Last month, I wrote about how automation and AI are dramatically changing all four fundamental relationships between buildings and machines. For example, nanotechnology, which manipulates individual atoms and molecules to assemble things, could make the modernist metaphor of a “machine for living in” into reality, since the building would actually be composed of many tiny machines.
In fact, that’s not quite accurate. The definition of “machine” is “an apparatus using or applying mechanical power and having several parts, each with a definite function and together performing a particular task.”
So machines are made of distinct parts, cobbled together to fulfill a function. They are characterized by their composition, as assemblages of singular bits and pieces in which the whole is greater than the sum.
SEE ALSO: Assessing AI's impact on the AEC profession and the built environment
But nanotech will completely change this. When entire buildings can be shaped from microscopic components, the visible distinction between the individual parts will evaporate. A structure built from invisible machines will not appear to be a machine at all, since it no longer will be perceived as an assembly of parts. An edifice made of congealed cybernetic butter will look to be all whole, no parts. The very concept of a “building” could become meaningless, since it will no longer be “built” in any traditional way.
Remember “Terminator 2”? Arnold Schwarzenegger’s T-800 is a machine: steel and servos wrapped in human skin. Robert Patrick’s T-1000 is made of liquid metal (“mimetic polyalloy”). He’s like sentient mercury, morphing into any shape he needs. A nanotech building (“nanotecture”?) would make conventional structures seem like Robby the Robot (of “Forbidden Planet” fame).
Buttery buildings could change everything we think and know about architecture. Frank Lloyd Wright felt that architectural form should stem from the inherent “nature” of its materials: “Each material speaks a language of its own.” In his mind, the proportions, heft, and texture of brick logically translated into structures such as the Robie House, which extends horizontally and hugs the land. But when the constituent parts of a building are too small to be seen with the naked eye, the relationships between form and materials will change. What is the “language” of a nanobot?
Because the character of a building could vary upon command—hard and opaque one minute, soft and transparent the next—the fabric of buildings could become fluid, fluctuating states from solid to liquid to gas and back. The notion of truth in materials will become irrelevant. In fact, the word material could go away. When the basic building blocks of architecture have no strict definition, structure and substance could separate. Matter may not matter.
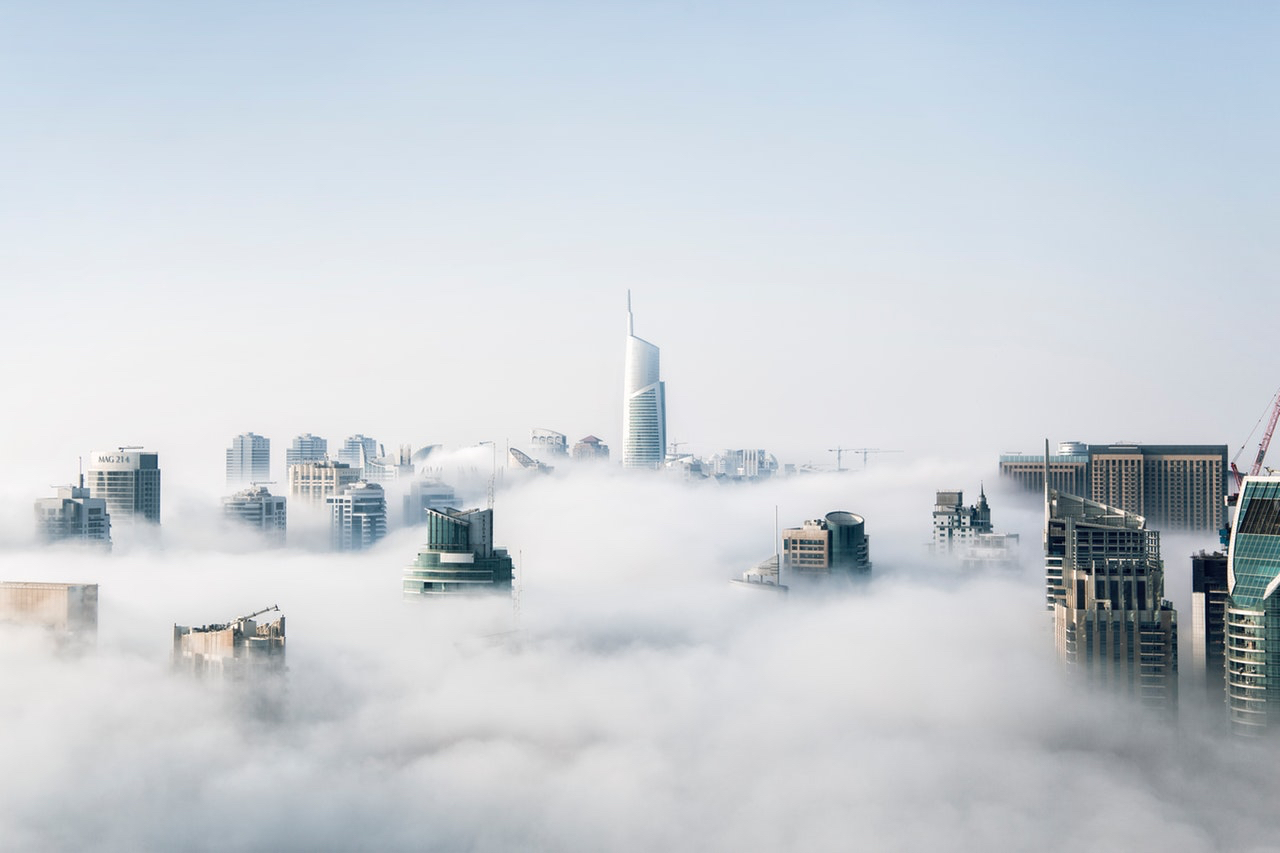
Could there come a time when buildings will become less about bricks and mortar and feel more like mists or fogs, vaguely enveloping space in ways we can barely picture now? What will it be like to live in a cloud?
Lance Hosey, FAIA, LEED Fellow, is a Design Director with Gensler. His book, The Shape of Green: Aesthetics, Ecology, and Design, has been an Amazon #1 bestseller in the Sustainability & Green Design category.
Related Stories
AEC Innovators | Aug 15, 2019
Oracle’s replica of a construction jobsite creates an immersive environment for AEC professionals
The Oracle Construction and Engineering Innovation Lab allows visitors to walk through five different stages of construction work, to test new AEC technologies and training techniques.
AEC Tech | Aug 14, 2019
ConTech VC discloses details about latest fund
Brick & Mortar Ventures has struck 16 deals in past 20 months.
AEC Innovators | Aug 9, 2019
Improving architectural designs through iteration
Computational design lets ZGF Architects see patterns that renderings and even models can’t show.
AEC Tech | Jul 29, 2019
2019 Bluebeam Extreme Conference: Peer-to-Peer Learning at Scale
XCON 2019 to focus on collaborative partnerships and what works in digital construction
Multifamily Housing | Jul 23, 2019
Is prefab in your future?
The most important benefit of offsite construction, when done right, is reliability.
AEC Tech | Jul 15, 2019
Lack of standards hampers development of exoskeleton industry
Guidelines, common terminology, and testing methodology are needed, says expert.
AEC Tech | Jul 15, 2019
Investors eye startups focused on automating construction
Investors could reap big payoffs in an industry that experts say is ready for automation.
AEC Tech | Jul 12, 2019
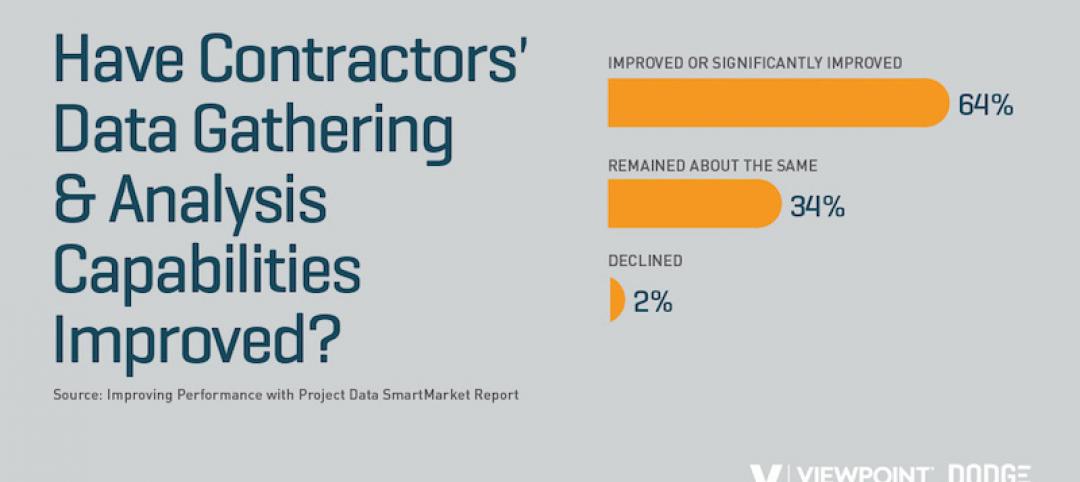
A new Dodge-Viewpoint report gauges how well contractors gather and use jobsite data
Information is power, but are contractors collecting what they need to make better decisions?
| Jul 11, 2019
Pepper Construction is using 3D models to help identify underground utilities on jobsites
Overlaying new installs and site surveys add precision to the construction process.
AEC Tech | Jul 10, 2019
Blue Collar Labs launches Builder’s Almanac, an online construction technology evaluation platform
The free online resource aims to eliminate subjective bias from the contech software evaluation process.