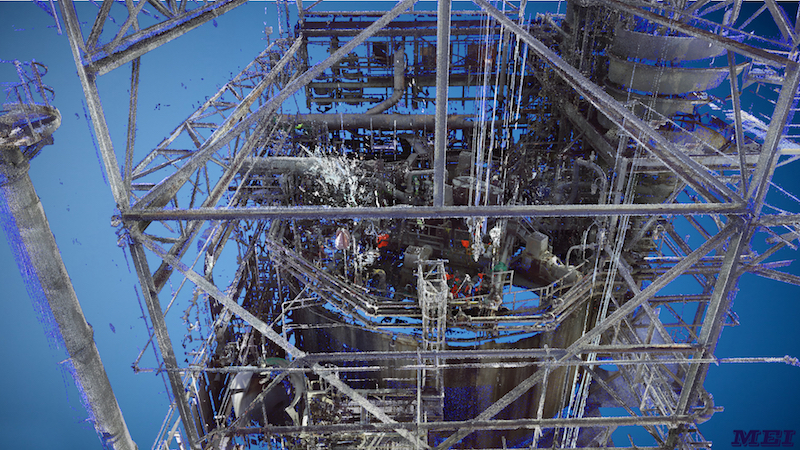
For an Acid Tank Remodel project in Florida, a major chemical plant owner called upon the expertise of Moody Engineering, Inc. (MEI), a Florida-based group of consulting engineers that specializes in engineering and construction management design for commercial and industrial projects. With Moody’s ability to bring in their valuable experience with state-of-the-art 3D scanning and modeling technology, the Moody team was able to provide a practical scan-to-BIM solution. By integrating creativity and ingenuity with practicality, they were able to address the project’s specific requirements in order to save the customer time and money on this challenging project.
CHALLENGES
For the Acid Tank remodel project, Moody Engineering, Inc. was charged with the task of providing mechanical, structural, and piping design. The scope of the work on this project dictated that Moody replace the roof on this tank. The whole tank, in fact, was falling in on itself. The main challenges at the job site included: 1) scanning the inside of the acid tank and its exterior surroundings while the plant was still in operation, and 2) navigating the scanner through an industrial structure while getting the right scan locations.
Without use of the scanner, Moody’s engineers couldn’t have taken field measurements without extensive mobile and safety equipment (high reach, scaffolding, etc.). The reality is that the owner might have decided to scrap the tank altogether, an option that was discussed along the way: Replacing vs. modifying. Moody sought to determine if, based of what they were able to do with the point cloud and the scans, they would be able to salvage at least the wall of the tank—rebuild the tank as opposed to pulling everything out and putting a new tank in, which would have been much more expensive.
The answer was yes.
SOLUTION
Perhaps the biggest benefit for Moody using the FARO® 3D Focus Laser Scanner —and the reason they got the scanner in the first place—is safety. Scanning allowed them to reduce the number of people they had going out in the field, not to mention the fact that is reduces the likelihood that they’d need to send people back out since they would already have captured the required information in the scan. Scanning eliminated the need for a high reach and for the operator needing to do the work by hand.
Of course, the operating cost and time savings were among the other tangible benefits. A scan that takes 30 minutes might otherwise take them two or three days. For the scanning process itself, Moody only needed one or two people doing the work. If they missed a spot that had to be in the scan, the portability and the ability to quickly go out and take care of it made the scanner an invaluable tool. As Steve Moody, P.E., MEI’s President and Director of Engineering notes, “3D scanning eliminated fit-up errors at a plant-critical time for a plant-critical system.”
For this project, Moody went in several times to scan. The first time, they went in to scan the top of the tank to get all the equipment in order to ensure the equipment would ultimately be put back in the same spot when they generated the drawings from the scan. Because the severely poor condition of the tank, they didn’t want a lot of people up there pulling tape and doing field measurements so they decided to scan it to get in and out as quickly as they could and develop their 3D model from that.
About a week later, Moody went back and did the ground scan. They then merged the two scans together to create a complete model so that they would not have to be around the tank in its unsafe condition. One of the two scanning operators also scanned the inside as well. All in all, there were three different sets of scans merged together. Using traditional methods, there would have been no way to pull tape on every single piece of equipment, pipe, ad everything that was out there. The scanner not only made the most sense—but was really the only practical option—and allowed for the opportunity repair rather than replace the tank.
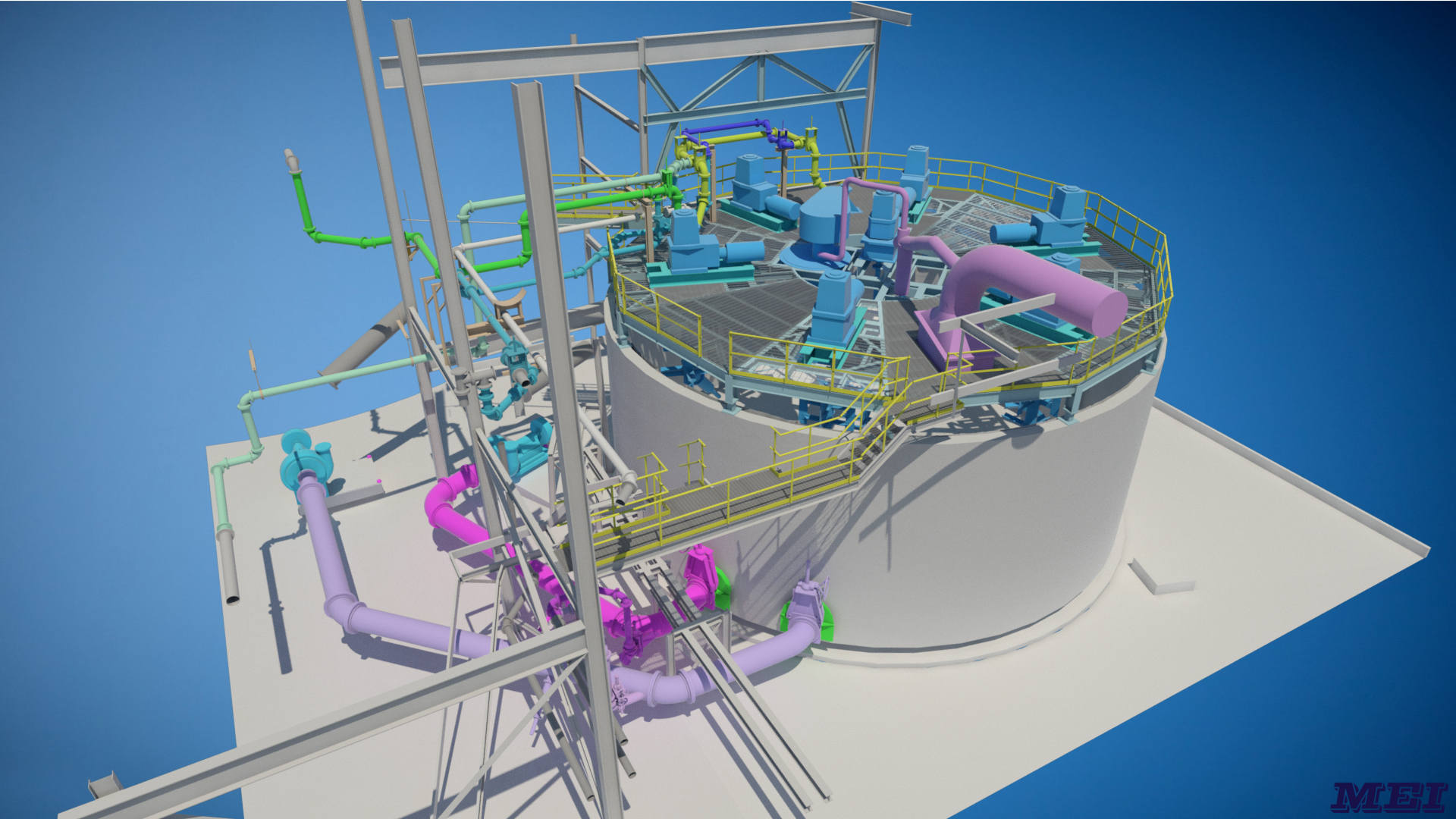 New reactor tank roof design model with optimized piping and equipment layout to allow for easier maintenance.
New reactor tank roof design model with optimized piping and equipment layout to allow for easier maintenance.
Workflow: Pre-Modeling
In terms of workflow particulars, Moody handled this job as they do on most jobs—they went in and walked the job down. Their engineers went with the PM to look at the job and see the challenges they would face, assess safety consideration and take pictures. They then came back and developed a plan of attack. The engineer set up the FARO Focus Laser Scanner in certain spots to make sure they could capture everything they needed, then figured out how they would actually do it by maximizing scanning and minimizing the time on site. Scanning time ran a total of about 25 hours, which is significantly better than bringing the whole crew out to the site.
The initial scan took only two days with a verification day. According to MEI engineers, without the scanner, it would have taken three people from six to nine days with multiple trips back and forth to get it done. This is because information gets lost when work is done manually. The scanner eliminates all the uncertainty—if scanned correctly, the team never has to take trips back to the site.
Additionally, had traditional methods been used on this particular job, Moody would have needed to take field measurements with tape measures, plumb-bobs, etc. Using the FARO FocusS 150 and 350 provided Moody with an “as-built” environment that the team was able to replicate in the 3D model, thereby eliminating the need for long hours of pain-staking field measurements.
Workflow: The Modeling Aspect
Once the scanning is done, the next part of the workflow is to register the scans, throw it into SCENE, spit out the .fls files, put them into EdgeWise, and then they can grab the pipe on its own. The engineer takes that information to model any structure needed for the job using the scan information to show everything pictorially not only in a 3D environment but also in ClearEdge3D EdgeWise to extract that existing steel and know where the interferences will be. Moody then finishes out the piping. MEI engineers acknowledge that it definitely helps to get an existing as-built condition with the scan, without which they wouldn’t know the details of what’s out there. They can then pull it into AutoCAD®, model that tank, and do an analysis on it. It’s not just to “see the pretty point cloud.” The engineers can use it for a lot of other things.
By using ClearEdge3D EdgeWise, Moody cut its 3D modeling time by at least 60 percent; AutoCAD Plant 3D provided the basis for the piping design for all of Moody’s piping runs.
As for the company’s success using the scanning technology, Steve Moody, P.E. explains, “The 3D scan and model lets us pull dimensions from my office rather than in the field. It eliminates any concern about fit-ups in the field during construction.”
RESULTS
Regarding deliverables, Moody ultimately provided the client (Mosaic) with 2D drawing documentation generated from a practical Navisworks 3D BIM model in order to facilitate the modification of the tank. Moody’s team kept Mosaic apprised all the way through, giving them models at various intervals so they could review it, rather than the old way of 2D drawings alone where you don’t know exactly what you’re looking at.
With a 3D model, you can spin it around, show the client the scans, and let them see in the point cloud how Moody was able to get around the interferences. Moody's engineers note, “Oftentimes, drawings are lacking and you have to make do. Without the scanner, we wouldn’t have anything. Having the scans is a huge advantage as sometimes 2D drawings do not provide correct or complete information.”
Estimated Cost and Time Savings
3D scanning greatly influenced the team’s strategy to repair the tank vs. replace-in-kind. The only real estate available for a new tank was far removed from the current tank location onsite. Consequently, the client would have had to endure the cost of not only building a new tank, but also the added high operations and capital expenses of piping the acid product to and from the remote location.
While an exact bottom line is difficult to say, the scanning technology undoubtedly allowed for substantial savings when you consider that the dollar value of the tank is in the multimillions—and not having to replace the acid tank may have saved the client anywhere from 50 to 90 percent TIC (total installed cost).
Additionally, the following assumptions can be made to help further quantify time and cost savings using scanning technology rather than traditional methods:
With 3D scanning:
- Two people for two 8-hr days: ~$4-5K
Without 3D scanning:
- Three people for six to nine days: ~$25-30K
- Equipment + Scaffolding: ~$6-15K
- Mileage + Travel time: ~$4-5K
Client Satisfaction
According to a client representative, “Feedback so far is everyone is very happy with the final product. I certainly appreciated the responsiveness of MEI to our requirements as they evolved—and particularly the exceptional efforts to adhere to our very tight schedule. We’re very thankful to the entire MEI team that worked on this project.”
CONCLUSION
With 3D Scanning technology, structures that would have normally been deemed unrepairable and previously demolished can now be modeled and engineered with precision. Embracing this technology has allowed us to become better, more creative engineers. We are now able to focus on the most value-added use of our time, and eliminate unnecessary costs.
Related Stories
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 14, 2015
Deep data: How greater intelligence can lead to better buildings
The buzzword may be “Big Data,” but the reality is that Building Teams need to burrow deep into those huge datasets in the course of designing and building new facilities. Much of the information is free. You just need to dig for it.
Smart Buildings | Jun 11, 2015
Google launches company to improve city living
The search engine giant is yet again diversifying its products. Google has co-created a startup, called Sidewalk Labs, that will focus on “developing innovative technologies to improve cities.”
Seismic Design | Jun 9, 2015
First building-specific earthquake warning system installed in North Portland, Ore.
The ShakeAlarm system recognizes and quantifies the faster but lower-energy seismic P-wave, which is the precursor to the more damaging S-wave.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 8, 2015
Ready for takeoff: Drones await clearance for job site flights
The fog is finally lifting on who will be allowed to pilot unmanned aerial vehicles.
Green | Jun 8, 2015
Diamond Schmitt Architects creates tool to compare energy use data across building types
The firm's new ecoMetrics tool allows for a comprehensive analysis of data from energy simulation models across a wide range of the company’s building types.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 5, 2015
Backpack becomes industry first in wearable reality capture
Combining five high-dynamic cameras and a LiDAR profiler, Leica's Pegasus:Backpack creates a 3D view indoors or outdoors for engineering or professional documentation creation.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 4, 2015
Why reality capture is essential for retrofits
Although we rely upon as-built drawings to help us understand the site for our design, their support is as thin as the paper they are printed on, write CASE's Matthew Nelson and Carrie Schulz.
BIM and Information Technology | Jun 3, 2015
More accurate GPS ready to change the way we shop, interact, and explore
New technology reduces location errors from the size of a car to the size of a nickel—a 100 times increase in accuracy. This is a major technological breakthrough that will affect how we interact with environments, the places we shop, and entertainment venues.
Sponsored | BIM and Information Technology | May 28, 2015
Does BIM Work as a Deliverable?
Sasha Reed sits down with industry professionals at the BIMForum in San Diego to talk about BIM technology.
BIM and Information Technology | May 27, 2015
4 projects honored with AIA TAP Innovation Awards for excellence in BIM and project delivery
Morphosis Architects' Emerson College building in Los Angeles and the University of Delaware’s ISE Lab are among the projects honored by AIA for their use of BIM/VDC tools.