The consensus among leading real estate investors is that market-scale climate risk assessment will play a role in future investment decisions, mirroring the recent advances in assessing physical risk at the asset level. However, valuation still lags recognition of climate risk. And investors question whether adaptation and resilience actions by high-risk cities sufficiently respond to the extent of the risk faced, and ultimately what the overall impact of real estate will be.
These are some of the conclusions of Climate Risk and Real Estate: Emerging Practices for Market Assessment, the latest study on this topic from the Urban Land Institute and Heitman, a real estate investment management firm, that dives into how forward-thinking real estate investors factor climate change into their business decisions.
The report is based, in part, on recent interviews with 28 major real estate investors and developers ranging from Arcadis, Goldman Sachs, and LaSalle to the City of Rotterdam. Arup and the actuarial firm Milliman contributed insights into specialist areas such as measuring city fiscal health and catastrophe models “that enrich our understanding of what tools we need to assess, price, and address climate risk.”
WEATHER EVENTS MORE FREQUENT AND FEROCIOUS
That risk has rarely been more palpable. Worldwide losses from extreme weather events from 2010 to 2020 totaled over $3 trillion, $1 trillion more than the previous decade. Over the past few months alone, wildfires in California have scorched four million acres of land and displaced 200,000 residents.
A 2019 study by Deloitte found that more than half of U.S. state insurance regulators “indicated that climate change was likely to have a high impact or an extremely high impact on coverage availability and underwriting assumptions.” And earlier this year, Larry Fink, CEO of BlackRock, the world’s largest asset manager, warned that climate change was now “a defining factor in companies’ long-term prospects.” He added “we are on the edge of a fundamental reshaping of finance.”
Real estate investment managers interviewed for the ULI-Heitman report noted that they are seeing increases in property insurance premiums, a trend many of those investors attributed to climate change and the increased frequency of storm events. In an extreme scenario, some investors envisioned a future where properties can’t qualify for insurance and therefore can’t borrow. In short, a loss of insurance could cause a downward spiral even in the absence of a peak climate event. Even without a worst-case scenario, the annual insurance pricing structure can underpredict risk for longer hold periods as well as for infrastructure.
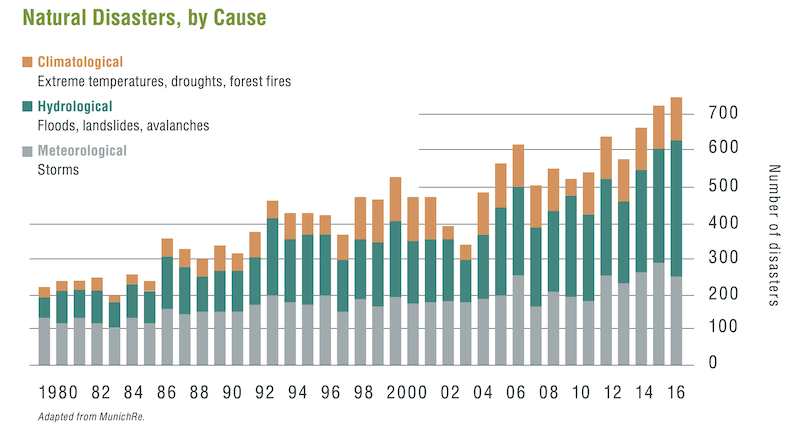
Anyway you call it, weather events are increasingly disastrous globally. Image: ULI and Heitman, data from MunichRe
INVESTORS SEARCHING FOR CLUES
Right now, it doesn’t appear as if investors are fleeing en masse from high-risk markets because of their fears of climate change. But the report identifies key considerations and next steps for the investment industry to improve awareness and understanding of market-level climate risk. These include:
•Developing strategies to measure market-level climate risk and resilience considering physical risk, resilient infrastructure, and public policy;
•Linking asset-level physical risk assessments with market-scale analysis;
•Exploring the role that the real estate industry plays in supporting funding mechanisms for future infrastructure and resilience initiatives;
•Facilitating collaboration between policymakers, chief resilience officers, and real estate investors and investment managers;
•Working with the insurance industry and actuaries to refine tools to reflect current and future climate risks; and
•Partnering with the valuation industry to accurately build climate change risk into appraisals.
MEASUREMENT TOOLS UNDERWHELMING
Perhaps the biggest challenge to climate-related risk assessment is the lack of qualitative measurement of climate change’s impact on cities and whether risk mitigation is enough. One investment manager interviewed for the report put in bluntly: “We have never found any [tools of frameworks] that cut to the chase and say, first, is this city impacted by climate change? And second, is the city’s reaction appropriate and sufficient given the risk?”
Compounding this problem is the lack of agreement among investors about how to qualify markets for climate risk in ways that incorporate vulnerability and resilience investments.
The study cites several considerations for climate-risk market analysis, including physical risk, city governance capacity, city resilience governance, building and land-use codes, and the extent, quality and implementation of a city’s resilience planning.
“The concept of urban resilience—and a city’s adaptive capacity in response to both major disruptions and chronic stresses—is fundamental to city governance,” the report states. That’s especially true today, as globally, most major economic hubs are in coastal, river delta, or other high-risk areas.
In 2020, McKinsey Global Institute explored Florida real estate as a theoretical example of this phenomenon, determining that if investments in flood preparedness are not made and flooding losses continue, homes in that state could be devalued by $30 billion to $80 billion, thereby leading to reductions in property tax revenue from 15 to 30 percent.
Investors are incorporating more factors into their risk management calculations. Image: ULI and Heitman
CATASTROPHE MODELING STILL NEEDS TWEAKING
The report observes that Investors are beginning to systematically follow how markets are making these infrastructure, policy, and investment decisions to contribute to their forecasts for the future economic health, vitality, and attractiveness of real estate investment in these markets.
But for catastrophe models to provide real estate investors with meaningful information, the report states that modifications are needed that take a longer-term focus on real estate value, and accept a dynamic view of the future.
The report warns, as well, that oversimplifying model results can lead to unintended consequences that undermine the risk management principles that the metrics were intended to support. “Under a changing climate, using a single-point estimate or metric that summarizes model results could be disastrous, as uncertainties compound over time.”
THINKING CREATIVELY ABOUT FUNDING
The report also touches on the need for cities to replace aging critical infrastructure as part of their resilience strategies. It notes that investments in stormwater management and coastal protection can have quality-of-life benefits. Some cities are also exploring value-capture strategies, where future high-value waterfront development would contribute funding to protective infrastructure nearby.
City governments implementing resilience plans are increasingly striving to make future investments in resilience in an equitable manner to ensure that all people benefit from climate solutions and to avoid further exacerbating patterns of discrimination.
Municipalities are also thinking outside the box when it comes to funding their resilience actions, looking beyond bond issues to explore partnerships with the private sector, whether through financial contribution, tax increment financing (TIF)-style funding districts, transfer of development rights, partnership in delivery of district-scale infrastructure, or by codifying resilience measures for new construction.
“In short, funding resilient infrastructure will require city staff to think creatively,” the report states.
Related Stories
Codes and Standards | Nov 27, 2023
Hoboken, N.J.’s street design policies are saving lives
Transportation policies enacted in Hoboken, N.J. over the past several years are paying off in the form of fewer pedestrian deaths and injuries. The city has adopted daylighting, bike lanes, lower speed limits, and intersection redesigns to make its roads safer.
Resiliency | Nov 27, 2023
All levels of government need to act to cope with climate-driven flooding and sea level rise
The latest National Climate Assessment highlights the need for local, state, and federal governments to adopt policies to mitigate the effects of climate-driven flooding and sea level rise, according to a policy expert with the National Resources Defense Council.
Resiliency | Nov 16, 2023
How inclusive design supports resilience and climate preparedness
Gail Napell, AIA, LEED AP BD+C, shares five tips and examples of inclusive design across a variety of building sectors.
Codes and Standards | Nov 10, 2023
Washington state building codes to protect structures from wildfire provoke controversy
New building codes in Washington state intended to protect structures from wildfires are provoking backlash from builders, cities, and environmentalists. Critics charge that the rules that are scheduled to take effect March 15 are confusing, will increase housing costs, and could cause too many trees to be cut down.
Sustainability | Nov 1, 2023
Researchers create building air leakage detection system using a camera in real time
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have developed a system that uses a camera to detect air leakage from buildings in real time.
Resiliency | Oct 19, 2023
Jacksonville unveils 50-year strategy for resiliency to flooding, extreme heat, wildfires
The City of Jacksonville, Fla., recently released plans for Resilient Jacksonville, a 50-year resiliency strategy to reduce the risks from flooding, hurricanes, excessive heat, and wildfires, and to respond better to those events. The plan includes ways to stop the St. Johns River from flooding vulnerable neighborhoods, including those prone to flooding during heavy rain or hurricanes.
Engineers | Oct 12, 2023
Building science: Considering steel sheet piles for semi-permanent or permanent subsurface water control for below-grade building spaces
For projects that do not include moisture-sensitive below-grade spaces, project teams sometimes rely on sheet piles alone for reduction of subsurface water. Experts from Simpson Gumpertz & Heger explore this sheet pile “water management wall” approach.
Urban Planning | Oct 12, 2023
Top 10 'future-ready' cities
With rising climate dilemmas, breakthroughs in technology, and aging infrastructure, the needs of our cities cannot be solved with a single silver bullet. This Point2 report compared the country's top cities over a variety of metrics.
Building Materials | Oct 2, 2023
Purdue engineers develop intelligent architected materials
Purdue University civil engineers have developed innovative materials that can dissipate energy caused by various physical stresses without sustaining permanent damage.
Resiliency | Sep 25, 2023
National Institute of Building Sciences, Fannie Mae release roadmap for resilience
The National Institute of Building Sciences and Fannie Mae have released the Resilience Incentivization Roadmap 2.0. The document is intended to guide mitigation investment to prepare for and respond to natural disasters.

















