Experts, including those in the AEC community, who have been insisting for years that indoor air quality affects occupants’ performance and health could soon have more ammunition to back up their claims.
The Wall Street Journal reports that Washington University at St. Louis last summer initiated what will be a yearlong experiment to test whether a newly constructed building, designed with easy access to stairways, natural daylight, and other “wellness” features, improves employees’ physical well being and promotes worker collaboration. The Journal also reports that the Well Living Lab, a research facility near the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, early next year will begin clinical trials designed to assess indoor environments, with the goal of creating healthier spaces.
On October 26, Environmental Health Perspectives—a monthly journal of news and research published with support from the National Institute of Environmental Sciences (NIES), the National Institutes of Health, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services—released in advance of publication a peer-reviewed paper that details a recent study of 24 participants—architects, designers, programmers, engineers, creative marketers, and managers—who spent six full workdays in an environmentally controlled office space, blinded to test conditions.
The study population was restricted to non-sensitive persons by excluding current smokers and people with asthma, claustrophobia, or schizophrenia.
On different days, the participants were exposed to Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) conditions with high and low concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that were representative of office buildings in the U.S. Additional conditions simulated a Green building with a high outdoor air ventilation rate and artificially elevated carbon dioxide levels independent of ventilation.
The study found that, on average, the participants’ cognitive scores were 61% higher on Green building days and 101% higher on days when the air ventilation was highest (so-called Green+ days), compared to the air quality during “Conventional” building days. “These findings have wide-ranging implications because this study was designed to reflect conditions that are commonly encountered every day in many indoor environments,” the study’s authors state.
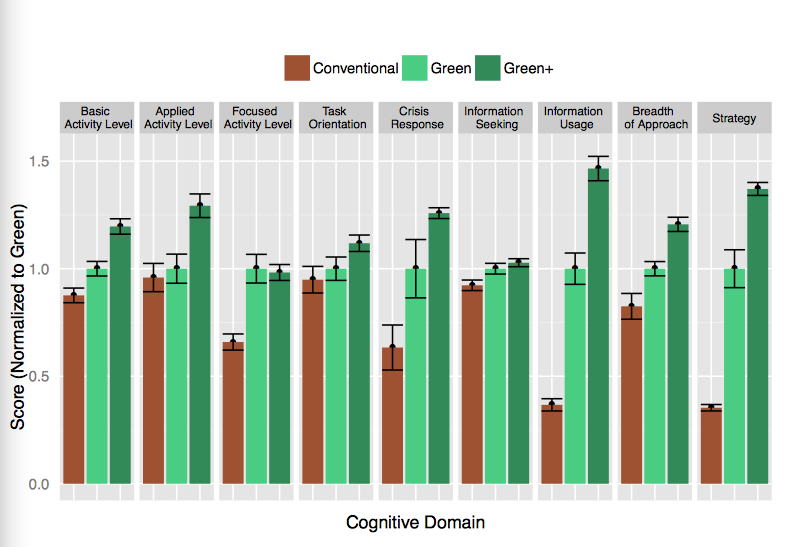 A recent study tested the cognition of 24 participants for nine activities, based on different levels of indoor air quality exposure. “Conventional” was air quality that's typical of most office buildings; Green+ indicated the highest level of air ventilation.
A recent study tested the cognition of 24 participants for nine activities, based on different levels of indoor air quality exposure. “Conventional” was air quality that's typical of most office buildings; Green+ indicated the highest level of air ventilation.
The study took place over two weeks in November 2014 at the Willis H. Carrier Total Indoor Environmental Quality Laboratory at the Syracuse Center for Excellence. The lab had two nearly identical office environments located adjacent to one another, each with 12 cubicles.
Cognitive assessment of the participants was performed daily using the Strategic Management Simulation software tool, a validated, computer-based test designed to test the effectiveness of management-level employees through assessments of higher-order decision-making.
The study found that the largest effects of conditions on cognition were seen for Crisis Response, Information Usage, and Strategy. For Crisis Response, for example, scores were 97% higher for the Green condition compared to the Conventional, and 131% higher for participants during Green+ days.
Conversely, “we found statistically significant declines in cognitive function scores when CO2 concentrations were increased to levels that are common in indoor spaces (approximately 950 ppm). In fact, this level of CO2 is considered acceptable because it would satisfy ASHRAE’s ventilation rate guideline for acceptable indoor air quality,” the authors state.
The paper, whose six authors worked under the auspices of NIES, was reviewed and approved by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Institutional Review Board. The participant group was 42% male, 58% female. One-third of the group was between the ages of 20 and 30, and 25% was between the ages of 41 and 50. Ninety-two percent of the group was Caucasian, 54% has a college degree, and 63% holds professional jobs.
Related Stories
| Nov 9, 2010
Designing a library? Don’t focus on books
How do you design a library when print books are no longer its core business? Turn them into massive study halls. That’s what designers did at the University of Amsterdam, where they transformed the existing 27,000-sf library into a study center—without any visible books. About 2,000 students visit the facility daily and encounter workspaces instead of stacks.
| Nov 2, 2010
11 Tips for Breathing New Life into Old Office Spaces
A slowdown in new construction has firms focusing on office reconstruction and interior renovations. Three experts from Hixson Architecture Engineering Interiors offer 11 tips for office renovation success. Tip #1: Check the landscaping.
| Oct 13, 2010
Editorial
The AEC industry shares a widespread obsession with the new. New is fresh. New is youthful. New is cool. But “old” or “slightly used” can be financially profitable and professionally rewarding, too.
| Oct 13, 2010
Prefab Trailblazer
The $137 million, 12-story, 500,000-sf Miami Valley Hospital cardiac center, Dayton, Ohio, is the first major hospital project in the U.S. to have made extensive use of prefabricated components in its design and construction.
| Oct 13, 2010
Modern office design accentuates skyline views
Intercontinental|Exchange, a Chicago-based financial firm, hired design/engineering firm Epstein to create a modern, new 31st-floor headquarters.
| Oct 13, 2010
Biloxi’s convention center bigger, better after Katrina
The Mississippi Coast Coliseum and Convention Center in Biloxi is once again open for business following a renovation and expansion necessitated by Hurricane Katrina.
| Oct 13, 2010
HQ renovations aim for modern look
Gerner Kronick + Valcarcel Architects’ renovations to the Commonwealth Bank of Australia’s New York City headquarters will feature a reworked reception lobby with back-painted glass, silk-screened logos, and a video wall.
| Oct 13, 2010
New health center to focus on education and awareness
Construction is getting pumped up at the new Anschutz Health and Wellness Center at the University of Colorado, Denver. The four-story, 94,000-sf building will focus on healthy lifestyles and disease prevention.
| Oct 13, 2010
Community center under way in NYC seeks LEED Platinum
A curving, 550-foot-long glass arcade dubbed the “Wall of Light” is the standout architectural and sustainable feature of the Battery Park City Community Center, a 60,000-sf complex located in a two-tower residential Lower Manhattan complex. Hanrahan Meyers Architects designed the glass arcade to act as a passive energy system, bringing natural light into all interior spaces.
| Oct 12, 2010
Holton Career and Resource Center, Durham, N.C.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards—Special Recognition. Early in the current decade, violence within the community of Northeast Central Durham, N.C., escalated to the point where school safety officers at Holton Junior High School feared for their own safety. The school eventually closed and the property sat vacant for five years.
















