As colleges and universities weigh how to reopen their campuses in the fall, the standard government, health, and academic guidelines—wearing masks, reducing densities, and physical distancing—may not be entirely practical for assembling large numbers of students in one place.
To contribute to this discourse, Leo A Daly recently convened planners, architects, and engineers specializing in higher education to study the facility impacts of physical distancing, and to envision solutions.
This group analyzed available guidelines, and then applied design thinking to three key areas. First, it studied infection dynamics on the campus overall and applied the idea of “cohorts” as a mechanism for limiting exposure. Next, the group conducted a detailed study of two campus building types where students congregate: a general purpose academic building and a “traditional” residence hall with shared toilet and shower facilities. These analyses identified “pinch points,” suggesting the need for behavioral and physical modifications to more closely comply with the intent of the guidelines.
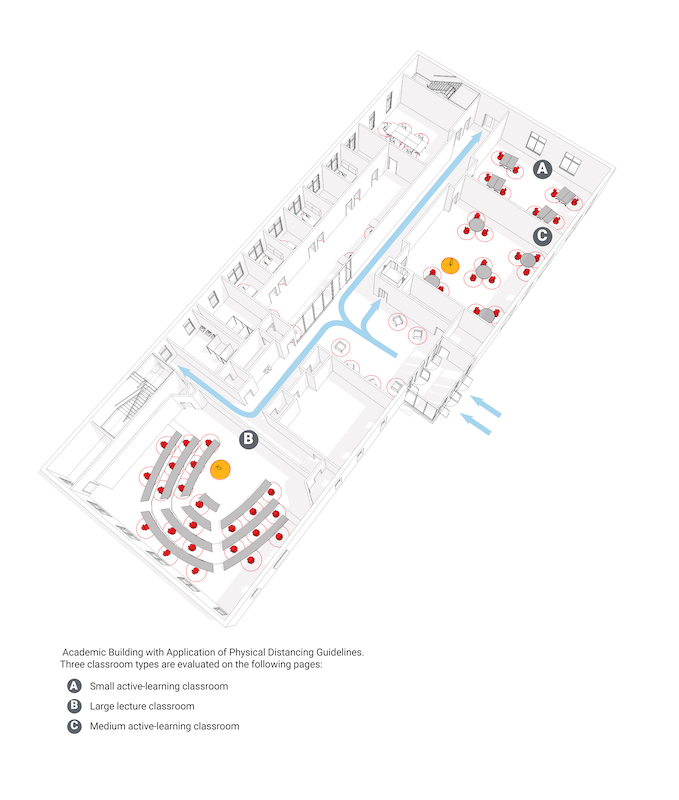
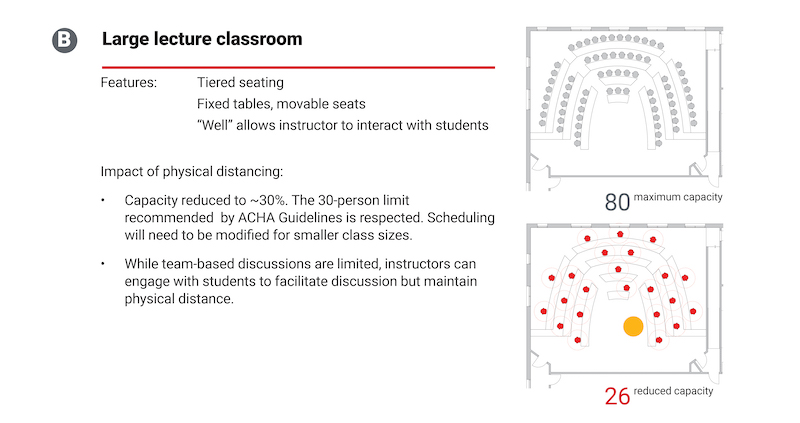 Reducing the number of students in a lecture hall might actually improve instructor engagement.
Reducing the number of students in a lecture hall might actually improve instructor engagement.
A white paper, “Returning to Campus During the Covid-19 Pandemic,” summarizes the group’s findings and recommendations. “The analysis suggests that organizing students into cohorts, and considering rental or toilet and shower facilities, can improve safety where strict compliance of guidelines isn’t feasible,” the report states.
Also see: How to convert college dorms to support the coronavirus crisis
ADDING SAFETY BY DIVIDING STUDENTS INTO SMALL GROUPS
Breaking students into smaller cohorts can help institutions determine roommates and how shared spaces are used. That division can also be extended to academic buildings to create live-learn facilities. The division of students further into micro-communities “would allow students to retain the benefits of social communication while reducing their exposure to pathways of disease common to a large, dense campus,” the white paper’s three authors write.
The paper stresses one-way circulation in academic buildings that would also have a single point of entry, directional signage, and multiple exits. To minimize disease transmission in restrooms, measures might include using alternating stalls and sings, no-touch fixtures and hardware, and frequent cleaning and disinfection. To reduce pinch points, the paper recommends adding toilet capacity by installing temporary trailers with single-use facilities inside trailers adjacent to the building.
The report provides guidelines for small and medium active-learning classrooms, large lecture classrooms (in which it recommends a 30% capacity reduction to a 30-person maximum).
MAKING RESIDENCE HALLS (AND THEIR BATHROOMS) SAFER
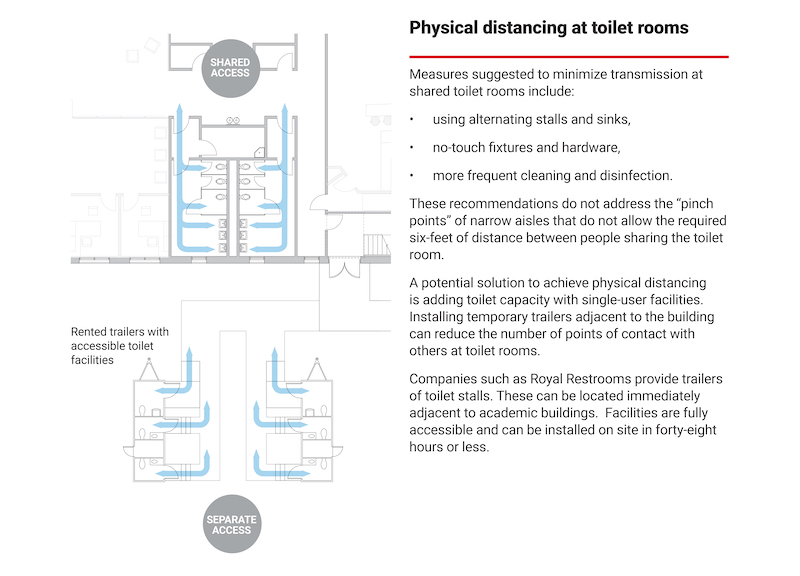 Extending restroom access by installing temporary facilities near academic and residence buildings would minimize disease transmission.
Extending restroom access by installing temporary facilities near academic and residence buildings would minimize disease transmission.
For residence halls, the report thinks that toilets and showers can still be shared, albeit with some changes that include the installation of automatic openings at common doors, assigning student rooms as single occupancy, and converting shower rooms to function as single-occupancy rooms by adding a door and restricting access.
The report suggests that assigning a shower stall to just two living units would reduce the potential for cross contamination among student residents. (Such separations could be achieved by color-coding the stalls.) At shared toilet sites, no-touch or at least reduced-touch fixtures should be standard.
Schools should treat existing shared bathrooms as single use, and reserve them for select students. Other students can be provided bathrooms in the form of temporary facilities adjacent to the resident hall and accessible by a covered hallway. (The report states that a three-unit combined shower, toilet, and lavatory can be rented for $5,500 per month, to start.)
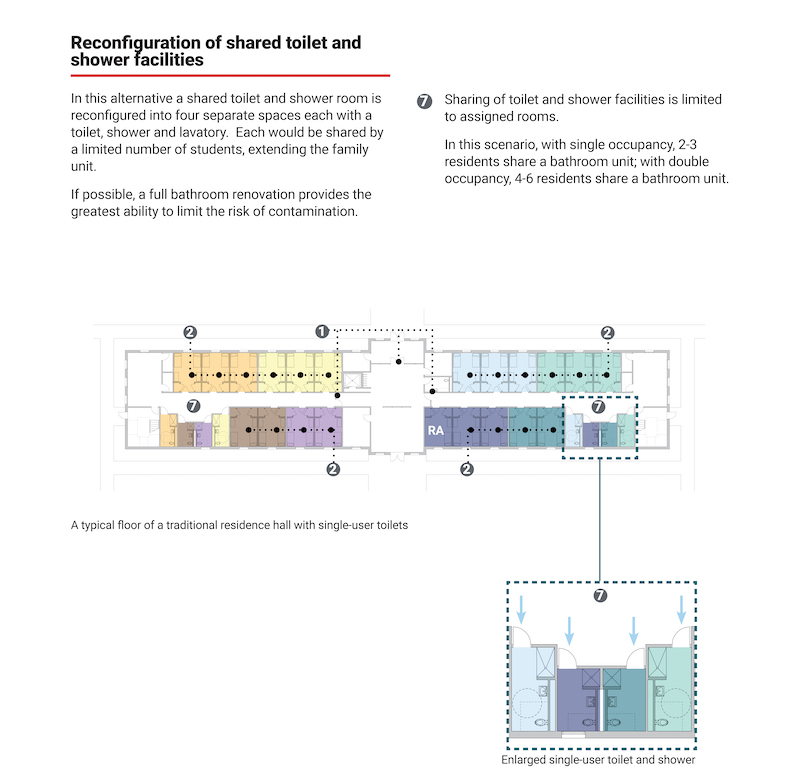
As an alternative, shared toilet and shower rooms can be reconfigured into four separate spaces, each shared by a limited number of students and assigned rooms.
Colleges and universities might also consider building systems that are more focused on occupant health, and incorporating UV-C lighting, which has been shown to kill pathogens.
Related Stories
Coronavirus | Apr 4, 2020
COVID-19: Architecture firms churn out protective face shields using their 3D printers
Architecture firms from coast to coast have suddenly turned into manufacturing centers for the production of protective face shields and face masks for use by healthcare workers fighting the COVID-10 pandemic.
Coronavirus | Apr 3, 2020
Cities will survive the pandemic
Density may make it easier for the virus to spread, but let’s not forget that cities are in many ways the heart of society, and a springboard of big ideas, inventions, art, and culture.
Coronavirus | Apr 3, 2020
Kogniz Health launches AI-based fever detection cameras for crowds to help limit coronavirus spread
System continuously scans crowds for fever as they enter facilities to locate and isolate risks.
Coronavirus | Apr 3, 2020
27% of construction firms report layoffs amid COVID-19 outbreak, says AGC
The fast-worsening COVID-19 pandemic has triggered layoffs at more than a quarter of construction firms responding to an online survey released today by the Associated General Contractors of America. The finding, based on responses from earlier this week, contrasts with the government’s monthly employment report for March, which found that construction employment declined by 29,000 as of mid-March.
Coronavirus | Apr 3, 2020
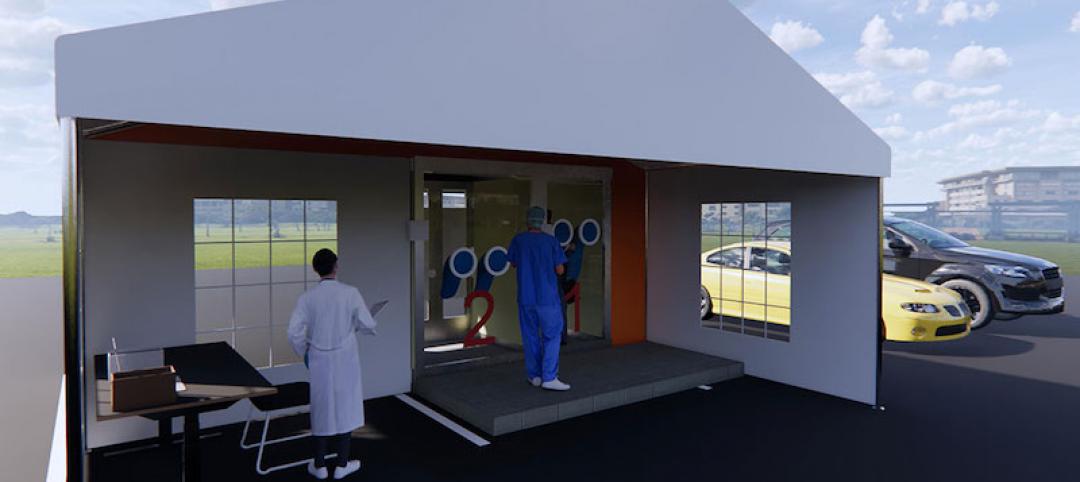
Test facility in a box: Modular, walk-in booth design for coronavirus testing
To address the need for testing in urban areas for those without vehicles, CannonDesign architect Albert Rhee created a walk-in testing booth that is slated for public use.
Coronavirus | Apr 3, 2020
Survey of U.S. code officials shows trends in code compliance during COVID-19
The results of the survey tell us how jurisdictions throughout the U.S. are keeping up with inspections, new building permits and new construction.
Coronavirus | Apr 3, 2020
CallisonRTKL buoyed by overseas demand
Customer service across the globe remains No. 1 priority, says new CFO.
Coronavirus | Apr 2, 2020
COVID-19: HMC Architects using 3D Printers to make face shields for healthcare workers
HMC staff is producing 3D-printed parts from their homes as they self-isolate.
Coronavirus | Apr 2, 2020
COVID-19: CannonDesign initiates industry coalition to make masks for healthcare providers
Coalition formed to make DIY face masks for healthcare workers in COVID-19 settings.
Coronavirus | Apr 2, 2020
As virus spreads across North America, software providers step up with cost-free offerings
The goal is to keep construction projects moving forward at a time when jobs are being postponed or canceled.