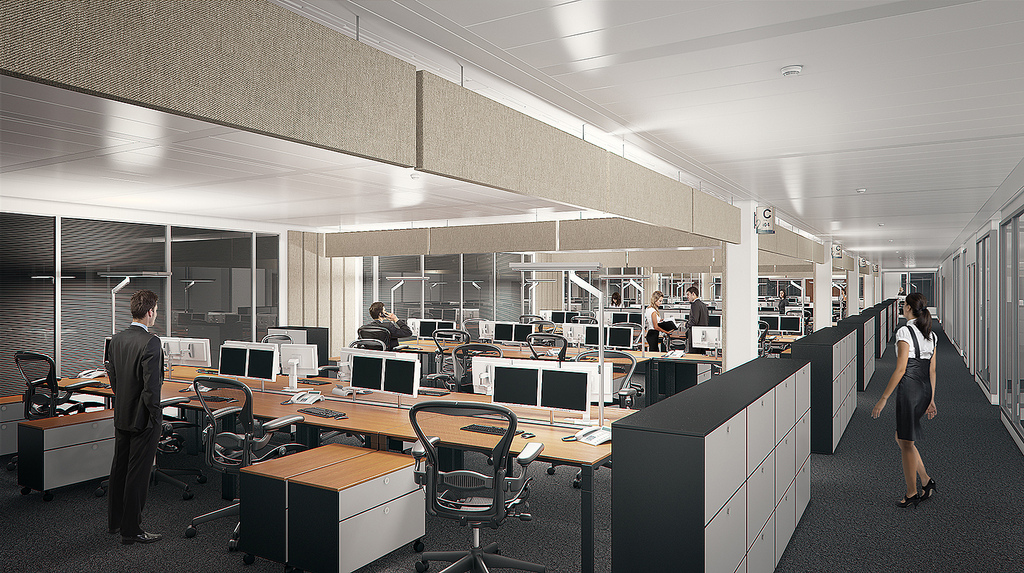
Experts, including those in the AEC community, who have been insisting for years that indoor air quality affects occupants’ performance and health could soon have more ammunition to back up their claims.
The Wall Street Journal reports that Washington University at St. Louis last summer initiated what will be a yearlong experiment to test whether a newly constructed building, designed with easy access to stairways, natural daylight, and other “wellness” features, improves employees’ physical well being and promotes worker collaboration. The Journal also reports that the Well Living Lab, a research facility near the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, early next year will begin clinical trials designed to assess indoor environments, with the goal of creating healthier spaces.
On October 26, Environmental Health Perspectives—a monthly journal of news and research published with support from the National Institute of Environmental Sciences (NIES), the National Institutes of Health, and the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services—released in advance of publication a peer-reviewed paper that details a recent study of 24 participants—architects, designers, programmers, engineers, creative marketers, and managers—who spent six full workdays in an environmentally controlled office space, blinded to test conditions.
The study population was restricted to non-sensitive persons by excluding current smokers and people with asthma, claustrophobia, or schizophrenia.
On different days, the participants were exposed to Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) conditions with high and low concentrations of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that were representative of office buildings in the U.S. Additional conditions simulated a Green building with a high outdoor air ventilation rate and artificially elevated carbon dioxide levels independent of ventilation.
The study found that, on average, the participants’ cognitive scores were 61% higher on Green building days and 101% higher on days when the air ventilation was highest (so-called Green+ days), compared to the air quality during “Conventional” building days. “These findings have wide-ranging implications because this study was designed to reflect conditions that are commonly encountered every day in many indoor environments,” the study’s authors state.
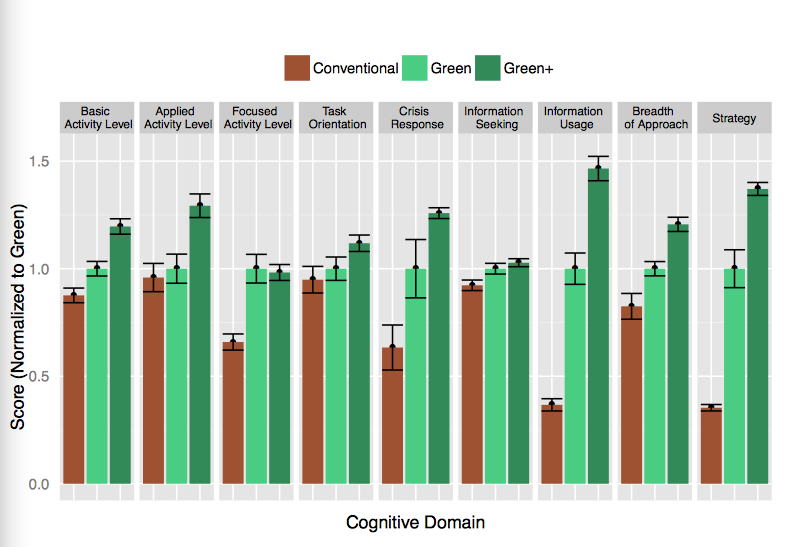 A recent study tested the cognition of 24 participants for nine activities, based on different levels of indoor air quality exposure. “Conventional” was air quality that's typical of most office buildings; Green+ indicated the highest level of air ventilation.
A recent study tested the cognition of 24 participants for nine activities, based on different levels of indoor air quality exposure. “Conventional” was air quality that's typical of most office buildings; Green+ indicated the highest level of air ventilation.
The study took place over two weeks in November 2014 at the Willis H. Carrier Total Indoor Environmental Quality Laboratory at the Syracuse Center for Excellence. The lab had two nearly identical office environments located adjacent to one another, each with 12 cubicles.
Cognitive assessment of the participants was performed daily using the Strategic Management Simulation software tool, a validated, computer-based test designed to test the effectiveness of management-level employees through assessments of higher-order decision-making.
The study found that the largest effects of conditions on cognition were seen for Crisis Response, Information Usage, and Strategy. For Crisis Response, for example, scores were 97% higher for the Green condition compared to the Conventional, and 131% higher for participants during Green+ days.
Conversely, “we found statistically significant declines in cognitive function scores when CO2 concentrations were increased to levels that are common in indoor spaces (approximately 950 ppm). In fact, this level of CO2 is considered acceptable because it would satisfy ASHRAE’s ventilation rate guideline for acceptable indoor air quality,” the authors state.
The paper, whose six authors worked under the auspices of NIES, was reviewed and approved by the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health Institutional Review Board. The participant group was 42% male, 58% female. One-third of the group was between the ages of 20 and 30, and 25% was between the ages of 41 and 50. Ninety-two percent of the group was Caucasian, 54% has a college degree, and 63% holds professional jobs.
Related Stories
| May 24, 2012
2012 Reconstruction Awards Entry Form
Download a PDF of the Entry Form at the bottom of this page.
| May 23, 2012
Summit Design+Build selected as GC for Chicago restaurant
Little Goat will truly be a multifunctional space. Construction plans include stripping the 10,000 sq. ft. building down to the bare structure everywhere, the installation of a new custom elevator and adding square footage at the second floor with an addition.
| Apr 27, 2012
Hampton Bays Middle School winner of the first National Green Ribbon Schools Program
School was the first LEED-certified public school in the state of New York.
| Apr 6, 2012
Flat tower green building concept the un-skycraper
A team of French designers unveil the “Flat Tower” design, a second place winner in the 2011 eVolo skyscraper competition.
| Mar 16, 2012
Temporary fix to CityCenter's Harmon would cost $2 million, contractor says
By contrast, CityCenter half-owner and developer MGM Resorts International determined last year that the Harmon would collapse in a strong quake and can't be fixed in an economical way. It favors implosion at a cost of $30 million.
| Mar 1, 2012
AIA: A clear difference, new developments in load-bearing glass
Earn 1.0 AIA/CES learning units by studying this article and successfully completing the online exam.
| Jan 3, 2012
New Chicago hospital prepared for pandemic, CBR terror threat
At a cost of $654 million, the 14-story, 830,000-sf medical center, designed by a Perkins+Will team led by design principal Ralph Johnson, FAIA, LEED AP, is distinguished in its ability to handle disasters.
| Dec 27, 2011
Ground broken for adaptive reuse project
Located on the Garden State Parkway, the master-planned project initially includes the conversion of a 114-year-old, 365,000-square-foot, six-story warehouse building into 361 loft-style apartments, and the creation of a three-level parking facility.
| Dec 20, 2011
Aragon Construction leading build-out of foursquare office
The modern, minimalist build-out will have elements of the foursquare “badges” in different aspects of the space, using glass, steel, and vibrantly painted gypsum board.
| Dec 16, 2011
Stalco Construction converts Babylon, N.Y. Town Hall into history museum
The project converted the landmark structure listed on the National Register of Historic Places into the Town of Babylon History Museum at Old Town Hall.















