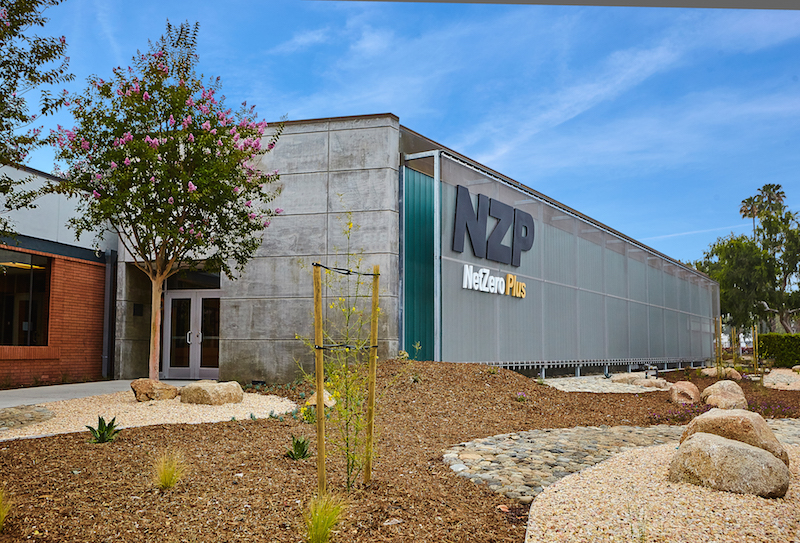
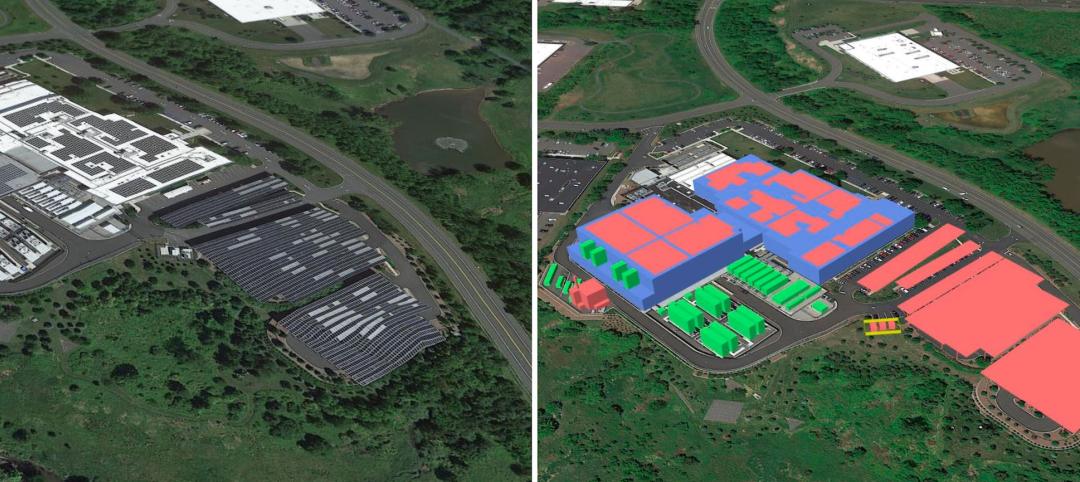
The Net Zero Plus Electrical Training Institute in Los Angeles trains about 1,500 electrical apprentices, journeymen, and contractors annually. It is also a demonstration center and living lab for advanced and energy clean energy technologies.
It seems appropriate, then, that this 144,000-sf building is now the country’s largest Net Zero Plus commercial building retrofit.
Net Zero Plus is a comprehensive set of strategies designed by the International Brotherhood of Electrical Workers Local 11 and the Los Angeles National Electrical Contractors Association, which finance the Institute through a Taft-Hartley trust, according to Brett Moss, the Institute’s Training Director.
Those strategies provide building owners and managers, developers, and architects with integrated energy efficiencies and advanced technologies aimed at changing the way buildings use, produce, store, and monitor energy.
The $15.5 million retrofit, which was completed a few months ago, is expected to reduce the building’s annual total energy usage by 51%, and lower its carbon footprint by 520 metric tons per year.
Moss says that one of the goals of this retrofit is for the building to produce 1.25 times the energy it consumes. In the first months since the retrofit was completed, the building has outperformed expectations.
“I think it’s important to point out that this was a retrofit,” says Moss, who spoke with BD+C last week. “A lot of people are under the assumption that the only way to achieve net zero is ground up.” He adds that the building remained operational during the upgrade.
This building, which dates back to the 1960s, had been expanded a number of times. About a dozen years ago a solar array was added.
The retrofit project started, says Moss, with a building audit that focused on the envelope. A new roof with foam insulation was installed. Stainless-steel mesh shades wall windows, letting in plenty of daylight but also reducing the temperature on the inside of the windows by 20%.
Electrochromatic glass was installed into another wall that’s part of the Institute’s classroom space.
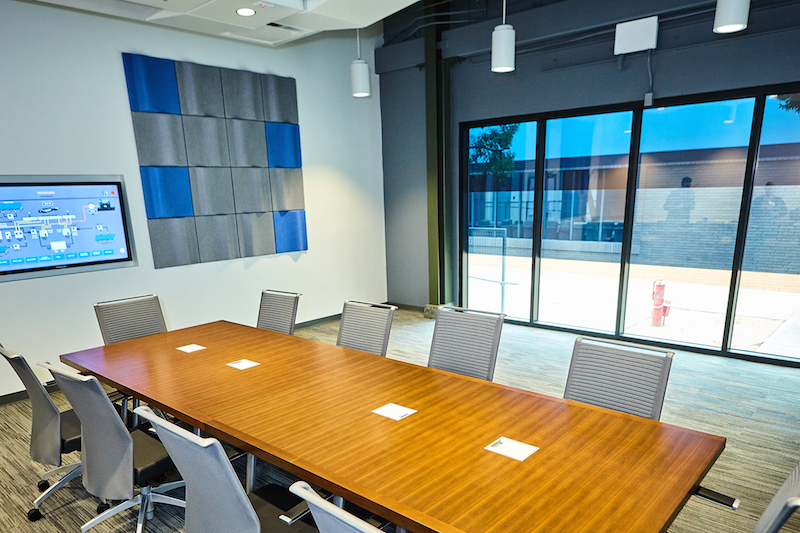

Electrochromatic windows help keep classrooms cool. Image courtesy of NZP ETI.
The building is essentially a warehouse with classrooms. Pre-retrofit, the warehouse door usually stayed open all day, letting hot air into common areas that weren't air conditioned to begin with. The retrofit installed an electric sliding door, and doors to the air-conditioned classrooms stay closed to keep them cool.
Moss says the Institute was an early adopter of LED lighting. “But what we had wasn’t tunable,” and were replaced with fixtures and a Lutron lighting system. And on the mechanical side, a series of package units on the roof was replaced by chillers and a cooling tower.
The building's energy storage system has 300 kilowatt-hours worth of energy stored. As the price of energy storage continues to fall—solar panels go for about 85 cents per watt now, compared to $5 per watt in 2002, when the Institute installed its first PV array—Moss says the Institute envisions this building serving as an emergency operations center that “can operate around the clock” by harvesting energy during the day, drawing down on that storage during the evening, and producing more energy than it uses.
“We should have enough energy in our battery to take the building through any catastrophic event,” says Moss.
Commercial buildings account for nearly 65% of L.A.’s energy consumption, and are responsible for huge amounts of CO2 emissions. The NZP ETI, as the Institute’s building is now known, could also serve as a model for transforming other existing buildings, said Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti, who was among the more than 500 dignitaries attending the June 6 dedication ceremony for the building.
California requires all commercial structures in the state to be net zero buildings by 2030.
The development team on the Institute's retrofit included contractors O’Bryant Electric and PDE Total Energy Solutions, as well as stok, Western Allied Mechanical, and SimonGlover Architects.
Moss notes that NZP ETI will be on the building tour during Greenbuild, which will be held in Los Angeles this fall.
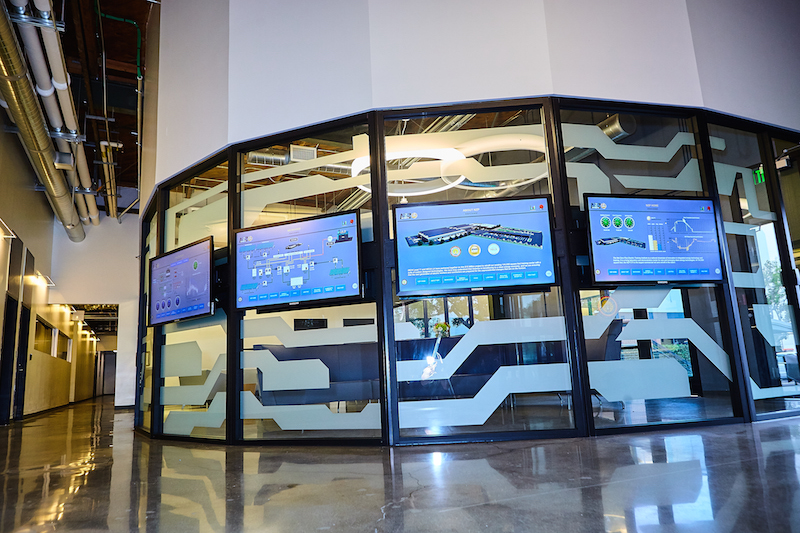

Glass walls surround the Institute's lobby area. A electric sliding glass door was installed to keep the inside of the building, which is mostly warehouse and common areas that aren't air conditioned, cooler. Image courtesy of NZP ETI.
Related Stories
Modular Building | Jul 6, 2023
Lennar, Mastry Ventures make multi-million dollar investment in net-zero prefab homes
Mastry Ventures and LENx, the venture arm of homebuilder Lennar, have co-invested in Vessel Technologies’ next-generation housing product.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Dallas high-rise multifamily tower is first in state to receive WELL Gold certification
HALL Arts Residences, 28-story luxury residential high-rise in the Dallas Arts District, recently became the first high-rise multifamily tower in Texas to receive WELL Gold Certification, a designation issued by the International WELL Building Institute. The HKS-designed condominium tower was designed with numerous wellness details.
Green | Jun 26, 2023
Federal government will spend $30 million on novel green building technologies
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies. The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 20, 2023
A new study presses for measuring embodied carbon in industrial buildings
The embodied carbon (EC) intensity in core and shell industrial buildings in the U.S. averages 23.0 kilograms per sf, according to a recent analysis of 26 whole building life-cycle assessments. That means a 300,000-sf warehouse would emit 6,890 megatons of carbon over its lifespan, or the equivalent of the carbon emitted by 1,530 gas-powered cars driven for one year. Those sobering estimates come from a new benchmark study, “Embodied Carbon U.S. Industrial Real Estate.”
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
Multifamily Housing | Jun 15, 2023
Alliance of Pittsburgh building owners slashes carbon emissions by 45%
The Pittsburgh 2030 District, an alliance of property owners in the Pittsburgh area, says that it has reduced carbon emissions by 44.8% below baseline. Begun in 2012 under the guidance of the Green Building Alliance (GBA), the Pittsburgh 2030 District encompasses more than 86 million sf of space within 556 buildings.
Resiliency | Jun 14, 2023
HUD offers $4.8 billion in funding for green and resilient building retrofit projects
The Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) recently released guidelines for its Green and Resilient Retrofit Program (GRRP) that has $4.8 billion for funding green projects.
Codes and Standards | Jun 6, 2023
California’s new power grid modernization plan furthers ambitious climate goals
California’s new $7.3 billion grid modernization plan is a crucial step in furthering its ambitious climate goals. The board of governors for the California Independent System Operator (CAISO), the state’s grid operator, recently approved a strategy to build thousands of miles of new high-voltage transmission lines.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 6, 2023
Minnesota expected to adopt building code that would cut energy use by 80%
Minnesota Gov. Tim Walz is expected to soon sign a bill that would change the state’s commercial building code so that new structures would use 80% less energy when compared to a 2004 baseline standard. The legislation aims for full implementation of the new code by 2036.
K-12 Schools | May 25, 2023
From net zero to net positive in K-12 schools
Perkins Eastman’s pursuit of healthy, net positive schools goes beyond environmental health; it targets all who work, teach, and learn inside them.