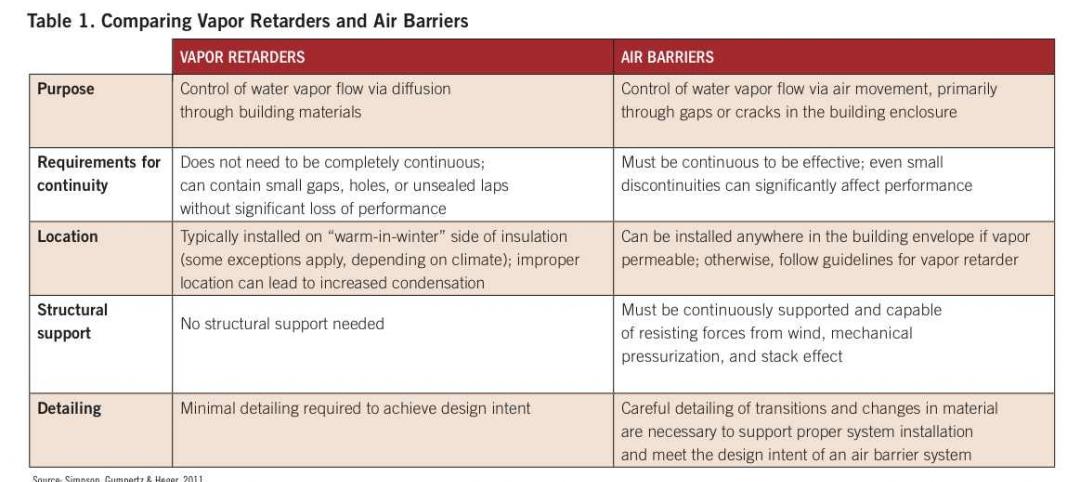
For architects looking to design sustainable buildings—especially in healthcare—smart technologies and renewable energy might be top of mind. But often overlooked, and perhaps the most important to get right from the outset, is designing an energy-efficient building enclosure.
“The sexy things are solar panels and windmills on your roof and vegetative roofs—and those are cool things—but the best bang for your buck is to make the building envelope as efficient as possible right from the beginning,” says Gale Tedhams, director of sustainability at Owens Corning. “The building envelope is your foundation for good energy efficiency.”
Since there are no real do-overs with the building envelope in any market sector, it’s important that AEC teams carefully plan their designs and select the right products. With the added goal of meeting at least one of the many green building certifications and standards in the industry, this process becomes more complex.
Architects looking for products created with sustainable materials can seek out Greenguard, Living Product Challenge, and Cradle to Cradle Material Health certifications, among others. Architects that are designing sustainable healthcare facilities can also turn to resources like the Green Guide for Healthcare, which offers tools and guidelines for designing green healthcare buildings.
Tedhams says at Owens Corning, building science experts are available to help builders navigate sustainability questions and figure out what the right solutions are for their specific projects and desired outcomes. The company also produces environmental product declarations (EPDs) that lay out the materials, certifications, and environmental impacts of products. “We make sure that we have the documentation and the transparency information for our products that's going to meet the needs of the criteria for a wide range of building programs,” Tedhams said.
Along with environmental impacts, sustainable building standards account for the impact of buildings on the health and well-being of occupants. Building envelopes play a significant role in this, as factors like indoor air quality and ventilation, acoustics, daylighting, and fire resistance are all of concern, especially in healthcare facilities where health is a priority.

From LEED to the Living Building Challenge to WELL, each sustainable building standard sets its own requirements for indoor air quality, acoustics, and thermal comfort. LEED v4 for Building Design and Construction has comprehensive requirements for air quality, which cover entryway systems, filtration, interior cross-contamination prevention, and more.
The LEED guideline also outlines rules for low-emitting materials, which must meet 100 percent of the compliance threshold in the area of building envelope materials. For healthcare buildings, there are additional requirements, including that batt insulation products can’t contain any formaldehyde.
LEED also offers LEED for Healthcare, which generally mirrors regular LEED requirements while tailoring guidelines to the unique demands and regulations of healthcare buildings. Areas of concern unique to this design sector include 24/7 operations, patient privacy, chemical use, and infection control requirements.
WELL has around 29 separate guidelines relating to air quality alone, with delineations for areas including microbe and mold control, healthy entryways, humidity control, air infiltration management, and toxic material reduction.
Similar to LEED, WELL’s guidelines limit the presence of formaldehyde in building materials. Companies like Owens Corning are expanding their offerings to provide additional formaldehyde-free options. Last year, the company introduced the first formaldehyde-free mineral wool insulation for the North American market, Thermafiber® SAFB™ Formaldehyde-Free. In 2018, the company intends to further expand its formaldehyde-free mineral wool product offerings.
“Our formaldehyde-free product is especially appropriate to achieve green building standards because now it brings the fire safety aspect of mineral wool insulation combined with indoor air quality into the healthcare sector,” says Stephanie Maxson, product manager at Owens Corning.
The Thermafiber® formaldehyde-free line has the International Living Future Institute’s Declare label and Greenguard Gold certification. The line provides acoustical control, thermal performance, and fire protection while not introducing harmful chemicals into the air.
Ultimately, as the green building industry continues to grow, so will the need for products that help architects meet guidelines and performance goals for sustainable design. AEC teams looking to stay relevant can look to manufacturers for transparency information as well as online databases and green building guidelines to help make good choices for a sustainable world.
Related Stories
| Oct 3, 2011
Balance bunker and Phase III projects breaks ground at Mitsubishi Plant in Georgia
The facility, a modification of similar facilities used by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Inc. (MHI) in Japan, was designed by a joint design team of engineers and architects from The Austin Company of Cleveland, Ohio, MPSA and MHI.
| Sep 12, 2011
Living Buildings: Are AEC Firms up to the Challenge?
Modular Architecture > You’ve done a LEED Gold or two, maybe even a LEED Platinum. But are you and your firm ready to take on the Living Building Challenge? Think twice before you say yes.
| Jul 22, 2011
Air barrier systems: Your guide to optimal performance
Expert advice on how to control wasteful air leakage in the building envelope.
| Jul 22, 2011
Five award-winning modular innovations
The Modular Building Institute's 2011 Awards of Distinction highlight fresh ideas in manufactured construction projects.
| Oct 13, 2010
Community college plans new campus building
Construction is moving along on Hudson County Community College’s North Hudson Campus Center in Union City, N.J. The seven-story, 92,000-sf building will be the first higher education facility in the city.
| Aug 11, 2010
Morphosis builds 'floating' house for Brad Pitt's Make It Right New Orleans foundation
Morphosis Architects, under the direction of renowned architect and UCLA professor Thom Mayne, has completed the first floating house permitted in the U.S. for Brad Pitt’s Make It Right Foundation in New Orleans.The FLOAT House is a new model for flood-safe, affordable, and sustainable housing that is designed to float securely with rising water levels.