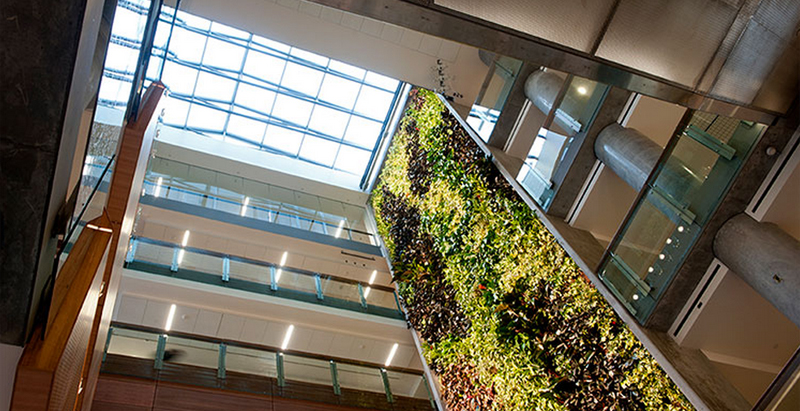
Located in the heart of University of Ottawa, the 15-story Vanier Hall functions as the new home of the large Faculty of Social Science and ‘stands tall’ as a living example of sustainable design boasting the intangibles of a rich and inspiring learning atmosphere, plus the measurable returns of energy saving technology.
From an exterior view, the green plant wall provides a striking contrast to the glass and steel structure. Once inside, visitors can fully appreciate a spectacular six-story-high feature – the largest living wall biofilter in North America at 1,370 square feet. In addition to the aesthetic impact, the biofilter is also part of the building’s sustainable design efforts.
Improves Air Quality and Building Performance
In simple terms, a Nedlaw Living Wall Biofilter is a working machine that harnesses nature’s remarkable ability to ‘eat’ pollutants. Contaminated indoor air is drawn through the biofilter where microorganisms on the root media consume airborne pollutants as food. This removal process cleans 80 – 85% of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from the air, creating virtual outside air. The cleansed air is then re-circulated through the buidling’s HVAC system.
The ‘soft’ benefits of the living wall include dust control, sound abatement, white noise in the form of running water, and a noticeable ‘smell’ of fresh air.
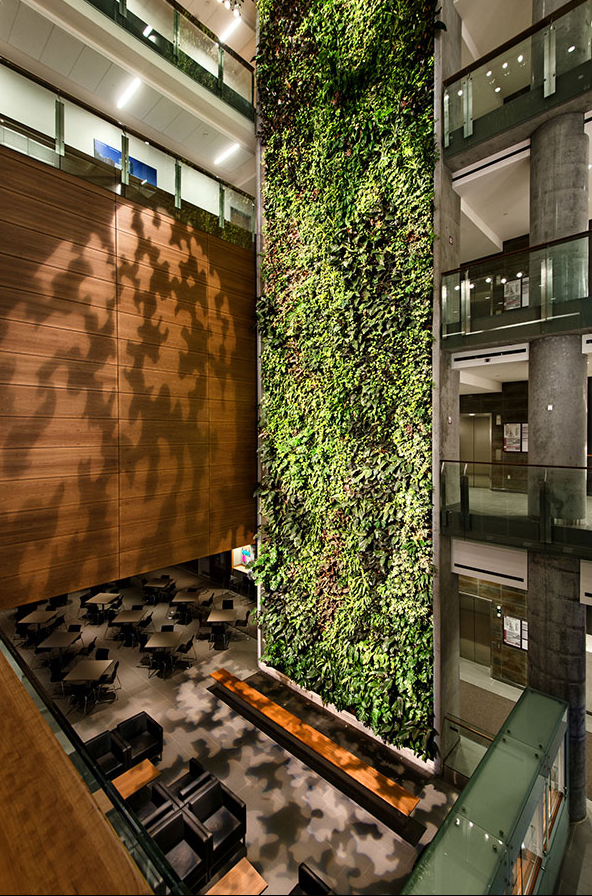

In terms of improving building performance, the biofilter at Vanier Hall can provide 75 – 80% of the building’s fresh air intake requirement, which not only enhances air quality but also significantly improves energy performance by reducing the amount of air intake and, consequently, heating and cooling costs. Additionally, the wall provides all of the building’s humidity and no mechanical humidification is needed.
The living wall biofilter at Vanier Hall includes energy smart features designed to address certain energy lapses in traditional building systems. For example, water recycled from storm water runoff and HVAC condensation is used for the hydroponic plant wall. According to Dr. Alan Darlington (founder of Nedlaw Living Walls), “We’ve done a lot of work to streamline and make this as efficient as possible without losing the aesthetics of this system.”
Calculating the ROI of Living Wall Biofilters
In recent years, Nedlaw has completed numerous studies to show the effectiveness of contaminant removal from indoor air and has now quantified the return on investment based on energy savings. By replacing outdoor air that needs to be conditioned, a Nedlaw Living Wall Biofilter reduces a building’s energy needs. In general terms, a fully-integrated biofilter can reduce energy costs by up to 30%, because the biofilters provide clean air at a fraction of the cost of traditional systems.
In a recent study completed for a major international retail chain, it was determined that the proposed living wall biofilter could provide 100 litres per second of outside air – meaning the building needed to take in that much less outside air.
Using the biofilter as a source of clean air would reduce the energy consumption of the HVAC system by 32.5 GJ of energy for square metre of biofilter used. If properly integrated into the building (for example, naturally lit and connected directly to the HVAC), the biofilter would require as little as 0.4 GJ of energy per square metre per year. This gives a total annual energy savings of the system of 32.1 GJ. This is equivalent to roughly 5 barrels of oil or 1.6 tonnes of CO2 saved per square metre of biofilter.
For this study, it was determined that approximately 400 m2 of biofilter would be used. Assuming a combined energy cost for electricity and natural gas of $10 USD per GJ and if the biofilter is used to its maximum potential then the payback period for the capital cost associated with the biofilter could be less than 3 - 5 years.
PROJECT DETAILS
Location: University of Ottawa, Vanier Hall
Architect: Diamond Schmitt Architects, KWC Architects
Award of Excellence / Interior Green Wall - Green Roofs for Healthy Cities
LEED Gold Certified
MEDIA COVERAGE
University of Ottawa Tower Wins 3 Awards
ABOUT NEDLAW LIVING WALL BIOFILTERS
Related Stories
Green | Jan 26, 2023
Corporations fall short on climate pledges by failing to embed net-zero actions into operations
Many corporations are failing to implement simple, practical steps needed for them to hit their stated decarbonization goals, according to a survey of more than 300 operations managers across key industrial sectors including construction, energy, and chemicals in the U.S., U.K., and Germany.
Multifamily Housing | Jan 24, 2023
Top 10 cities for downtown living in 2023
Based on cost of living, apartment options, entertainment, safety, and other desirable urban features, StorageCafe finds the top 10 cities for downtown living in 2023.
Green | Jan 17, 2023
Top 10 U.S. states for green building in 2022
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) released its annual ranking of U.S. states leading the way on green building, with Massachusetts topping the list. The USGBC ranking is based on LEED-certified gross square footage per capita over the past year.
Sustainability | Jan 9, 2023
Innovative solutions emerge to address New York’s new greenhouse gas law
New York City’s Local Law 97, an ambitious climate plan that includes fines for owners of large buildings that don’t significantly reduce carbon emissions, has spawned innovations to address the law’s provisions.
Cladding and Facade Systems | Dec 20, 2022
Acoustic design considerations at the building envelope
Acentech's Ben Markham identifies the primary concerns with acoustic performance at the building envelope and offers proven solutions for mitigating acoustic issues.
Green | Dec 9, 2022
Reaching carbon neutrality in building portfolios ranks high for organizations
Reaching carbon neutrality with their building portfolios ranks high in importance among sustainability goals for organizations responding to a Honeywell/Reuters survey of senior executives at 187 large, multinational corporations. Nearly nine in 10 respondents (87%) say that achieving carbon neutrality in their building portfolio is either extremely (58%) or somewhat (29%) important in relation to their overall ESG goals. Only 4% of respondents called it unimportant.
Green | Dec 9, 2022
Newly formed Net Zero Built Environment Council aims to decarbonize the built world
Global management consulting firm McKinsey recently launched the Net Zero Built Environment Council, a cross-sector coalition of industry stakeholders aiming to decarbonize the built world. The council’s chief goal is to collaboratively create new pathways to cut greenhouse gas emissions from buildings.
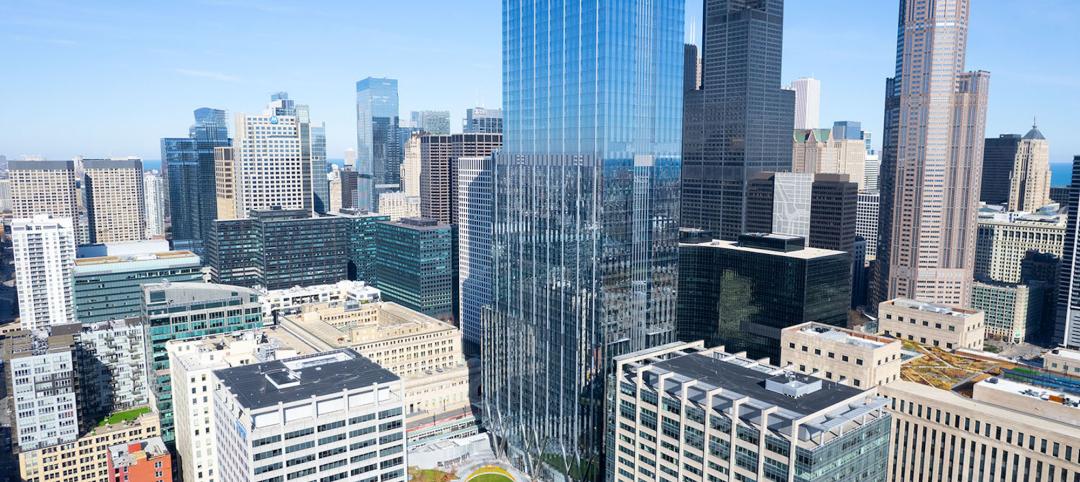
Office Buildings | Dec 6, 2022
‘Chicago’s healthiest office tower’ achieves LEED Gold, WELL Platinum, and WiredScore Platinum
Goettsch Partners (GP) recently completed 320 South Canal, billed as “Chicago’s healthiest office tower,” according to the architecture firm. Located across the street from Chicago Union Station and close to major expressways, the 51-story tower totals 1,740,000 sf. It includes a conference center, fitness center, restaurant, to-go market, branch bank, and a cocktail lounge in an adjacent structure, as well as parking for 324 cars/electric vehicles and 114 bicycles.
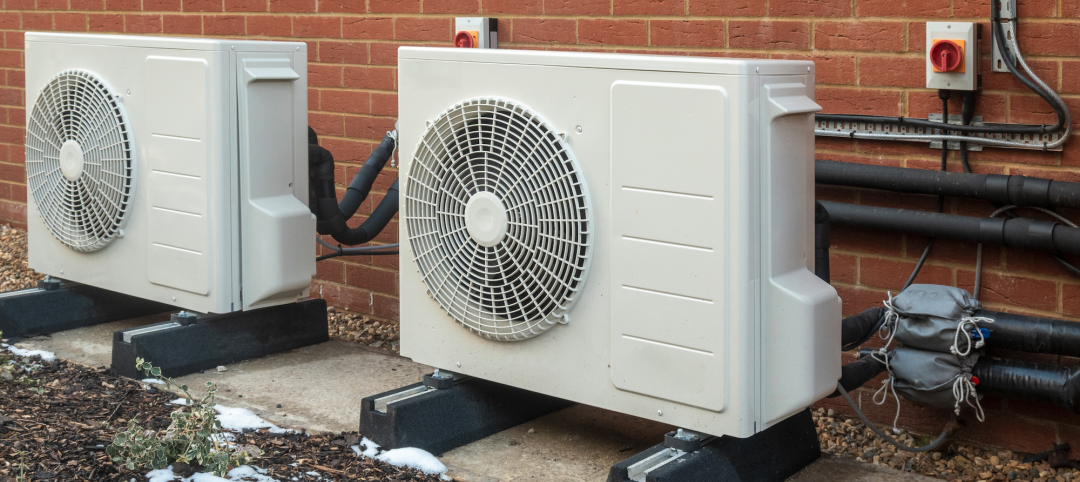
Energy Efficiency | Dec 6, 2022
Washington state’s Building Code Council mandates heat pumps in all new residential construction
The Washington State Building Code Council has voted to require heat pumps for all new residential construction starting in July 2023. The new mandate has drawn criticism over concerns that it will add costs to housing construction, especially given current supply chain challenges for heat pumps.
Geothermal Technology | Dec 6, 2022
Google spinoff uses pay-as-you-go business model to spur growth in geothermal systems
Dandelion Energy is turning to a pay-as-you-go plan similar to rooftop solar panel leasing to help property owners afford geothermal heat pump systems.