet service demand, and ability to offer services and recruit new staff. If a department is downsized to allow another area to grow and still remain within budget, make sure the downsized department is not rendered dysfunctional. If this happens, you may pay once the facility is operational.
There is great risk and cost to unfettered scope creep and a poorly defined project; therefore, proper planning and controls must be in place to prevent your project from being derailed. Items to consider:
● Thoroughly understand the project vision and involve all stakeholders in defining and documenting the project scope
● Utilize tools to monitor and control scope, and track the departmental “units” (e.g. number of rooms) and departmental space
● Expect changes; develop processes and criteria to evaluate proposed scope changes and to decide which changes are necessary to fulfill the intended vision
Start with acutely defining and documenting scope on the front end of the project. Control scope throughout the process to position yourself to control your project, instead of your project controlling you.
If you build it, will they come?
In summary, too often healthcare executives employ an “If you build it, they will come” mentality to a project. Sure, a new facility or space frequently have a halo effect and activity may spike initially. But if the services aren’t what the patient, caregivers, and physicians require, then they will stop coming. The analyses conducted in the planning phase will help to accurately define project scope; meet the strategic, market, and financial goals of leadership; and meet the needs of the healthcare organization’s community.
Related Stories
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 5, 2023
Modernizing mental health care in emergency departments: Improving patient outcomes
In today’s mental health crisis, there is a widespread shortage of beds to handle certain populations. Patients may languish in the ED for hours or days before they can be linked to an appropriate inpatient program.
Healthcare Facilities | Jun 1, 2023
High-rise cancer center delivers new model for oncology care
Atlanta’s 17-story Winship Cancer Institute at Emory Midtown features two-story communities that organize cancer care into one-stop destinations. Designed by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM) and May Architecture, the facility includes comprehensive oncology facilities—including inpatient beds, surgical capacity, infusion treatment, outpatient clinics, diagnostic imaging, linear accelerators, and areas for wellness, rehabilitation, and clinical research.
Healthcare Facilities | May 19, 2023
A new behavioral health facility in California targets net zero energy
Shortly before Mental Health Awareness Month in May, development and construction firm Skanska announced the topping out of California’s first behavioral health facility—and the largest in the nation—to target net zero energy. Located in Redwood City, San Mateo County, Calif., the 77,610-sf Cordilleras Health System Replacement Project is slated for completion in late 2024.
3D Printing | May 12, 2023
World’s first 3D-printed medical center completed
3D construction printing reached new heights this week as the world’s first 3D-printed medical center was completed in Thailand.
Sustainability | May 11, 2023
Let's build toward a circular economy
Eric Corey Freed, Director of Sustainability, CannonDesign, discusses the values of well-designed, regenerative buildings.
Digital Twin | May 8, 2023
What AEC professionals should know about digital twins
A growing number of AEC firms and building owners are finding value in implementing digital twins to unify design, construction, and operational data.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 27, 2023
BD+C's 2023 Design Innovation Report
Building Design+Construction’s Design Innovation Report presents projects, spaces, and initiatives—and the AEC professionals behind them—that push the boundaries of building design. This year, we feature four novel projects and one building science innovation.
Sustainability | Apr 20, 2023
13 trends, technologies, and strategies to expect in 2023
Biophilic design, microgrids, and decarbonization—these are three of the trends, technologies, and strategies IMEG’s market and service leaders believe are poised to have a growing impact on the built environment.
Design Innovation Report | Apr 19, 2023
HDR uses artificial intelligence tools to help design a vital health clinic in India
Architects from HDR worked pro bono with iKure, a technology-centric healthcare provider, to build a healthcare clinic in rural India.
Healthcare Facilities | Apr 17, 2023
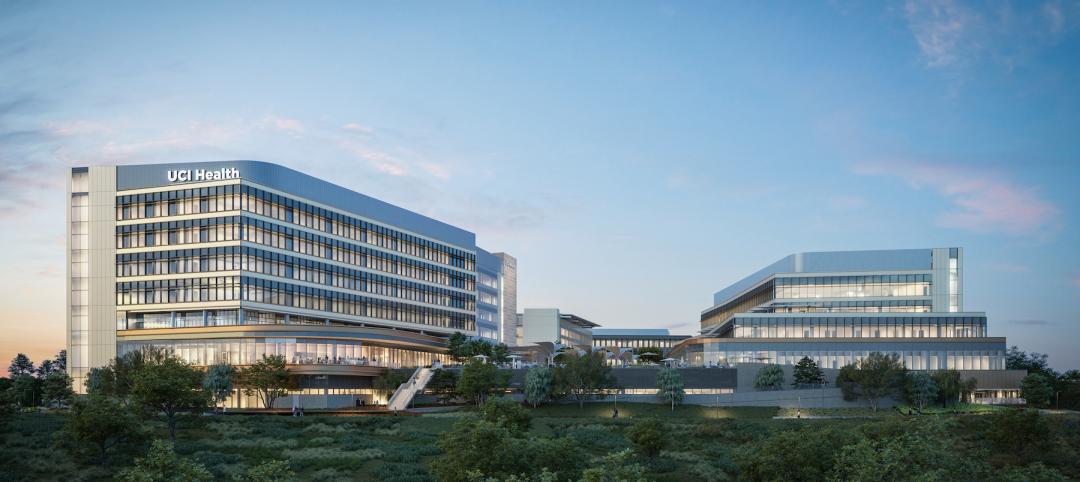
UC Irvine takes sustainability to new level with all-electric medical center
The University of California at Irvine (UCI) has a track record for sustainability. Its under-construction UCI Medical Center is designed, positioned, and built to preserve the nearby San Joaquin Marsh Reserve, to reduce the facility’s solar gain by 85%, and to be the first medical center in the country to operate on an all-electric central plant.