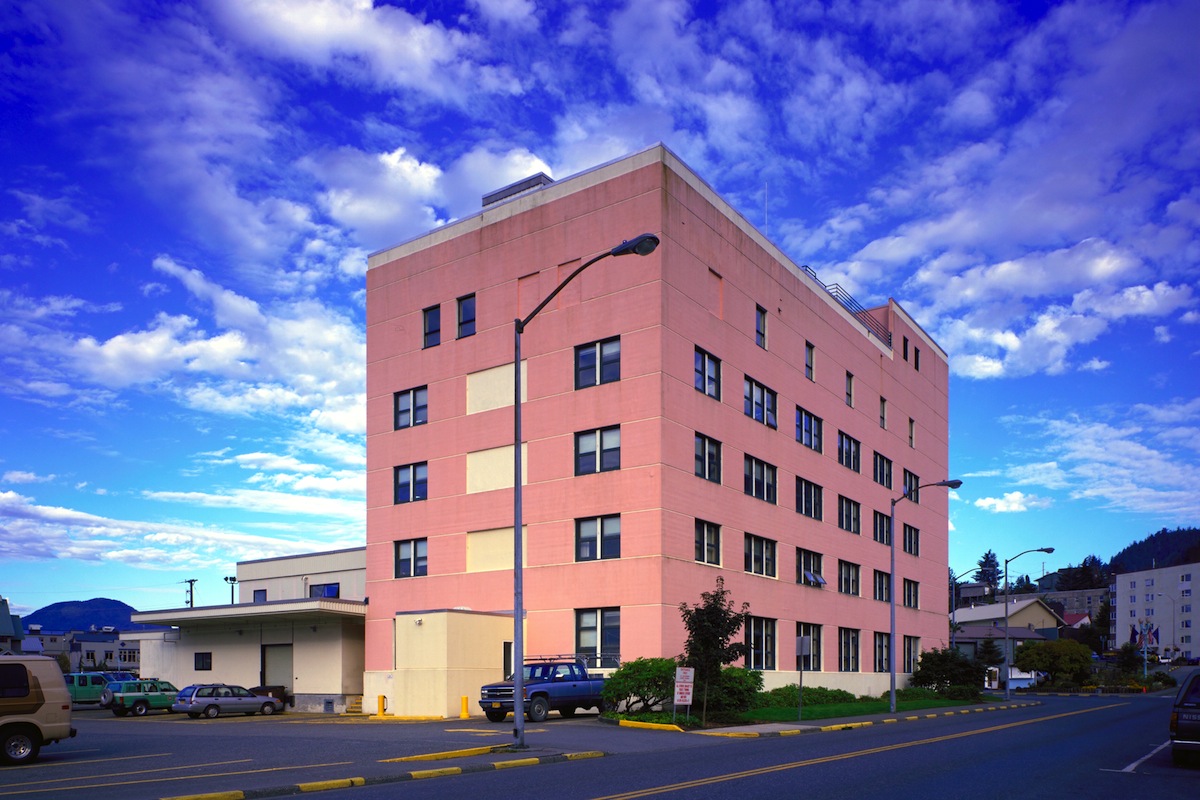
After operating the first biomass boiler in the Ketchikan, Alaska, Federal Building, the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) has concluded that biomass boilers are a viable alternative for hot-water-heated buildings where natural gas is unavailable.
According to a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL), biomass boilers will be most cost-effective for buildings in cold northern climates within 50 miles of a wood pellet mill. Of the more than 1,500 GSA-owned buildings, researchers identified approximately 150 assets as potential candidates for biomass heating technology.
“This study allowed us to pilot a sustainable technology that supports GSA’s goal of improving the efficiency of federally owned buildings,” said GSA Regional Administrator George Northcroft. “And the results are extremely encouraging and hopefully continue a larger conversation about overall movement toward a more sustainable, abundant and locally-produced energy source in Southeast Alaska.”
The biomass boiler is a renewable energy technology that powers hot-water-heating systems with solid wood fuel—such as wood pellets, chips, or sawdust. Biomass is one tactic the federal government is turning to as part of an effort to make the federal government more sustainable.
The boiler, installed at the Ketchikan Federal Building in March 2012 by Southwest Construction, a small, woman-owned business with operations in Anchorage, is part of the GSA’s Green Proving Ground (GPG) program. GSA replaced the building’s outdated, inefficient 1964 steam heating system with an energy efficient hydronic heating system that includes one biomass boiler and one high-efficiency oil-fired boiler that will serve as a back-up.
During the first year of operation, GSA ran the new system to test the efficiency and effectiveness of biomass to heat the federal office building. By using both boilers, GSA expected reduced fuel oil consumption by at approximately 50 percent in the first year with potential for greater reductions after the first winter. The Ketchikan Federal Building historically burned up to 9,000 gallons of fuel oil each year.
The Green Proving Ground program leverages GSA’s real estate portfolio to evaluate emerging sustainable building technologies. The program aims to drive innovation in environmental performance in federal buildings and help lead market transformation through deployment of new technologies.
Find this report, two other new reports, other previously released reports and more information about GSA’s Green Proving Ground program at www.gsa.gov/GPG.
Related Stories
Codes and Standards | Sep 28, 2017
New tool compares HVAC system efficiency
IAPMO and Hydronics Industry Alliance unveil BEST to evaluate systems in early design phase.
HVAC | Sep 7, 2017
See the Latest HVACR Innovations, Products and Technologies at the Highly-Anticipated 2018 AHR Expo in Chicago
Showcase features hundreds of products and technologies for contractors, engineers, facility managers, OEMs and other HVACR industry professionals.
Sponsored | HVAC | May 15, 2017
Student residences get the PEX hydronic treatment
The Bricker Residence required a retrofit that was designed to have fan coil units located in each of the suites, and a new piping system to supply heating and cooling water in a two-pipe switch-over system.
Sponsored | HVAC | Apr 6, 2017
Viega ProPress shines in SolarCity construction
Buffalo will be the first city to produce the first-ever true solar roof – a roofing product with solar panels built in.
Religious Facilities | Mar 9, 2017
St. Patrick’s Cathedral in NYC launches new geothermal plant
The plant is the first in a series of upgrades planned for 2017 to adapt one of New York’s earliest landmarks.
Sponsored | HVAC | Oct 31, 2016
The Chicago Motor Club building gets a new LG HVAC system
It was imperative that the renovated building maintain its original appearance as a tribute to car culture – a vital facet of historic Chicagoan life.
HVAC | Mar 18, 2016
ASHRAE funds efficiency projects including aerial vehicle for energy audits
Undergraduates at 24 universities awarded grants.
Building Materials | Jan 25, 2016
Johnson Controls to merge with Tyco International
The $20 billion deal is the latest corporate inversion maneuver.
HVAC | Dec 29, 2015
Energy Dept. announces historic new commercial air conditioner and furnace standards
Businesses will save $167 billion over life of products.