As a result of the coronavirus pandemic, higher education is confronting its history of questionable facilities investment decisions and an unprecedented transformation on campuses that has made it imperative to reimagine construction, space allocation, and sustainability.
Gordian, a leading provider of facility and construction cost data, software, and services, analyzes the complexities of this transformation in the latest edition of its State of Facilities in Higher Education report, which this year Gordian conducted with APPA, an organization that represents more than 18,000 educational facilities professionals from over 1,300 learning institutions.
The report advocates for the increasing relevance of facilities managers at a time when campuses are building more space (schools in Gordian’s database were up 16% since 2007), but have also ill-advisedly deferred renovation on existing buildings, to the point where their backlog of asset renewal has increased by 35% since 2007, and their investment shortfall grew to 25%.
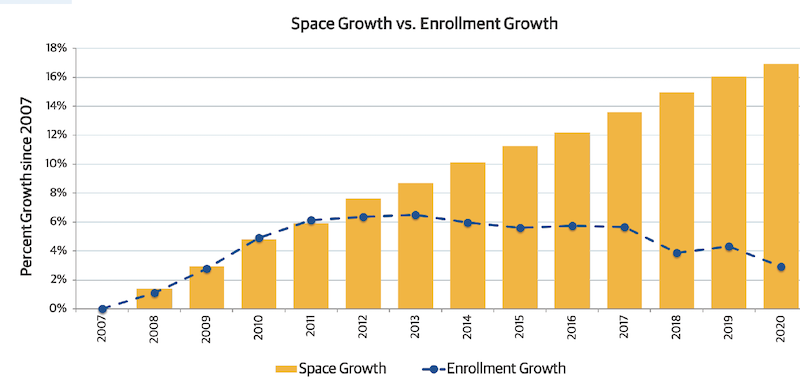
Colleges in Gordian's database have increased their space by 16% since 2007, but their student enrollment has increased only 2%. Images: Gordian and APPA
HOW MUCH SPACE WILL BE REQUIRED?
The pandemic has disrupted institutional improvement budgets by reducing student enrollment and shifting learning to remote and digital platforms that have lessened the need for campus spaces such as offices, dining halls, and residences. Outdoor spaces “were the rare bright spot, when weather has allowed,” the report states.
Consequently, campus planners are raising questions about what kinds of spaces will be needed in the future, and why. But adaptively reusing campus space is easier said than done. “Facilities offices aren’t sized and organized to maintain, clean and renovate according to student and staff activity. Rather, these offices maintain campus buildings independent of activity level,” the report observes.
Finding ways to fund facilities improvements and upgrades won’t be simple, either. The American Council on Education projects that the industry needs at least $180 billion to offset revenue losses and COVID-related expenses to maintain safe operations during the pandemic. But with between 50% and 70% of campus expenditures earmarked for employee compensation, the opportunities for addressing budget shortfalls without touching staffing are limited. For the whole of 2020, the industry lost 650,000 jobs.
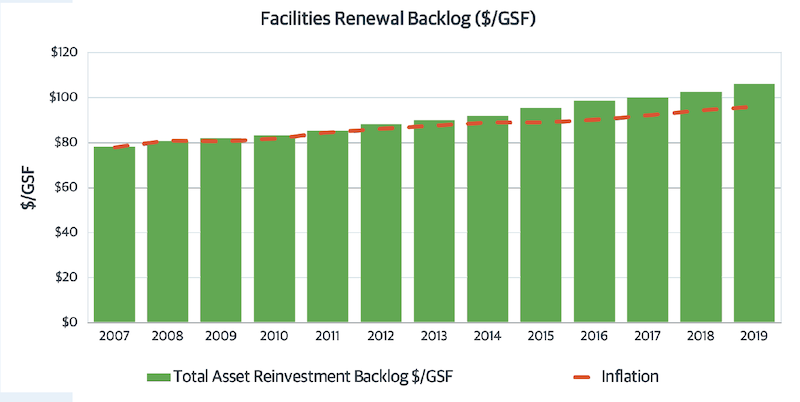
Backlogs of campuses' asset renewal needs have grown to $106 per gross sf, and 35% increase since 2007.
WHAT DOES ‘COMMUNITY’ MEAN TODAY?
The report notes that in the 2020 fall semester, 44% of schools were fully or primarily online, with another 21% operating in hybrid teaching mode. However, Gordian and APPA contend that the virtual world is not yet able to replace the in-person [educational] experience. “Community continues to be reliant on the physical gatherings of people, which will be an expected element of the collegiate experience for some time to come.”
If schools can’t provide this meaningful engagement, as well as some demonstrable evidence of a return on students’ investment, enrollments will continue to drop. The 13% decline in last year’s incoming freshman class “will have a ripple effect across the next three to five years,” the report states.
And schools can no longer rely on international students to help bridge their financial gaps.
The whole concept of campus “community” is changing. And the sudden embrace of digital tools for teaching opens endless interpretations of what an academic community looks like. “An opportunity clearly exists to reimagine campus space. The window is open to embrace digital, distant and trust-based work environments, and [schools] should leap to take advantage of the moment.”
More to the point, “the data say we need to use less space because [schools] simply can’t care for what [they’ve] built,” says the report.
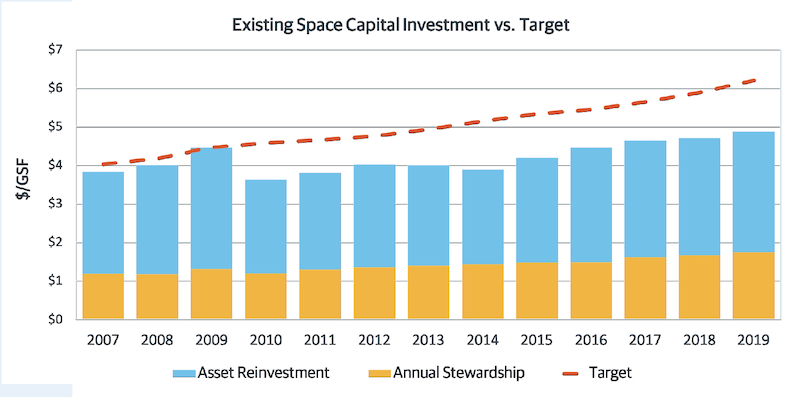
The investment shortfall in existing campus facilities has grown to 25% over the past 13 years.
HARD CHOICES WILL BE NECESSARY
So what are colleges and universities to do?
A start would be to document real operating costs, including the accrual of deferred needs with altered staffing and reduced capital investment. Facilities managers must prioritize space going forward, and clarify how students are likely to be taught. “Create a coherent narrative, incorporating the expectations of the community and the demands of the facilities, that represents a shared agreement for how to best optimize service to academic aspirations and institutional mission.”
Regarding future investments, schools must define their risk tolerances, especially it comes to keeping building systems operable to avoid shutdowns. Finance and facilities leaders must jointly understand how best to invest in a school’s physical plant, and develop a suitable investment strategy based on future need. That strategy, states the report, should have buy-in from the school’s senior leadership as well as stakeholders—students, faculty, workers—who will be affected by those decisions.
To meet the challenges of more dynamic campuses with fluid spaces and use, the report suggests that, at a minimum, institutions need to honestly appraise their facilities management teams, and determine what skills they will need for the next crisis but also routine times.
“Assess the type or work that has been required and is anticipated to be required to match hiring practices with the skills of the future,” the report states.
Related Stories
| Sep 4, 2013
K-12 school design that pays off for students
More and more educators are being influenced by the Reggio Emilia approach to pedagogy, with its mantra of “environment as the third teacher”—an approach that gives Building Teams a responsibility to pay even closer attention to the special needs of today’s schools.
| Sep 4, 2013
Smart building technology: Talking results at the BUILDINGChicago/ Greening the Heartland show
Recent advancements in technology are allowing owners to connect with facilities as never before, leveraging existing automation systems to achieve cost-effective energy improvements. This BUILDINGChicago presentation will feature Procter & Gamble’s smart building management program.
| Sep 3, 2013
'School in a box' project will place school in San Diego public library
Thinking outside the box, LPA Inc. is designing a school inside a box. With an emphasis on three E’s—Engage, Educate, and Empower—e3 Civic High is now being constructed on the sixth and seventh floors of a public library in downtown San Diego. Library patrons will be able to see into the school via glass elevators, but will not have physical access to the school.
| Aug 30, 2013
Modular classrooms gaining strength with school boards
With budget, space needs, and speed-to-market pressures bearing down on school districts, modular classroom assemblies are often a go-to solution.
| Aug 27, 2013
College of the Desert in Palm Springs to produce more energy than it consumes
A 60-acre solar farm next to the College of the Desert in Palm Springs, Calif., along with a number of sustainable building features, are projected to help the campus produce more energy than it uses.
| Aug 26, 2013
What you missed last week: Architecture billings up again; record year for hotel renovations; nation's most expensive real estate markets
BD+C's roundup of the top construction market news for the week of August 18 includes the latest architecture billings index from AIA and a BOMA study on the nation's most and least expensive commercial real estate markets.
| Aug 26, 2013
13 must-attend continuing education sessions at BUILDINGChicago
Building Design+Construction's new conference and expo, BUILDINGChicago, kicks off in two weeks. The three-day event will feature more than 65 AIA CES and GBCI accredited sessions, on everything from building information modeling and post-occupancy evaluations to net-zero projects and LEED training. Here are 13 sessions I'm planning to attend.
| Aug 22, 2013
Energy-efficient glazing technology [AIA Course]
This course discuses the latest technological advances in glazing, which make possible ever more efficient enclosures with ever greater glazed area.
| Aug 14, 2013
Five projects receive 2013 Educational Facility Design Excellence Award
The American Institute of Architects (AIA) Committee on Architecture for Education (CAE) has selected five educational and cultural facilities for this year’s CAE Educational Facility Design Awards.
| Aug 14, 2013
Green Building Report [2013 Giants 300 Report]
Building Design+Construction's rankings of the nation's largest green design and construction firms.

















