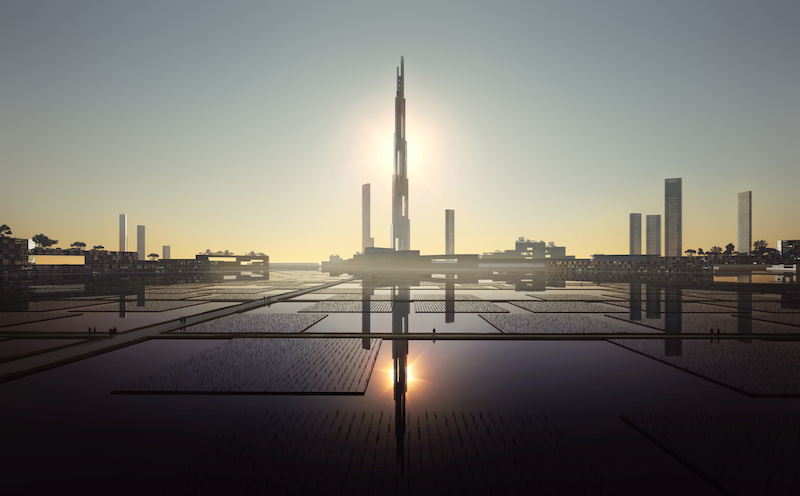
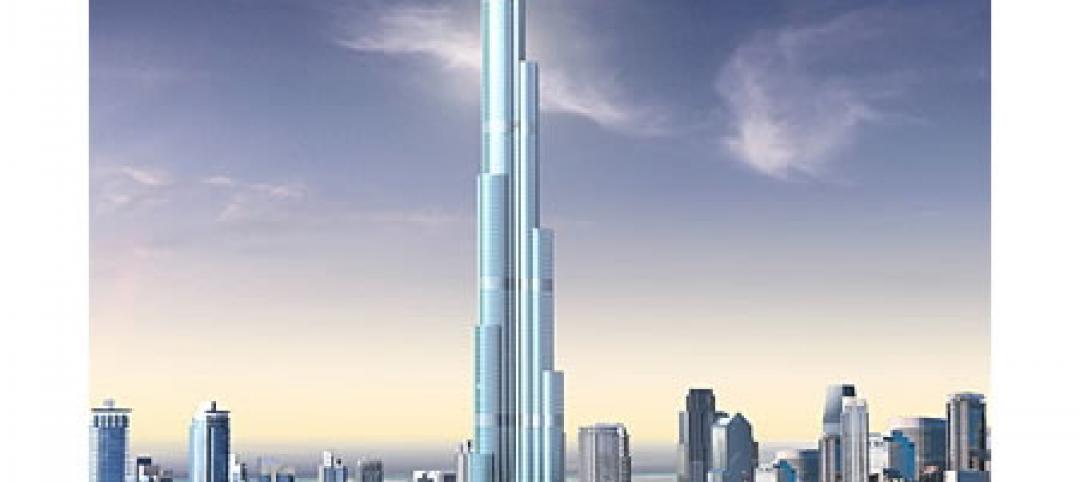
The Burj Khalifa in Dubai is currently the tallest building in the world at 2,716.5 feet. But in 2019, when the Jeddah Tower is completed in Saudi Arabia, its height of 3,280 feet will set the new mark for megatall structures.
An increase of over 500 feet is pretty significant, but not significant enough in the eyes of Kohn Pederson Fox, whose Sky Mile Tower design would stand only 419 feet shorter than the Burj Khalifa and the Jeddah Tower put together (yes, you read that correctly). At 5,577 feet, Sky Mile Tower would be the first structure to stretch one mile into the sky and beyond.
A building that height his hard to even fathom. If you have ever seen a picture of the Burj Khalifa and how it dwarfs the rest of the buildings around it or, better yet, have seen the massive structure in person, picture two of them stacked on top of each other. This would still be over 100 feet shorter than the proposed height of Sky Mile Tower. Again, it’s almost unfathomable.
While there are currently no construction plans, Kohn Pederson Fox is putting in the research to show how a structure like this could be possible, and it’s pretty fascinating stuff.
The tower would be the centerpiece of what the firm is calling “Next Tokyo,” part of a “megacity, adapted to climate change through the realization of a high-density ecodistrict built on resilient infrastructure,” according to a CTBUH research paper that was authored by members of Kohn Pederson Fox Associates and Leslie E. Robertson Associates. The city would be a chain of manmade, hexagonal islands strategically situated at a bottleneck in Tokyo Bay.
The hexagonal infrastructural rings, which would range from 150 to 1,500 meters in width, would be arrayed in such a way as to disrupt wave action intensity in multiple layers, which would create the potential for the current industrial focus of Tokyo Bay to allow for more mixed-use development and recreational activity in its upper portion.
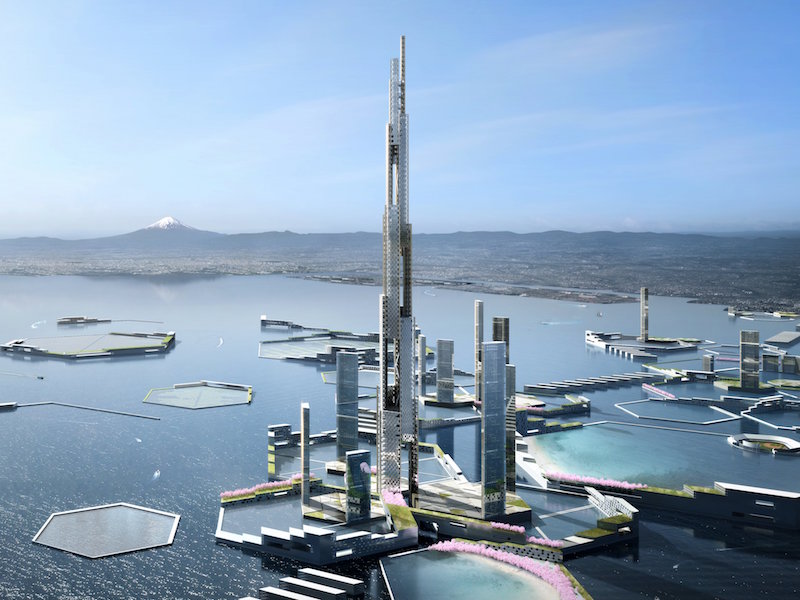 Rendering courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
Rendering courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
The rings would be connected to each other, Sky Mile Tower, and to the opposing shores via tunnels that include regional rail lines and a “Hyperloop” Maglev-vacuum-tube transport system (the same one Elon Musk is currently developing). There will also be a monorail system and a water bus network.
But let’s get back to the tower. With living space reaching 1,600 meters into the air and an overall apex of right around 1,700 meters, Sky Mile Tower is envisioned as a vertical network of segmented residential communities linked together by multi-level sky lobbies that would offer such public amenities as restaurants, hotels, gyms, libraries, and clinics. There would even be open-air spaces, designed for areas of protected pockets with lower wind speeds as identified through the use of wind tunnel testing.
The building would consist of multiple sets of three building legs interconnected to fit within a hexagonally shaped footprint. These building legs would overlap with one another in a rotated plan all the way up the tower. Each leg would have between 60 and 90 floors and would overlap with another every 320 meters. The overlaps would be full floors that extend across the entire central space to provide the connection spaces between the buildings six legs. This is where elevator and stair transfers would happen.
 Rendering courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
Rendering courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
With a building this tall, the primary concern from a structural engineering standpoint is how to deal with the motions and stresses caused by the wind. The six-leg design of the building helps in this aspect, as it allowed for the design team to "vent" the middle of the building in order to let winds pass through with less resistance.
Sky Mile Tower would also feature its own shuttle system to get all of the 55,000 residents to and from their units quickly and safely. The design would call for local elevator car shafts to run within a single residential zone and also express shuttles that would run on longer loops through multiple residential zones.
Just because this would be a massive structure does not mean the designers wanted an equally massive ecological impact. That is why many features of the structure have been incorporated to make Sky Mile Tower as sustainable as possible. For example, the building will help meet cooling and water loads by utilizing the stratified air and lower outdoor air temperatures.
Another problem would be pumping water from the ground all the way to the top units on the building. Not only would it take forever, but it would also be very costly. In an effort to alleviate this trouble, the tower would take advantage of cloud harvesting as a water source by using an articulated façade around its legs to increase surface area and then collect this "harvested" water for treatment and storage at various levels. Then, gravity would be used as a method of distribution to lower levels.
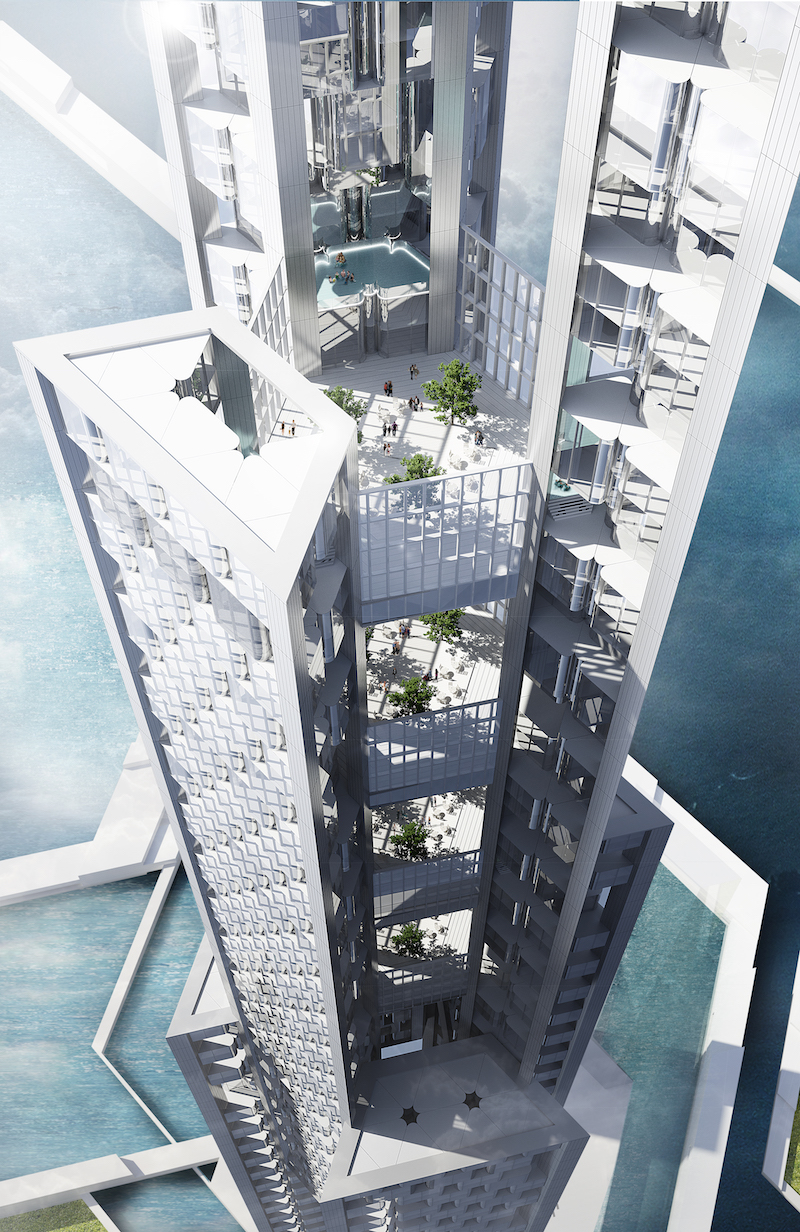 Rendering courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
Rendering courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
The entire district dubbed as Next Tokyo would occupy 12.5 square kilometers with artificial land accounting for 25% of the total area. Almost all of the high-density development will occur on the smallest of the hexagonal rings and will be clustered around the major transit exchanges. Overall, New Tokyo would be able to accommodate 500,000 residents.
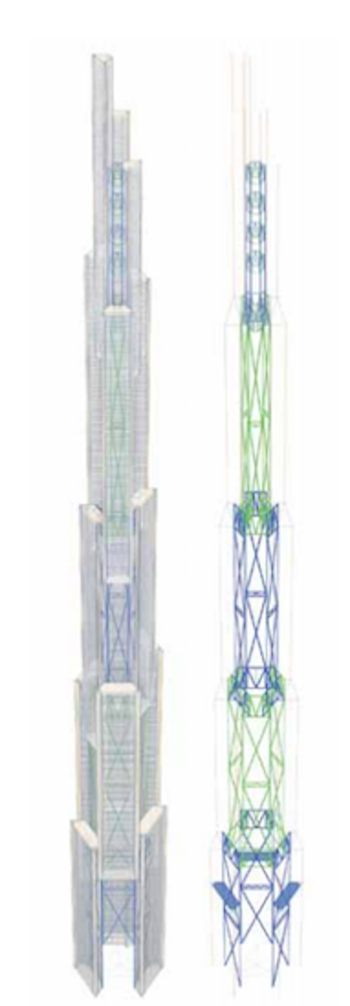 Sky Mile Tower Structural System. Rendering courtesy Leslie E. Robertson Associates
Sky Mile Tower Structural System. Rendering courtesy Leslie E. Robertson Associates
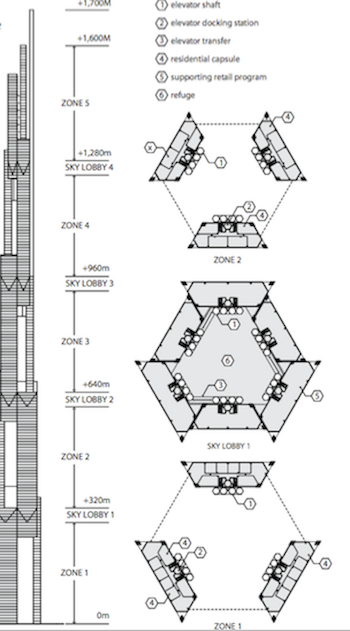 Image courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
Image courtesy Kohn Pedersen Fox Associates
You can view a PDF of the CTBUH Research Paper here.
Related Stories
| Dec 14, 2011
Belfer Research Building tops out in New York
Hundreds of construction trades people celebrate reaching the top of concrete structure for facility that will accelerate treatments and cures at world-renowned institution.
| Dec 12, 2011
AIA Chicago announces Skidmore, Owings & Merrill as 2011 Firm of the Year
SOM has been a leader in the research and development of specialized technologies, new processes and innovative ideas, many of which have had a palpable and lasting impact on the design profession and the physical environment.
| Dec 2, 2011
What are you waiting for? BD+C's 2012 40 Under 40 nominations are due Friday, Jan. 20
Nominate a colleague, peer, or even yourself. Applications available here.
| Nov 22, 2011
Suffolk Construction selected as contractor for Boston luxury residential tower
Project team breaks ground on 488,000-sf building that will feature world-class amenities.
| Nov 15, 2011
Suffolk Construction breaks ground on the Victor housing development in Boston
Project team to manage construction of $92 million, 377,000 square-foot residential tower.
| Oct 20, 2011
Johnson Controls appoints Wojciechowski to lead real estate and facilities management business for Global Technology sector
Wojciechowski will be responsible for leading the continued growth of the technology vertical market, while building on the expertise the company has developed serving multinational technology companies.
| Oct 18, 2011
Michel Bruneau wins 2012 AISC T.R. Higgins Award
The AISC T.R. Higgins Lectureship Award is presented annually by the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) and recognizes an outstanding lecturer and author whose technical paper(s) are considered an outstanding contribution to the engineering literature on fabricated structural steel.
| Oct 12, 2011
Vertical Transportation Systems Reach New Heights
Elevators and escalators have been re-engineered to help building owners reduce energy consumption and move people more efficiently.
| Oct 6, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: NEXT Living EcoSuite showcased
Tridel teams up with Cisco and Control4 to unveil the future of green condo living in Canada.
| Oct 5, 2011
GREENBUILD 2011: Johnson Controls announces Panoptix, a new approach to building efficiency
Panoptix combines latest technology, new business model and industry-leading expertise to make building efficiency easier and more accessible to a broader market.
















