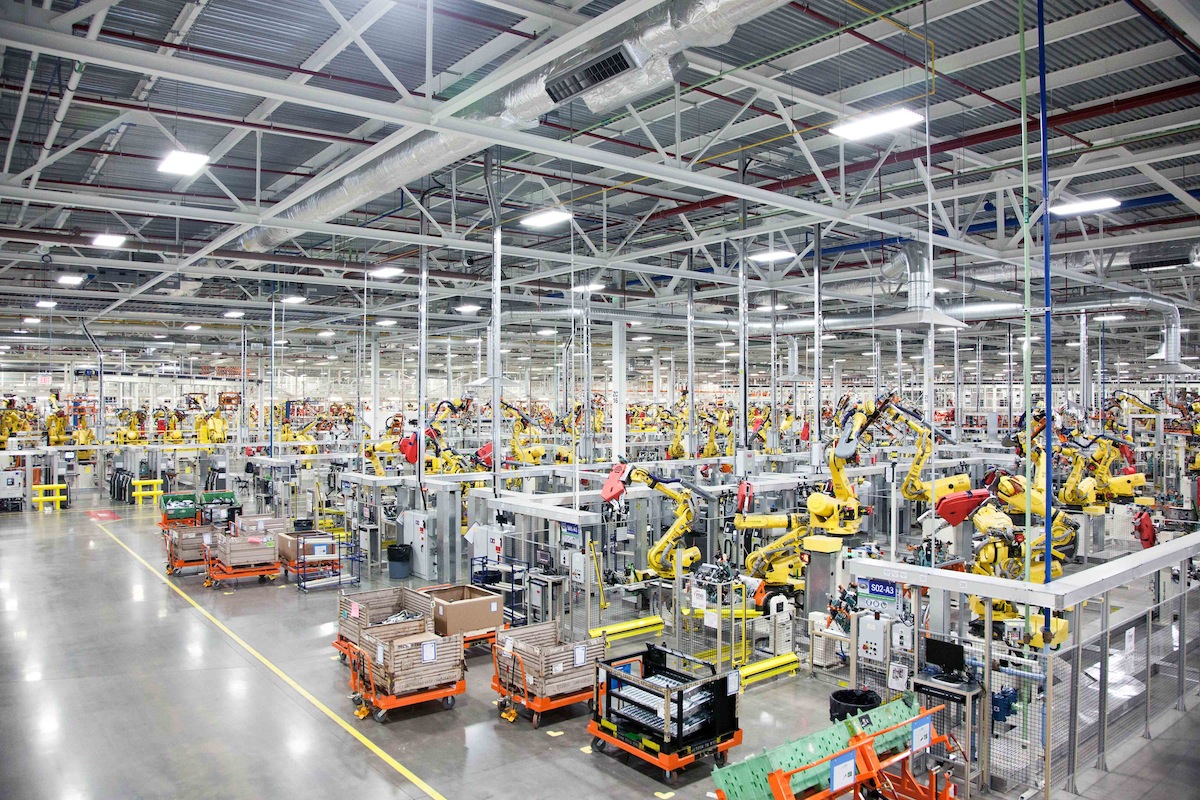
Global engineering and design consultantcy Arup launched "Rethinking the Factory," a report exploring the emerging trends, processes, and technologies that are transforming the manufacturing landscape. The report examines how the introduction of new technologies such as 3D printing, self-cleaning and self-healing materials, human/robot collaboration will lead to faster, more efficient and environmentally friendly production.
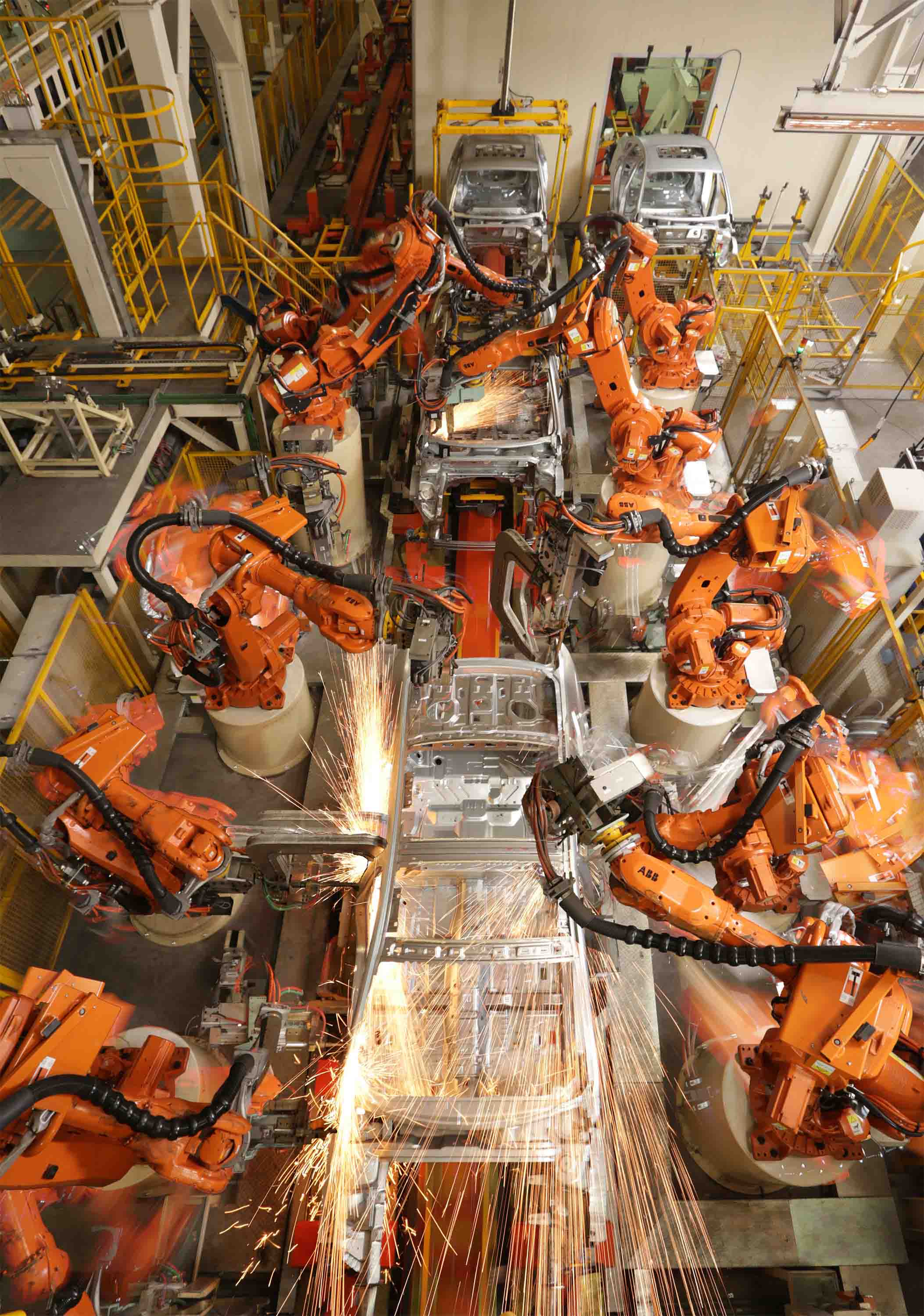
While many believe robots will replace humans in the factories of the future, the report, developed by Arup’s Foresight + Research + Innovation and Science and Industry teams, suggests collaboration between the two will be key. The integration of cameras and smart sensors already allow robots to adapt to their external environments.
Increasingly intuitive, their ability to infer a full task after being shown just a portion of it will enable workers to serve as robot supervisors, operating machinery and controlling smart production processes such as program and systems management and data analysis, rather than participating in manual labor. The increasing technicality of factories will mean that employees with STEM[1] skills will be particularly sought after, further exacerbating the international shortage of highly skilled workers, set to reach 40 million by 2020.
Beyond machines, new materials have the potential to improve the production process and increase product performance. A variety of self-healing and self-cleaning materials are being developed—such as bio-inspired plastic, which replicate the strength, durability, and versatility of a natural insect cuticles—which are capable of repairing damage without human intervention. These technologies will extend the lifetime of manufactured goods and reduce demand for raw materials.
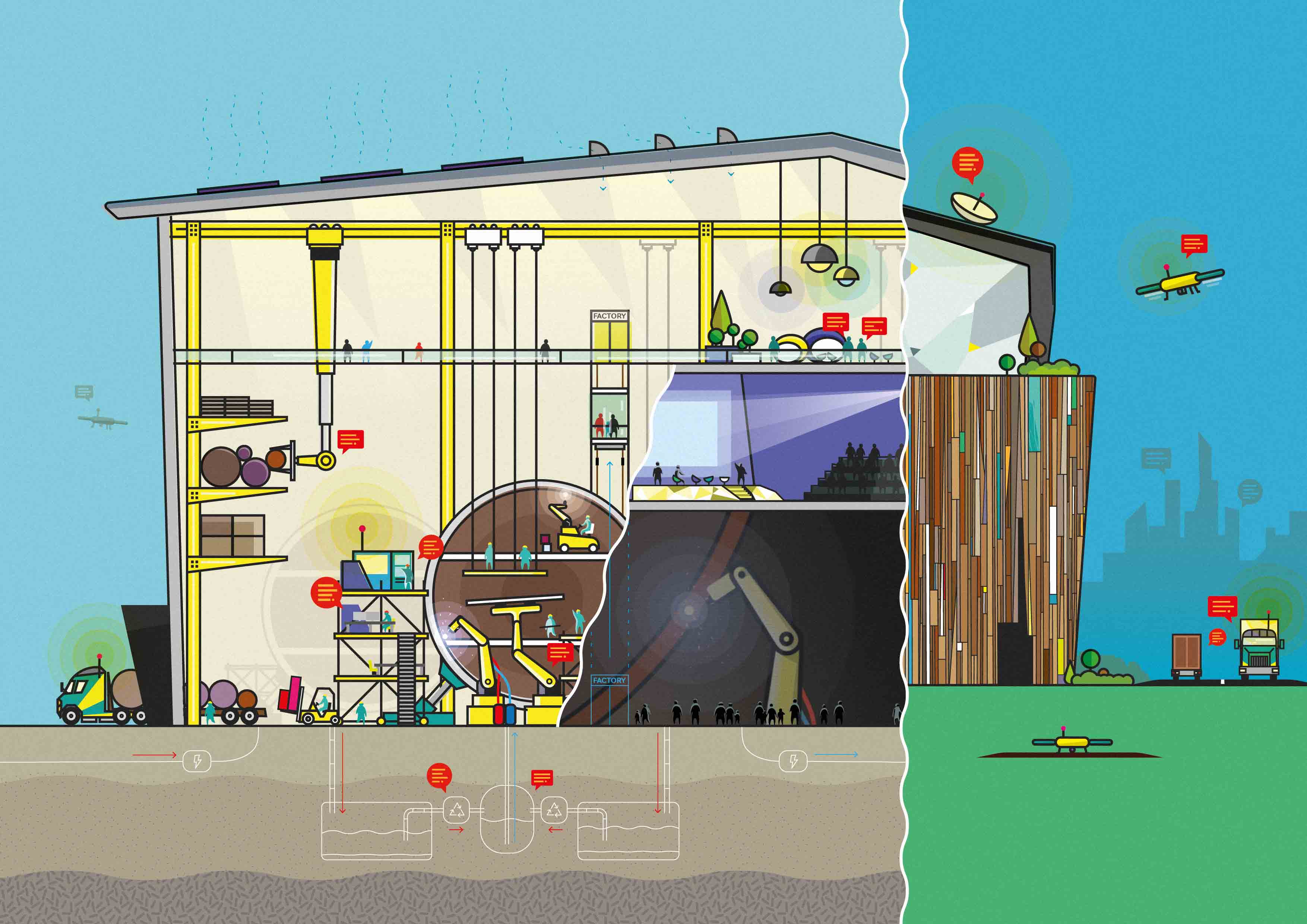
Big data, technology, and 3D printing
The utilization of 3D printing—or more accurately, additive manufacturing—will allow manufacturing to be more mobile and dispersed. Factory locations are therefore likely to become both more varied and closer to the consumer, including the emergence of nontraditional spaces such as small offices in a city center. This will allow production to take place closer to the point of use, lowering transport costs and emissions.
Intelligence based on Big Data, advanced analytics, and the Internet of Things will create new opportunities for competitive advantage. Analysis of data will reveal detailed customer insights, identify new product opportunities sooner, and get new products and designs to market faster. Additive manufacturing and digital technologies will also make this mass customisation, faster, easier and more affordable.

Resilient and Adaptive Spaces
Flexibility will be critical to tackling changing consumer demands and shifting market trends. Factories will be adaptable, with modular building techniques to enable efficient re-scaling and diversification of production across various locations. This will also allow energy, water, and material consumption to be managed more effectively in an increasingly constrained resource market, while producing an environment best suited to meet the multiple needs of its highly skilled workforce.
Using tools such as BIM in factory design, planning and management will play a critical role in allowing manufacturers to foresee and mitigate issues based on access to resources, location choices, weather risks and transportation needs.
The design of the factory will also be more focused on consumer experience, utilising the factory as a showroom. The concept of the "transparent factory" will gain increased importance as more people get involved in making products or as they expect closer insight into how products are manufactured, especially at a customised level. The opportunity for factory owners and operators lies in adapting their existing spaces to enable these types of experiences to take place.
“The convergence of the physical and digital worlds means that manufacturers have to continue to adapt and adopt new processes quicker than ever before," Duncan White, Science and Industry Leader at Arup said in a press release. "While developing sustainable and resilient practices will be essential, having access to a skilled pool of workers will prove to be equally important and challenging as these changes are made. As such, it is critical that companies and policy-makers have a comprehensive understanding of the changing manufacturing landscape."
Rethinking the Factory is part of Arup’s Future of… series that envisages the possible futures by highlighting innovations from around the world. Previous reports include the Future of Highways, Future of Rail, Cities Alive, and It’s Alive.
For further information on Rethinking the Factory please download the report.
Related Stories
BIM and Information Technology | Jan 18, 2019
BIM: Sharing is caring
Sharing of and reliance on BIM data is central to the idea that BIM will lead to a more efficient, more economical, and more collaborative construction process.
BIM and Information Technology | Jan 10, 2019
'BIM to AR' comes to the masses
Could new technology that simplifies the transfer of BIM models to augmented reality push AEC firms to go all in on extended reality?
Building Technology | Dec 20, 2018
Autodesk is spending $1.15 billion to acquire two construction tech providers
PlanGrid and BuildingConnected are the latest pieces in the company’s quest to digitize the construction industry.
Building Technology | Dec 18, 2018
Data and analytics are becoming essential for EC firms competing to rebuild America’s infrastructure
A new paper from Deloitte Consulting advises companies to revise their strategies with an eye toward leveraging advanced technologies.
Sponsored | BIM and Information Technology | Oct 15, 2018
3D scanning data provides solutions for challenging tilt-up panel casino project
At the top of the list of challenges for the Sandia project was that the building’s walls were being constructed entirely of tilt-up panels, complicating the ability to locate rebar in event future sleeves or penetrations would need to be created.
Sponsored | BIM and Information Technology | Oct 15, 2018
3D scanning data provides solutions for challenging tilt-up panel casino project
At the top of the list of challenges for the Sandia project was that the building’s walls were being constructed entirely of tilt-up panels, complicating the ability to locate rebar in event future sleeves or penetrations would need to be created.
BIM and Information Technology | Aug 16, 2018
Say 'Hello' to erudite machines
Machine learning represents a new frontier in the AEC industry that will help designers create buildings that are more efficient than ever before.
BIM and Information Technology | Aug 16, 2018
McKinsey: When it comes to AI adoption, construction should look to other industries for lessons
According to a McKinsey & Company report, only the travel and tourism and professional services sectors have a lower percentage of firms adopting one or more AI technologies at scale or in a core part of their business.
BIM and Information Technology | Jul 30, 2018
Artificial intelligence is not just hysteria
AI practitioners are primarily seeing very pointed benefits within problems that directly impact the bottom line.
AEC Tech | Jul 24, 2018
Weidt Group’s Net Energy Optimizer now available as software as a service
The proprietary energy analysis tool is open for use by the public.