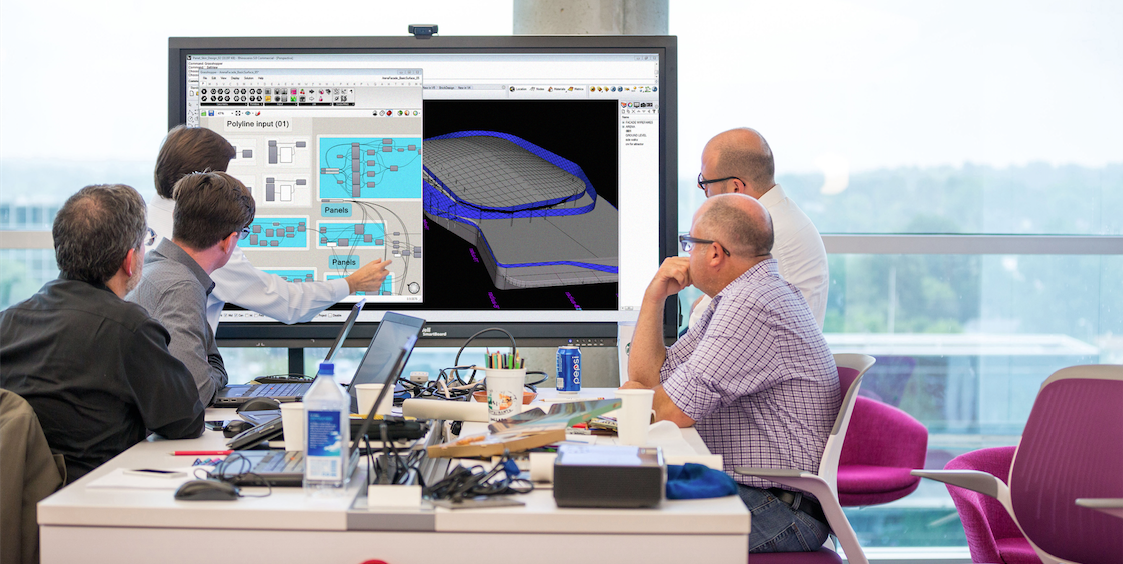
Should architects learn to code? This question was posed by computational design consultant Nathan Miller, Founder and Managing Director of Proving Ground, in a recent blog post about the rise of data-driven design. Miller’s answer: “Well, maybe.”
While Miller and other computation experts don’t expect every design professional to become Mark Zuckerberg in “The Social Network” (“Don’t interrupt him. He’s plugged in!”), there is no denying the growing importance of the utilization of data and computation in the design process. HDR, NBBJ, Populous, Thornton Tomasetti, and Woods Bagot are among the firms that are investing in talent and training to advance their CD capabilities.
ALSO SEE
6 ways smart AEC firms are using computational design methods
During his four-plus years as a CD consultant, Miller has assisted these firms and others in developing a business roadmap for breaking into data-driven design. We asked him for tips and advice on getting started. He offered the following:
1. Define the business value of computational design. Computational design is an open-ended methodology, not a class of software tools with predefined features for a specific uses.The value of computation is greatly dependent on how well an AEC organization positions the new skill sets, tools, and workflows relative to the business.
“I’m often confronted with questions akin to some variation of, ‘Can Grasshopper or Dynamo do X,’” says Miller. “The reality is quite the opposite: Computational design is about the process of creating solutions. The question is better framed as, ‘What can we create that will help us better solve X design problem?’”
It could involve developing an algorithm that can greatly increase the speed of solving repetitive design problems, or creating a tool for a project or market that can provide an advantage for a firm looking to differentiate its services in a competitive marketplace.
For CD to be meaningful to a business at scale means determining the desired outcomes, coupled with a strategic framework for developing a team capable of creating high-impact solutions, says Miller.
2. Pilot computational design services in the areas where your firm takes the most risks. AEC firms tend to be risk adverse when it comes to changing process. Factor in increasingly tighter deadlines and shrinking fees, and it can make computational design a hard sell to firm leaders.
‘Design organizations should be looking for do-it-yourself creative thinkers that have a knack for making digital tools.’
—Nathan Miller, Proving Ground
Miller says a number of his AEC clients have had success winning over firm leaders and scaling up CD operations by piloting these tools and processes in the areas of the practice where the firm traditionally takes more risks, namely project pursuits, RFPs, and design competitions.
“When you know you’re going up against strong competition and you want to take some calculated risks, those become very good entry points for computational design,” says Miller. “By going the computation route with an RFP or competition submission, it may allow the firm to explore a problem a little differently, or capture that process and fold it into the overall narrative.”
Win a few projects and light bulbs will start going off throughout the practice.
3. Hire for passion of building design, not for coding prowess. It’s much tougher to teach a game designer or software engineer about the building design process than it is to teach an architect or engineer basic coding skills. Many firms, however, are looking to the tech markets—computer science, simulation, software engineering, game development—to build their CD teams.
“Where the real moment with computational design concepts comes to bear is when you engage the opposite—give a couple of designers who are really passionate about buildings the skills to be able to code,” says Miller.
He has advised AEC clients to modify their job requisitions for entry-level designers coming out of school to include skill sets like experience with computational design software. “If you’re a firm looking to grow your CD capability, you need to change the demographic of the people applying for the position,” says Miller.
4. Invest in people, not software. Computational design software is a drop in the bucket compared to the six- and seven-figure investments firms have had to make in CAD and BIM software tools. Grasshopper is a free plug-in. Dynamo is open source. The tools are essentially free. The real investment is in finding the right people and then advancing their computation capabilities.
“As with most things that drive success in service organizations, people should be the focus of business investment for executing a successful computational design strategy,” says Miller. “Design organizations should be looking for do-it-yourself creative thinkers that have a knack for making digital tools.”
5. Apply the 70/20/10 ratio when assembling your computation-enabled design team. While no two firms are the same, Miller has discovered a sweet spot for the makeup of computation-enabled design teams: the 70/20/10 ratio. Seventy percent should have enough working knowledge to be able to “pull the levers” on pre-made computational tools; 20% should have a high comfort level with building simple tools and modifying complex project algorithms; 10% should have an advanced skill set in creating sophisticated tools and solutions.
Having a team with a range of skill sets, says Miller, will encourage broader participation, skill growth, and engagement across the organization.
Project leaders and firm management need to be active participants in the implementation process. “They don’t need to know the nuts and bolts of the tools, but they do need to understand how the project process is changing so they can give the team a platform to deliver valuable design solutions,” says Miller.
For more on computational design, read Proving Ground’s blog.
Related Stories
| May 16, 2011
Dassault Systèmes to distribute Gehry Technologies’ digital project
Dassault Systèmes and Gehry Technologies announced that Gehry Technologies’ Digital Project products will be integrated into the Dassault Systèmes’ portfolio and distributed through Dassault Systèmes. Digital Project is a suite of 3D BIM applications created by Gehry Technologies using Dassault Systèmes’ CATIA as a core modeling engine.
| May 3, 2011
Scott Simpson of KlingStubbins on how to get more value from BIM
Too few AEC professionals have developed a strategic idea of how BIM can and should re-shape professional practices and drive dramatic improvements in both creativity and production, according to Scott Simpson, FAIA, senior director of KlingStubbins. While BIM enables the exploration of design ideas quickly and in new and different ways, it can lead people to think they’re making more progress than they actually are. A simple adjustment in perspective is all it takes to put things right.
| May 2, 2011
URS acquires Apptis Holdings, a federal IT service provider
SAN FRANCISCO, CA and CHANTILLY, VA– April 28, 2011 – URS Corporation and Apptis Holdings, Inc., a leading provider of information technology and communications services to the federal government, announced that they have signed a definitive agreement under which URS will acquire Apptis.
| Apr 12, 2011
BIM Grows Up: Separating Hype from Reality in a 3D World
While BIM adoption still lags in both design and construction, some enterprising owners, architects, and contractors are unlocking the potential of this dynamic technology.
| Apr 5, 2011
Are architects falling behind on BIM?
A study by the National Building Specification arm of RIBA Enterprises showed that 43% of architects and others in the industry had still not heard of BIM, let alone started using it. It also found that of the 13% of respondents who were using BIM only a third thought they would be using it for most of their projects in a year’s time.