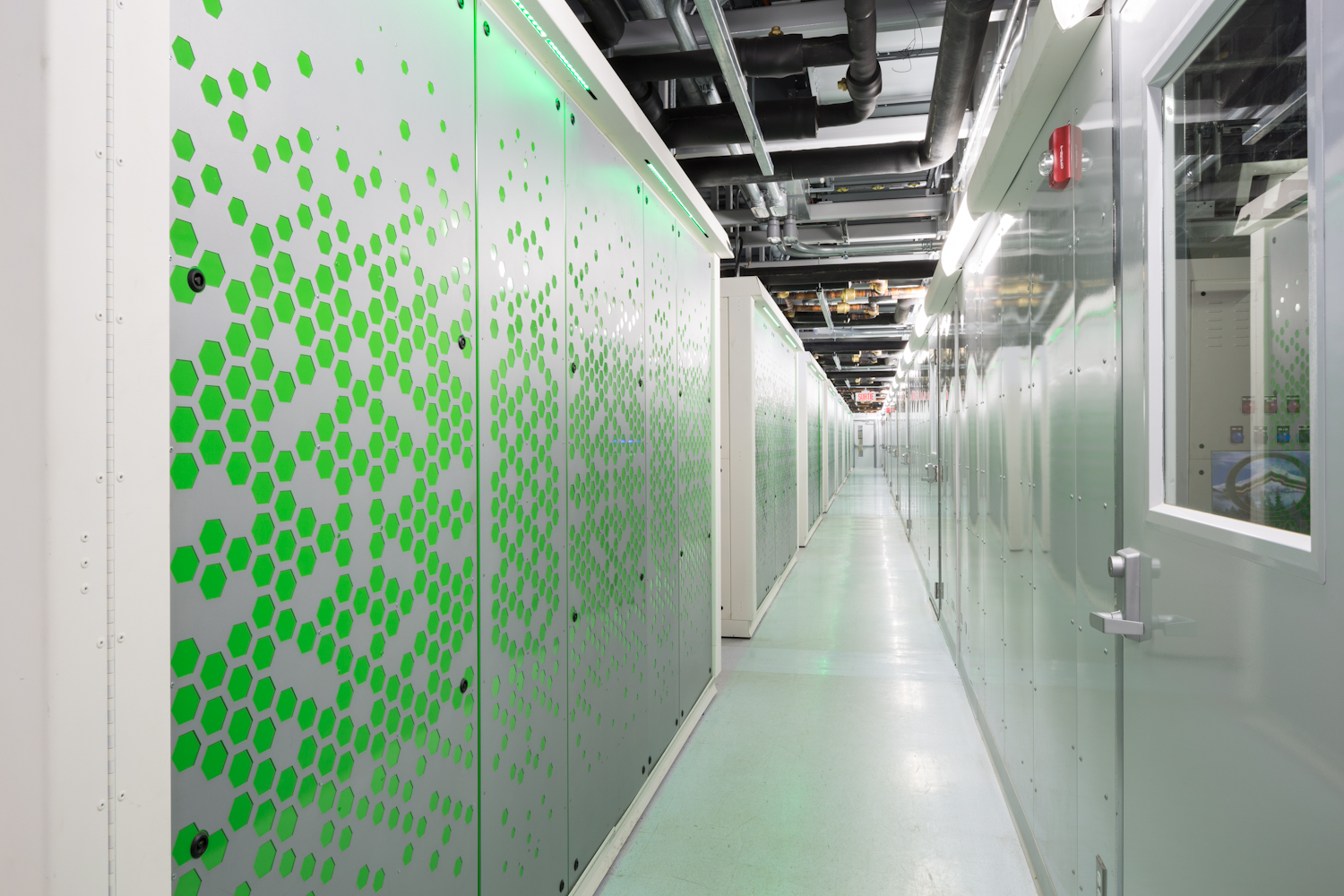
If all goes as planned, Canada’s third-largest telecommunications company, Telus, next month will open what has been billed as one of the most energy-efficient data centers in the world. The $75 million, 215,000-sf facility, located in Kamloops, B.C., is projected to use up to 80% less power and 86% less water than a typical data center of its size. Its peak power utilization effectiveness (PUE)—the ratio of total energy used by the data center to the energy delivered to the computing equipment—is estimated at a minuscule 1.15.
The “secret sauce,” according to the facility’s contractor, Skanska, is a patented cooling technology, called eOPTI-TRAX, that replaces the traditional chiller plant. Together with its modular data center partner, Inertech, Skanska supplied the distributed, closed-loop system, which greatly expands the temperature range at which a facility can utilize outdoor air for “free” cooling. Telus’ Kamloops Internet Data Centre, for instance, will be able to use 100% outside air for cooling when temperatures are as high as 85°F—a huge improvement over the 45°F threshold typical with traditional chiller plant setups.
In lieu of underfloor air distribution, which requires numerous fans to push cold air toward the racks to cool the servers, the eOPTI-TRAX approach uses a contained hot- and cold-aisle design with optimized air circulation in the server aisles and liquid refrigerant coils lining the inside of the rear walls of the server rack to draw and absorb the heat. The scheme reduces hot-aisle temperatures from 160°F to just 75°F, according to Skanska.
The Telus project is among a handful of recently completed data centers that are raising the bar for energy and water efficiency. Building Teams are employing a range of creative solutions—from evaporative cooling to novel hot/cold-aisle configurations to heat recovery schemes—in an effort to slash energy and water demand. In addition, a growing number of data center developers are building facilities in cool, dry locations to take advantage of 100% outdoor air for cooling.
The National Center for Atmospheric Research’s new $70 million, 153,000-sf Wyoming Supercomputing Center in Cheyenne, for instance, uses the cool, dry air in combination with evaporative cooling towers to chill the supercomputers 96% of the year. Even when factoring the facility’s administrative offices, the building’s ultimate PUE is projected to be 1.10 or less, placing it in the top 1% of energy-efficient data centers worldwide. Where possible, the data center reuses waste heat for conditioning the office spaces and for melting snow and ice on the walkways and loading docks. Chilled beams provide efficient cooling in the administrative areas.
Facebook’s new model for data centers
While a temperate climate can be hugely advantageous for data center owners, it’s not a requirement for achieving a low PUE and WUE (water usage effectiveness), say data center design experts. Building Teams and technology providers continue to develop schemes that can operate efficiently at higher temperatures and relative humidity levels.
Take Facebook’s data center in Forest City, N.C., for example. Unlike the company’s other data center locations in Prineville, Ore., and Lulea, Sweden, the Forest City facility sits in a warm, humid climate—yet it has been able to achieve a PUE on par with the other installations, at 1.07, according to Daniel Lee, PE, Data Center Design Engineer at Facebook.
“Last summer, we had the second-hottest summer on record in Forest City and we didn’t have to use our DX system (direct expansion coils) system,” says Lee. “Although it was hot, with highs of 103°F, the relative humidity was low enough so that we could use the water (evaporative cooling) to cool the space.”
The trick, says Lee, is a simplified, holistic approach to data center design that optimizes not only the building mechanical systems, but also the computer hardware (servers and racks) and software applications—all with an eye toward reliability and energy efficiency. Traditional mechanical components—UFAD, chillers, cooling towers, etc.—are replaced with a highly efficient evaporative cooling scheme that uses 100% airside economization and hot-aisle containment. An open-rack server setup with exposed motherboards greatly reduces the energy required to cool the equipment. The result is a facility with fewer moving parts to break down that can operate efficiently at interior temperatures in excess of 85°F.
Facebook made waves in 2011 when it made public its design specs for its first in-house data center, in Prineville, under a program called the Open Compute Project. Modeled after open-source software communities, the program relies on crowd sourcing to share and improve on Facebook’s base data center scheme.
“We give the design away; you can take it and build it yourself,” says Chuck Goolsbee, Datacenter Site Manager at Facebook’s Prineville location. “All the components are there to build it in sort of a LEGO-like manner, from the building itself down to the servers.”
Facebook expects big things from the Open Compute Project. Many of the core component suppliers are involved—including Dell, Hewlett-Packard, Intel, and AMD—and thousands of data center experts have participated in engineering workshops and have given feedback to the group.
“Fifteen years from now, the DNA from Open Compute will be in every data center in the world,” says Goolsbee.
Related Stories
AEC Tech Innovation | Oct 7, 2021
How tech informs design: A conversation with Mancini's Christian Giordano
Mancini's growth strategy includes developing tech tools that help clients appreciate its work.
Digital Twin | May 24, 2021
Digital twin’s value propositions for the built environment, explained
Ernst & Young’s white paper makes its cases for the technology’s myriad benefits.
AEC Tech | Mar 4, 2021
The Weekly show, March 4, 2021: Bringing AI to the masses, and Central Station Memphis hotel
This week on The Weekly show, BD+C editors speak with AEC industry leaders about the award-winning Central Station Memphis hotel reconstruction project, and how Autodesk aims to bring generative design and AI tools to the AEC masses.
AEC Tech | Jan 28, 2021
The Weekly show, Jan 28, 2021: Generative design tools for feasibility studies, and landscape design trends in the built environment
This week on The Weekly show, BD+C editors speak with AEC industry leaders from Studio-MLA and TestFit about landscape design trends in the built environment, and how AEC teams and real estate developers can improve real estate feasibility studies with real-time generative design.
AEC Tech | Nov 12, 2020
The Weekly show: Nvidia's Omniverse, AI for construction scheduling, COVID-19 signage
BD+C editors speak with experts from ALICE Technologies, Build Group, Hastings Architecture, Nvidia, and Woods Bagot on the November 12 episode of "The Weekly." The episode is available for viewing on demand.
Smart Buildings | Oct 26, 2020
World’s first smart building assessment and rating program released
The SPIRE Smart Building Program will help building owners and operators make better investment decisions, improve tenant satisfaction, and increase asset value.
BIM and Information Technology | Oct 8, 2020
4 challenges of realizing BIM's value for an owner
In recent years, we have found our consulting practice engaging more and more with owners that are questioning the value of BIM and how they can make use of potentially data-rich BIM assets.
AEC Tech | Feb 5, 2020
BIM London: A glimpse of BIM discussions across the pond
Digital twin, ISO standards, blockchain, and data were the hot topics at the recent The Digital World: BIM event.
Building Technology | Mar 6, 2019
Australia’s prefab construction sector is trying to break out from its 'getting there' stage
A paper by Deloitte looks back at an origin case study. But the country has yet to develop a fully formed industry.
BIM and Information Technology | Jan 18, 2019
BIM: Sharing is caring
Sharing of and reliance on BIM data is central to the idea that BIM will lead to a more efficient, more economical, and more collaborative construction process.