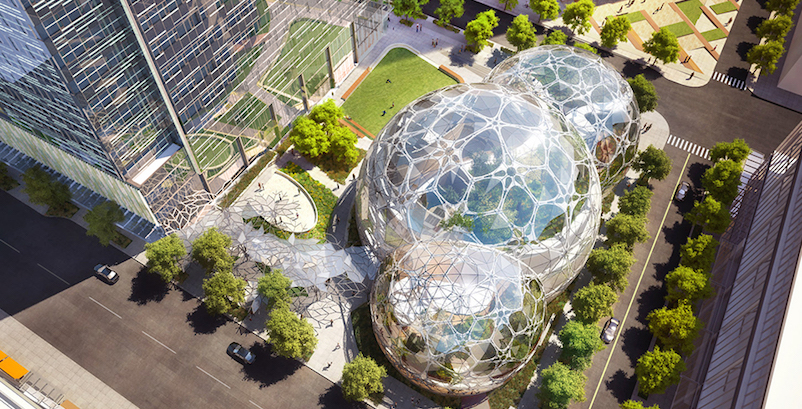
Next month, Amazon.com is scheduled to open the first phase of its massive Denny Triangle campus in Seattle. Through a unique partnership, the spheres and towers that comprise Amazon’s four-block, 4-million-sf campus will be heated by waste heat recovered from the 34-story Westin Building Exchange across the street.
The Seattle Times reports that 70% of the Westin Building Exchange’s 400,000 sf is dedicated to data centers that are throwing off tremendous amounts of excess heat.
The building produces heat equivalent to 11 megawatts per day. Through an agreement with Pacific Northwest, which routes nearly all of its Internet traffic through the data centers in Westin, the building will transfer up to five megawatts to Amazon, which is purchasing the energy at a discounted rate. Recapturing this waste heat is expected to save about 4 million kilowatt-hours of energy per year.
Here’s how this system will work, according to the Times and the Seattle Post-Intelligencer: When the Amazon buildings need heat, that will signal two heat pumps that collect heat from the data centers in the Westin Building Exchange, and use it to heat water traveling via pipes from the roof of the Westin building and through its floors to a refrigerator-sized steel-plated heat exchanger in Westin’s basement.
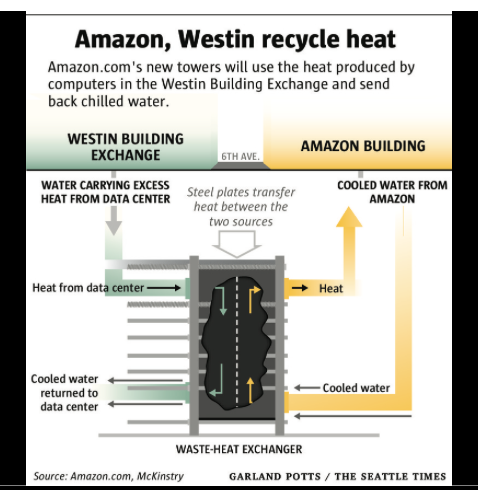 Image courtesy Amazon.com and McKinstry.
Image courtesy Amazon.com and McKinstry.
By the time that water reaches the exchanger, its temperature exceeds 70 degrees Fahrenheit. The exchanger transfers that heat through pipes running under the street to Amazon’s campus, which returns cooler water via the exchanger to the data centers.
When this system is fully functional, it will be circulating up to 3,000 gallons of water per minute.
Several entities collaborated on this project, which has been in the works for three years. They include McKinstry, which designed the heat-exchange system; and Clise Development, which co-owns the Westin Building Exchange with Digital Realty Trust, and sold Amazon the four blocks for its campus. Clise and McKinstry formed a partnership called Eco District for this project.
The agreement also involved several city agencies including its office of sustainability and environment. The Post-Intelligencer reports that one of Amazon’s building is already using this so-called district heating system that will ultimately provide heat for more than 3 million sf of office space.
Richard Stevenson, Clise Properties’ president, estimates the cost of this system in “the low millions” that would pay for itself in energy savings.
While heat exchange isn’t a new concept, it usually involves only one building, and rarely on the scale of this project. The Times quotes Susan Wickwire, executive director of the Seattle 2030 District—which aims to significantly reduce energy and water use in buildings in Seattle by 2030—who believes the arrangement between Amazon and Pacific Northwest could provide “a smooth path” for similar agreements where building occupants work together to save energy and make their operations more efficient.
“We’re showing people it can be done,” John Schoettler, Amazon’s director of global real estate, told the Times. “If other developments can model this, that’s a win-win.”
Amazon’s Denny Triangle campus, designed by NBBJ, will include three intersecting glass spheres that form a five-story office building, a 38-story tower, and 18,000 sf of retail. Amazon expects to be fully moved into these buildings in a couple of years.
Related Stories
| Sep 22, 2022
Gainesville, Fla., ordinance requires Home Energy Score during rental inspections
The city of Gainesville, Florida was recently recognized by the U.S. Dept. of Energy for an adopted ordinance that requires rental housing to receive a Home Energy Score during rental inspections.
| Sep 7, 2022
Use of GBCI building performance tools rapidly expanding
More than seven billion square feet of project space is now being tracked using Green Business Certification Inc.’s (GBCI’s) Arc performance platform.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Aug 24, 2022
Solutions for cladding performance and supply issues
This course covers design considerations and cladding assembly choices for creating high-performance building envelopes — a crucial element in healthy, energy-efficient buildings.
| Aug 23, 2022
New Mass. climate and energy law allows local bans on fossil fuel-powered appliances
A sweeping Massachusetts climate and energy bill recently signed into law by Republican governor Charlie Baker allows local bans on fossil fuel-powered appliances.
| Aug 22, 2022
Less bad is no longer good enough
As we enter the next phase of our fight against climate change, I am cautiously optimistic about our sustainable future and the design industry’s ability to affect what the American Institute of Architects (AIA) calls the biggest challenge of our generation.
| Aug 16, 2022
DOE funds 18 projects developing tech to enable buildings to store carbon
The Department of Energy announced $39 million in awards for 18 projects that are developing technologies to transform buildings into net carbon storage structures.
| Aug 15, 2022
Boston high-rise will be largest Passive House office building in the world
Winthrop Center, a new 691-foot tall, mixed-use tower in Boston was recently honored with the Passive House Trailblazer award.
Hotel Facilities | Aug 12, 2022
Denver builds the nation’s first carbon-positive hotel
Touted as the nation’s first carbon-positive hotel, Populus recently broke ground in downtown Denver.
Energy Efficiency | Aug 11, 2022
Commercial Energy Efficiency: Finally “In-the-Money!”
By now, many business leaders are out in front of policymakers on prioritizing the energy transition.
| Aug 8, 2022
Mass timber and net zero design for higher education and lab buildings
When sourced from sustainably managed forests, the use of wood as a replacement for concrete and steel on larger scale construction projects has myriad economic and environmental benefits that have been thoroughly outlined in everything from academic journals to the pages of Newsweek.

















