No matter how things play out with the American Health Care Act, the proposed replacement for Obamacare, hospital administrators agree on one thing: “They’re going to have less money available for the care they provide,” says Collin Beers, AIA, Senior Principal, Stantec.
That has put the pinch on large-scale projects. “With uncertainty over reimbursement rates, we’re seeing fewer proposals for greenfield hospitals,” says Randy Keiser, Vice President, National Healthcare Director, Turner Construction Company. For approved projects, one popular cost-saving tactic has been to shrink rooms. “There’s been a downsizing of about 10% over the past decade,” says Keiser. “Now, many hospitals are under 2,000 sf per bed.”
Healthcare organizations continue to look for merger and acquisition opportunities to realize economies of scale, restructure their organizations, expand their geographic reach, and “rightsize” to eliminate redundant services. Stantec’s master planning service helps hospital systems with strategic planning, programming, project sequencing, and cost estimating for capital projects.
Mergers can sometimes result in improved quality of care, Beers says. “They can aggregate specialty services and create centers of excellence,” he says. A larger, more financially sound organization could have the resources to build a centralized, state-of-the-art facility in, say, cardiology or ophthalmology, with the aim of attracting top-notch specialists and fortifying the organization’s brand.
ALSO SEE: BD+C GIANTS 300 HEALTHCARE RANKINGS
Top 125 healthcare architecture firms
Top 80 healthcare engineering firms
Top 110 healthcare construction firms
Malls and strip malls have become popular locations for specialty centers and other outpatient facilities. There’s usually a lot of parking, and there may even be bus service. “In retail zones, patients have things they can do before and after their appointments,” Beers says.
Adaptive reuse of big-box stores offers unique advantages. The high ceilings of a former Kmart provide flexibility to install the extensive networks of infrastructure, Beers says. The fact that only the front elevation may need a facelift is also a plus. And with the shell already in place, the construction timetable could be faster than new construction.
But extensive and costly HVAC renovations are often necessary. Many spaces have to be partitioned. Existing systems that served big open spaces have to be rebuilt. In the end, the cost savings of turning a big-box store into an outpatient facility may not be that great. “All in all, it might be only slightly more affordable than it would be to build new,” Beers says.
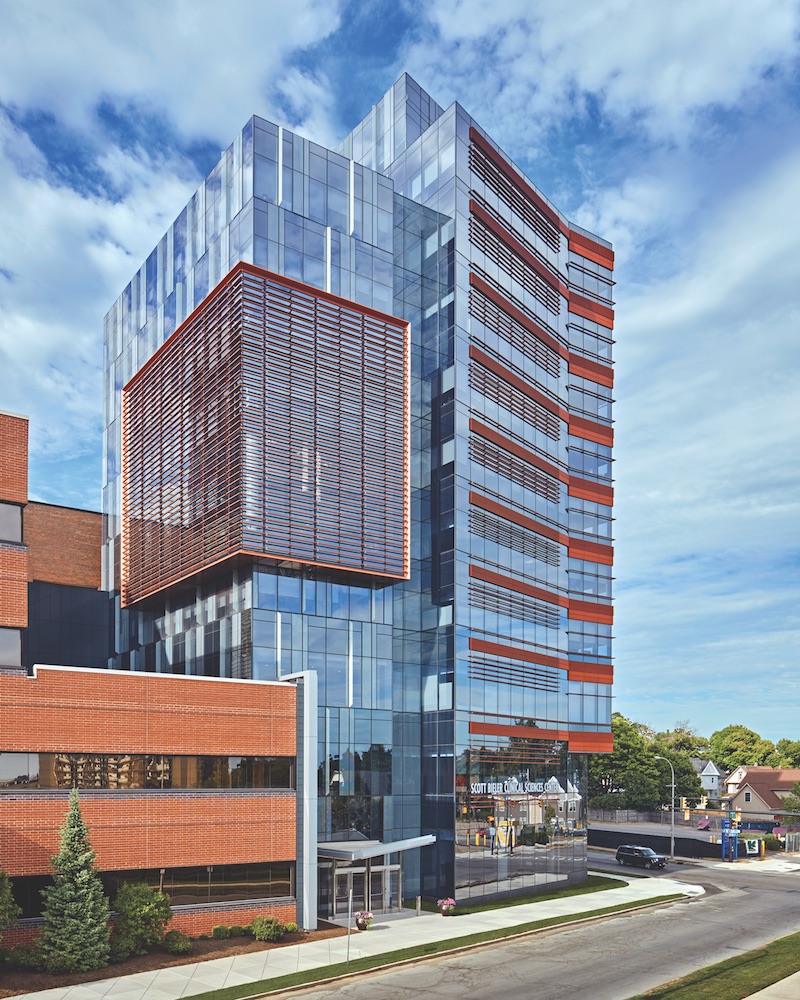 The 142,000-sf Scott Bieler Clinical Science Center serves as the new campus entryway for the 15-building, 24-acre Roswell Park Cancer Institute in downtown Buffalo, N.Y. The tower’s angular glass exterior is accented with a three-story “infusion box” with highlights of copper-mesh-embedded glass. On the Building Team: FXFOWLE (architect), Severud Associates (SE), Watts Engineering (MEP), C & S Companies (CE), and Axis Facades USA (façade consultant). © Robert Benson.
The 142,000-sf Scott Bieler Clinical Science Center serves as the new campus entryway for the 15-building, 24-acre Roswell Park Cancer Institute in downtown Buffalo, N.Y. The tower’s angular glass exterior is accented with a three-story “infusion box” with highlights of copper-mesh-embedded glass. On the Building Team: FXFOWLE (architect), Severud Associates (SE), Watts Engineering (MEP), C & S Companies (CE), and Axis Facades USA (façade consultant). © Robert Benson.
BETTER HEALING THROUGH TECHNOLOGY innovation
Some hospitals have adopted mobile tracking technology so that nurses can quickly locate equipment. “This can reduce the amount of equipment needed and the amount of spaces for their storage,” Beers says.
Technology can also come in the form of a wristband worn by patients. Instead of stewing in a noisy, stressful waiting room, patients (and their families) can relax in the cafeteria or healing garden and be notified instantly when it is their turn for a test or X-ray. This improves the patient experience and allows the facility to reduce or repurpose waiting areas.
Another technology-related trend to watch: telehealth, which offers virtual monitoring of a patient’s condition. Fifty-four hospitals have opened telehealth ICUs across the country, according to Crain’s Chicago Business. They look like air traffic control rooms, with giant monitors filled with patients’ medical data. High-definition cameras and audio equipment allow doctors and nurses to zoom in on patients and speak to them from afar.
The $54 million, 125,000-sf Mercy Virtual Care Center, in Chesterfield, Mo., enables more than 300 medical professionals to watch over patients at 38 hospitals in seven states. A Mercy official has stated that a 40% reduction in expected mortality rates in its ICUs was largely due to early interventions enabled by the Virtual Care Center’s monitoring capability.
Hospital designers are helping healthcare organizations improve patient outcomes, especially for preventable, never-should-happen occurrences like infections and slips, trips, and falls, says Keiser. Light fixtures that can kill deadly microorganisms such as MRSA and Aspergillus are gaining favor, as are antimicrobial hardware and curtains. Medical facilities are doubling down on handrails and slip-resistant flooring in patient rooms and bathrooms to reduce injuries.
In surgical units Keiser notes that advances in cardiology have made it possible for less invasive heart surgery. This makes for not only faster recovery times but also faster surgeries. As a result, some hospitals have reduced the number of ORs for cardiology and converted those spaces to catheter labs.
At a time of great uncertainty for healthcare providers, facilities designers need to be open to finding new approaches as a project progresses.
“The vast majority of healthcare projects have changes during design and construction,” Keiser says. “This seems more prevalent than it was 20 years ago.”
Related Stories
Healthcare Facilities | Feb 15, 2022
New outpatient ophthalmology surgical center opens in Newington, N.H.
JSA Design designed the project.
Resiliency | Feb 15, 2022
Design strategies for resilient buildings
LEO A DALY's National Director of Engineering Kim Cowman takes a building-level look at resilient design.
Healthcare Facilities | Feb 10, 2022
Respite for the weary healthcare worker
The pandemic has shined a light on the severe occupational stress facing healthcare workers. Creating restorative hospital environments can ease their feelings of anxiety and burnout while improving their ability to care for patients.
Coronavirus | Jan 20, 2022
Advances and challenges in improving indoor air quality in commercial buildings
Michael Dreidger, CEO of IAQ tech startup Airsset speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield about how building owners and property managers can improve their buildings' air quality.
Healthcare Facilities | Jan 7, 2022
Supporting hope and healing
Five research-driven design strategies for pediatric behavioral health environments.
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 20, 2021
Stantec will design the new Queensway Health Centre
The project is located in Toronto.
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 16, 2021
Leo A Daly designs mental health clinic for veterans in Tampa
The new facility will consolidate all mental health services the VA offers into one clinic.
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 15, 2021
COVID-19 has altered the speed and design of healthcare projects, perhaps irrevocably
Healthcare clients want their projects up and running quicker, a task made more complicated by the shortage of skilled labor in many markets.
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 15, 2021
MEP design considerations for rural hospitals
Rural hospitals present unique opportunities and challenges for healthcare facility operators. Oftentimes, the infrastructure and building systems have not been updated for years and require significant improvements in order to meet today’s modern medical demands. Additionally, as these smaller, more remote hospitals are acquired by larger regional and national healthcare systems, the first step by new ownership is often to update and rehabilitate the building. But how can this be done thoughtfully, economically, and efficiently in ways that allow the engineering and facility staff to adapt to the changes? And how can the updates accurately reflect the specific needs of rural communities and the afflictions with which these areas most commonly face?
Healthcare Facilities | Dec 7, 2021
Wheeler Kearns Architects completes Howard Brown Health’s Broadway Youth Center in Chicago
The new facility will provide medical and social service programs to LGBTQI+ youth.