Ken Soble Tower, an affordable housing high-rise for seniors in Hamilton, Ont., is now arguably the world’s largest residential building retrofitted to the Passive House standard.
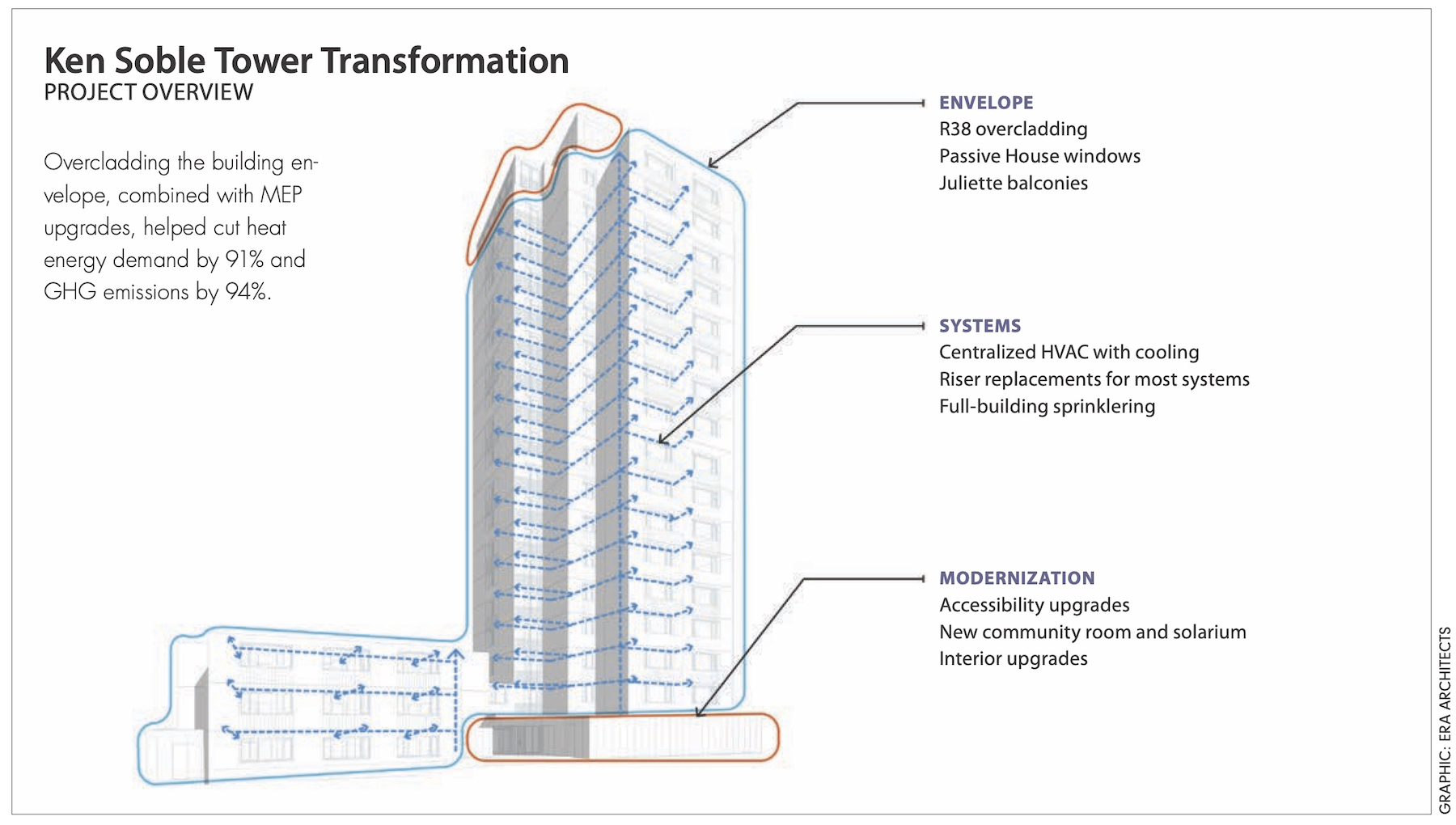
Led by ERA Architects and PCL Construction, the project team slashed the 80,000-sf, 18-story building’s greenhouse gas emissions by 94% and its heating energy demand by 91% en route to achieving EnerPHit certification. The total energy needed to heat and cool one of its 146 units is now equivalent to that needed to power three 100-watt light bulbs.
Built in 1967 as part of the “North End Renewal” of West Harbour, an industrial neighborhood on Lake Ontario, the tower and an accompanying three-story walkup provided one-bedroom and bachelor apartments for families and single workingmen.
At the time, the complex, named after the founder of a local radio station and a local TV station, was considered a showcase property in the portfolio of CityHousing Hamilton, the municipal housing authority.
By 2012, however, the property was showing its age. The elevators constantly failed; so, too, the heating and cooling system. Mold, peeling paint, and water damage were apparent everywhere.
Worst of all: the pest problem. Forty-two percent of maintenance calls were for cockroaches, rodents, and bedbugs. The bedbug infestation was so bad the housing agency had to move whole floors of tenants to temporary housing on the 16th floor while crews tried to kill the critters. The bedbugs kept coming back.
The housing agency started relocating tenants. In less than four years, two-thirds of the apartments in Ken Soble Tower were vacant, despite a citywide waitlist of 6,000 families seeking affordable housing.
In 2015, CityHousing Hamilton, which manages 7,000 apartments in 1,265 properties, for 13,000 residents, surveyed the tower’s remaining residents about the future of the property; 83% responded. Their message to the agency: “Keep Ken Soble Tower.” A year later, the financial consulting firm Deloitte, acting on behalf of CityHousing Hamilton, studied the options—sell, demolish and rebuild, perform basic capital repairs, or refurbish—and came to the same conclusion: renovate.
The housing agency gave the go-ahead to completely retrofit Ken Soble Tower, a project that became part of Canada’s National Housing Strategy to modernize and decarbonize older affordable apartments. The project was folded into the Tower Renewal Partnership, an initiative by the nonprofit Centre for Urban Growth and Renewal (cugr.ca) to transform Southern Ontario’s stock of post-war apartment towers into more healthy, resilient, and complete communities.
A FIVE-PRONGED APPROACH TO RESTORATION
The renewal effort had five objectives:
- Modernize all 146 dwelling units.
- Attain EnerPHit certification, based on 2050 temperature projections, to cut GHG emissions by 94% and energy intensity by 70%.
- Allow for aging-in-place, by creating 31 barrier-free residences and reconfiguring elevators, doorways, and residential garbage areas to allow for barrier-free movement throughout the building.
- Address the housing authority’s 30-year capital repair program.
- Maintain “deep affordability,” through Hamilton’s Rent Geared to Income subsidy.
The building envelope consisted of composite masonry walls with minimal interior insulation and vapor control layers; it was sorely deteriorated. The design team’s first thought was to build an entire wall assembly outside the brick. Instead, the team overcladded the structure: first, with a liquid-applied air barrier; followed by a DuROCK PUCCS NC noncombustible rainscreen EIFS system, which incorporated 50,000 sf of a six-inch-thick layer of Rockwool stone wool insulation into the façade; finally, a stucco finish. Another four inches of mineral wool was added to the interior.
The EIFS system helped the project realize the R-38 effectiveness required to achieve EnerPHit certification. The retrofit resulted in a 94% reduction in GHG emissions and a 91% cut in heating energy demand. In practical terms, it meant that the building would stay warm in winter for up to two days and below dangerous heat levels in summer for up to four days.
Concrete slab balconies were replaced with juliettes to meet maintenance and accessibility requirements and eliminate thermal bridging. Easily operable triple-glazed windows and doors were installed to encourage natural ventilation. The roof membranes and below-grade waterproofing were replaced with fluid-applied products and upgraded with up to 16 inches of insulation.
Mechanical systems were completely overhauled with new central systems that provide tempered fresh air to each suite from rooftop energy recovery ventilators (ERVs), and individual control with in-suite variable-air volume (VAV) dampers with reheat. Common areas are served by smaller ERVs that are activated by occupancy sensors. A sophisticated building automation system will measure and verify that all building systems are functioning as designed.
The project came in at $34 million ($233,000/unit), 70% of which was for base building renewal, 30% for low-energy initiatives.
COMPREHENSIVE AIR TIGHTNESS TESTING
To achieve EnerPHit certification from Passive House Canada, the team developed a comprehensive air tightness testing and quality management program, led by PCL’s in-house building envelope engineering and construction team. Final operational whole building air tightness tests came in at 0.235 air changes/hr at 50 pa, beating the target by more than 50%.
One novel effort was that all building trades’ foremen and supervisors participated in a Passive House trades training session, with a focus on airtightness and reducing thermal bridging.
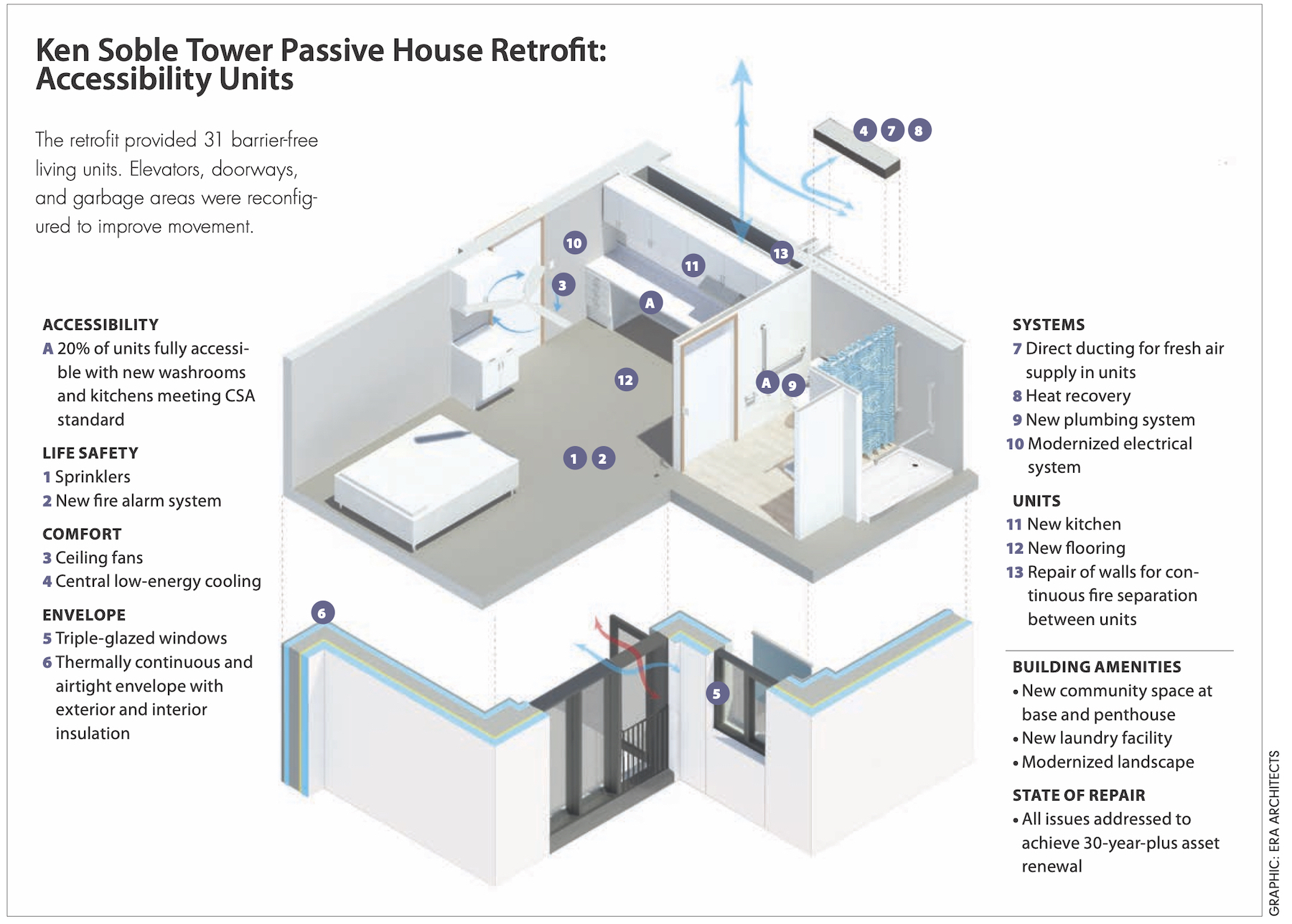
“Social sustainability” also played a part in the retrofit program. A dingy laundry room on the 18th floor was turned into a solarium, with views of the harbor. High-contrast wayfinding and bright color palettes were added to support community cohesion. Higher delivery of fresh air directly to units and the selection of low-VOC interior finishes greatly improved indoor air quality.
Adding to its distinctions, the Ken Soble Tower will become a teaching laboratory. CityHousing Hamilton, the University of Toronto, ERA Architects, and PCL Construction will, over the next two years, measure the impacts of the building on its residents and the surrounding environment, including building performance, occupant health and safety, and economic benefit.
PROJECT TEAM | KEN SOBLE TOWER
Owner: CityHousing Hamilton
Lead Architect/Interiors/Landscape Design: ERA Architects
Structural Engineer/Building Envelope Consultant: Entuitive
Mechanical Engineer: Reinbold Engineering Group
Electrical Engineer: Nemetz (S/A) & Associates
Passive House Consultants: JMV Consulting; Transsolar
Passive House Certifier: Herz & Lang GmbH
Building Envelope Testing: Engineering Link
Commissioning Consultant: CFMS Consulting Inc.
Elevators: Soberman Engineering
Building Code Consultant: LMDG Security/Telecoms Zerobit
Construction Consultant: SCR Consulting
Construction Manager: PCL Construction
Related Stories
| Nov 3, 2010
Rotating atriums give Riyadh’s first Hilton an unusual twist
Goettsch Partners, in collaboration with Omrania & Associates (architect of record) and David Wrenn Interiors (interior designer), is serving as design architect for the five-star, 900-key Hilton Riyadh.
| Nov 1, 2010
Sustainable, mixed-income housing to revitalize community
The $41 million Arlington Grove mixed-use development in St. Louis is viewed as a major step in revitalizing the community. Developed by McCormack Baron Salazar with KAI Design & Build (architect, MEP, GC), the project will add 112 new and renovated mixed-income rental units (market rate, low-income, and public housing) totaling 162,000 sf, plus 5,000 sf of commercial/retail space.
| Nov 1, 2010
Vancouver’s former Olympic Village shoots for Gold
The first tenants of the Millennium Water development in Vancouver, B.C., were Olympic athletes competing in the 2010 Winter Games. Now the former Olympic Village, located on a 17-acre brownfield site, is being transformed into a residential neighborhood targeting LEED ND Gold. The buildings are expected to consume 30-70% less energy than comparable structures.
| Oct 13, 2010
Apartment complex will offer affordable green housing
Urban Housing Communities, KTGY Group, and the City of Big Bear Lake (Calif.) Improvement Agency are collaborating on The Crossings at Big Bear Lake, the first apartment complex in the city to offer residents affordable, eco-friendly homes. KTGY designed 28 two-bedroom, two-story townhomes and 14 three-bedroom, single-story flats, averaging 1,100 sf each.
| Oct 13, 2010
Residences bring students, faculty together in the Middle East
A new residence complex is in design for United Arab Emirates University in Al Ain, UAE, near Abu Dhabi. Plans for the 120-acre mixed-use development include 710 clustered townhomes and apartments for students and faculty and common areas for community activities.
| Oct 13, 2010
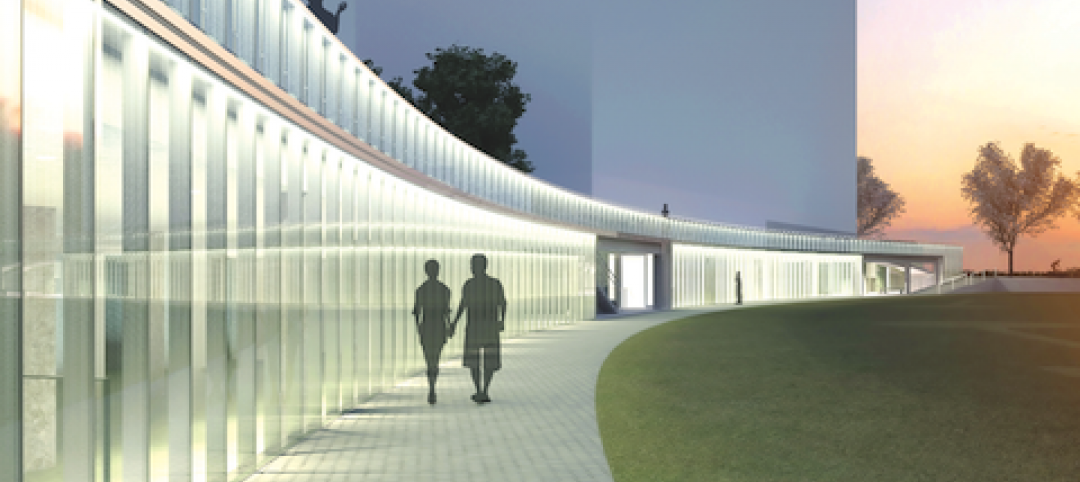
Community center under way in NYC seeks LEED Platinum
A curving, 550-foot-long glass arcade dubbed the “Wall of Light” is the standout architectural and sustainable feature of the Battery Park City Community Center, a 60,000-sf complex located in a two-tower residential Lower Manhattan complex. Hanrahan Meyers Architects designed the glass arcade to act as a passive energy system, bringing natural light into all interior spaces.
| Oct 12, 2010
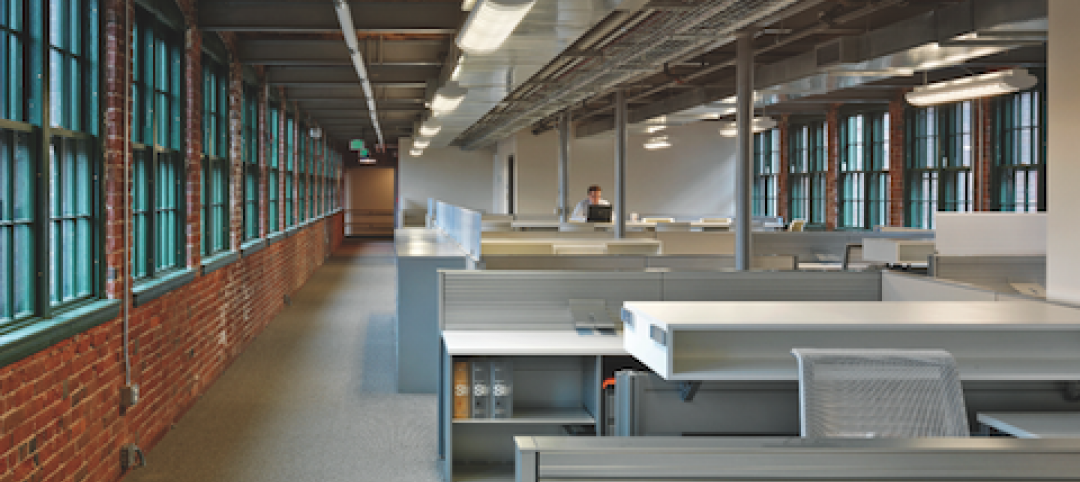
The Watch Factory, Waltham, Mass.
27th Annual Reconstruction Awards — Gold Award. When the Boston Watch Company opened its factory in 1854 on the banks of the Charles River in Waltham, Mass., the area was far enough away from the dust, dirt, and grime of Boston to safely assemble delicate watch parts.
| Sep 13, 2010
Richmond living/learning complex targets LEED Silver
The 162,000-sf living/learning complex includes a residence hall with 122 units for 459 students with a study center on the ground level and communal and study spaces on each of the residential levels. The project is targeting LEED Silver.
| Sep 13, 2010
Committed to the Core
How a forward-looking city government, a growth-minded university, a developer with vision, and a determined Building Team are breathing life into downtown Phoenix.















