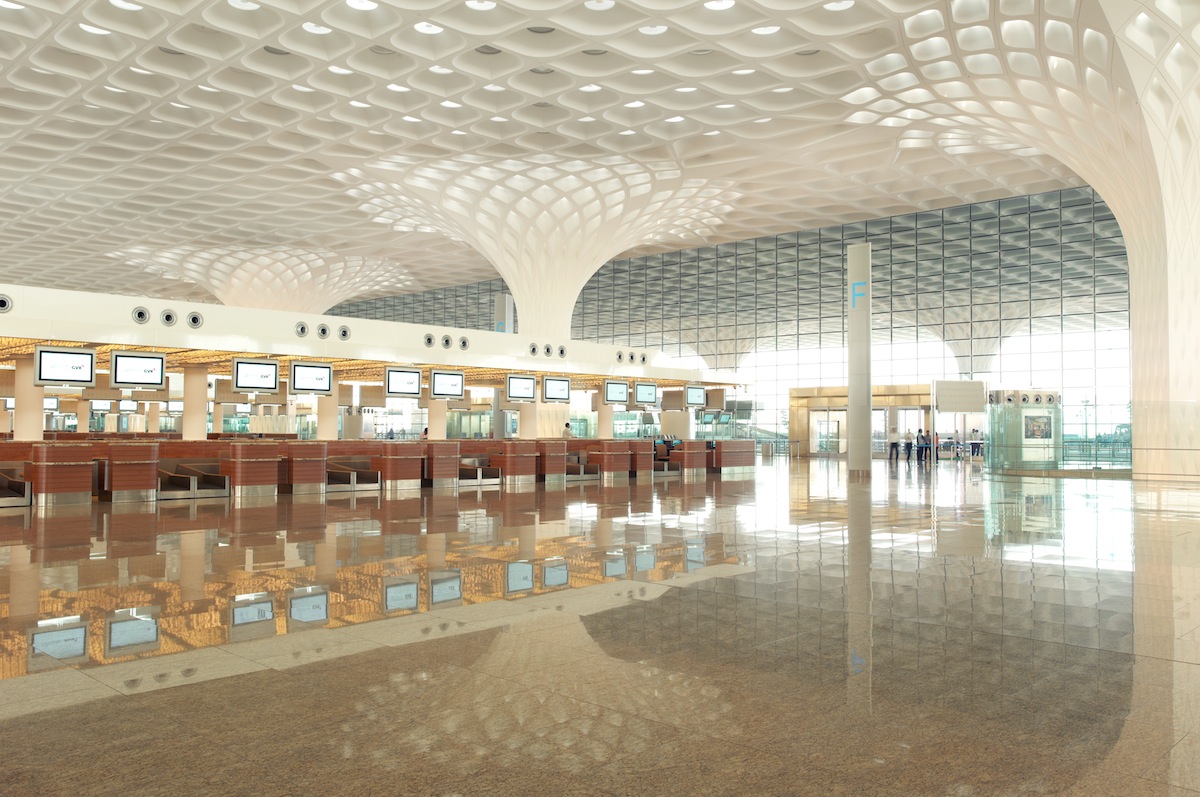
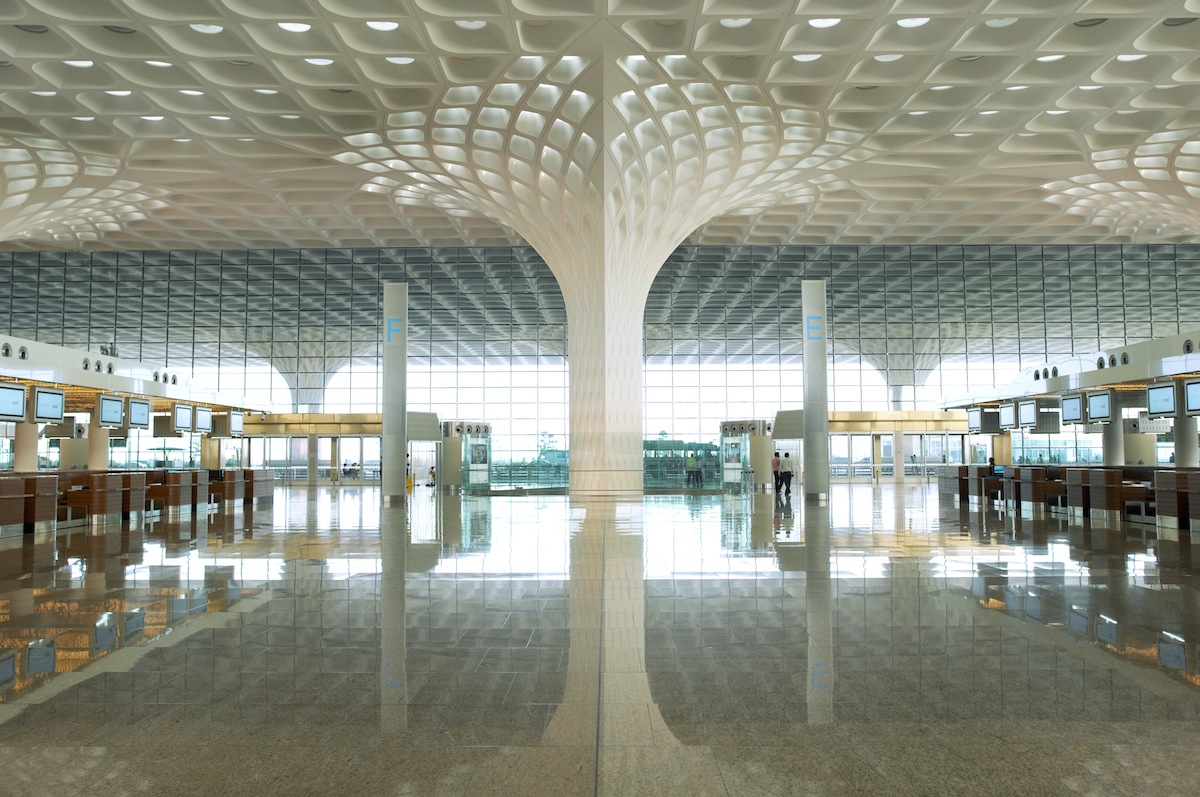
A little over a month ago, Terminal 2 of Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport was opened in Mumbai. Designed by Skidmore, Owings & Merrill (SOM), the new terminal added 4.4 million sf to accomodate 40 million passengers per year.
In a press release, Mr. G V Sanjay Reddy, the Managing Director of GVK Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd. (MIAL), said that “the new Terminal 2 at CSIA is a monument to the beautiful spirit of Mumbai and its people. This terminal will make CSIA a gateway to the city of Mumbai and India with international and domestic passengers.”
The terminal merges new technology and traditional regional architecture, notably in the fractal roof canopy that runs throughout the terminal. Skylights in the entrance hall will cut energy usage by 23 percent, and responsive controls will balance external and internal light levels in order to save the maximum amount of energy.
The Building Team included:
Owner: GVK, Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
Architect, structural engineer, MEP engineer: Skidmore, Owings & Merrill
Architect and engineer of record: Larsen & Toubro Limited
Lighting design: Brandston Partnership Inc.
Acoustics: Cerami & Associates
Communication, IT, Security & Special Systems: Mulvey & Banani
Signage & Wayfinding: Pentagram & Entro Communication
Baggage Handling: BNP Associates
Vertical Transportation: Van Deusen & Associates
Cultural Design Collaboration: Abu Jani - Sandeep Khosla
Here is SOM's press release on the new terminal:
Ten years ago, Mumbai’s Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport welcomed six million passengers per year through its gates; today it serves nearly five times that number. With the city’s emergence as India’s financial capital and the country’s rapidly expanding and economically mobile middle class, the existing airport infrastructure proved unable to support the growing volume of domestic and global traffic, resulting in frequent delays.
By orchestrating the complex web of passengers and planes into a design that feels intuitive and responds to the region’s rocketing growth, the new Terminal 2 asserts the airport’s place as a preeminent gateway to India.

The columns are meant to invoke traditional regional architecture. Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport Terminal 2 adds 4.4 million square feet of new space to accommodate 40 million passengers per year, operating 24 hours a day. The terminal combines international and domestic passenger services under one roof, optimizing terminal operations and reducing passenger walking distances. Inspired by the form of traditional Indian pavilions, the new four-story terminal stacks a grand “headhouse,” or central processing podium, on top of highly adaptable and modular concourses below. Rather than compartmentalizing terminal functions, all concourses radiate outwards from a central processing core and are therefore easily reconfigured to “swing” between serving domestic flights or international flights.
But just as the terminal celebrates a new global, high-tech identity for Mumbai, the structure is imbued with responses to the local setting, history, and culture. Gracious curbside drop-off zones designed for large parties of accompanying well-wishers accommodate traditional Indian arrival and departure ceremonies.
Regional patterns and textures are subtly integrated into the terminal’s architecture at all scales. From the articulated coffered treatment on the headhouse columns and roof surfaces to the intricate jali window screens that filter dappled light into the concourses, Terminal 2 demonstrates the potential for a modern airport to view tradition anew.
The prominent location of the airport within the city of Mumbai bestows it with a strong presence within a portion of the city that is experiencing rapid growth and redevelopment. Terminal 2 is a significant part of this renaissance as an infrastructural anchor for the neighborhood, and as a landmark within the surrounding community.
By integrating into the existing transportation fabric and by furthering connectivity through the simultaneous development of a new road network to service the airport, the terminal helps knit together the historic heart of Mumbai to the south with the city’s burgeoning peripheries to the east and north. Plans are also in place for the construction of an underground metro station at the terminal’s entrance, providing further connectivity to the growing city.
A Gateway to India
All international and domestic passengers enter the terminal headhouse on the fourth floor, accessed from a sweeping elevated road. At the entrance, the lanes split, making room for wide drop-off curbs with ample space for departure rituals. From the moment of arrival, the terminal embraces travelers. Above, the headhouse roof extends to cover the entire arrivals roadway, protecting passengers and their guests from Mumbai’s heat and unpredictable monsoon weather.
A 50-foot-tall glass cable-stayed wall—the longest in the world—opens to the soaring space of the check-in hall. The transparent façade also allows accompanying well-wishers, who must remain outside of the terminal due to Indian aviation regulations, to watch as their friends and family depart.
Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
Once inside, travelers enter a warm, light-filled chamber, sheltered underneath a long-span roof supported by an array of multi-story columns. The monumental spaces created beneath the 30 mushrooming columns call to mind the airy pavilions and interior courtyards of traditional regional architecture. Small disks of colorful glass recessed within the canopy’s coffers speckle the hall below with light. The constellation of colors makes reference to the peacock, the national bird of India, and the symbol of the airport.
The check-in hall leads to a retail hub—a common space that allows passengers to shop, eat, and watch planes take off though expansive, floor-to-ceiling windows. Centrally located at the junction of the concourses and the terminal core, these commercial plazas provide a focal point of activity in close proximity to the gates.
Within these spaces and throughout the concourses, culturally referential fixtures and details, such as custom chandeliers inspired by the lotus flower and traditional mirror mosaic work created by local artists, ground the traveler to a community and culture beyond the airport. Regional artwork and artifacts are displayed on a central, multi-story Art Wall, illuminated by skylights above. The prevalence of local art and culture, coupled with the use of warm colors and elegant accents, elevates the ambience of terminal beyond the typical, often unimaginative airport experience.
Although the terminal is four stories, interconnecting light slots and multi-story light wells ensure that light penetrates into the lower floors of the building, acting as a constant reminder of the surrounding city and landscape. At dusk, illuminated from within, the terminal glows like a sculpted chandelier.
A Flexible Footprint
The construction site of the new terminal building was located in close proximity to the existing terminal which had to remain fully operational during construction. This site requirement inspired the elongated X-shape plan of the terminal, which could both mold around existing structures and incorporate modular designs to accommodate rapid and phased construction.
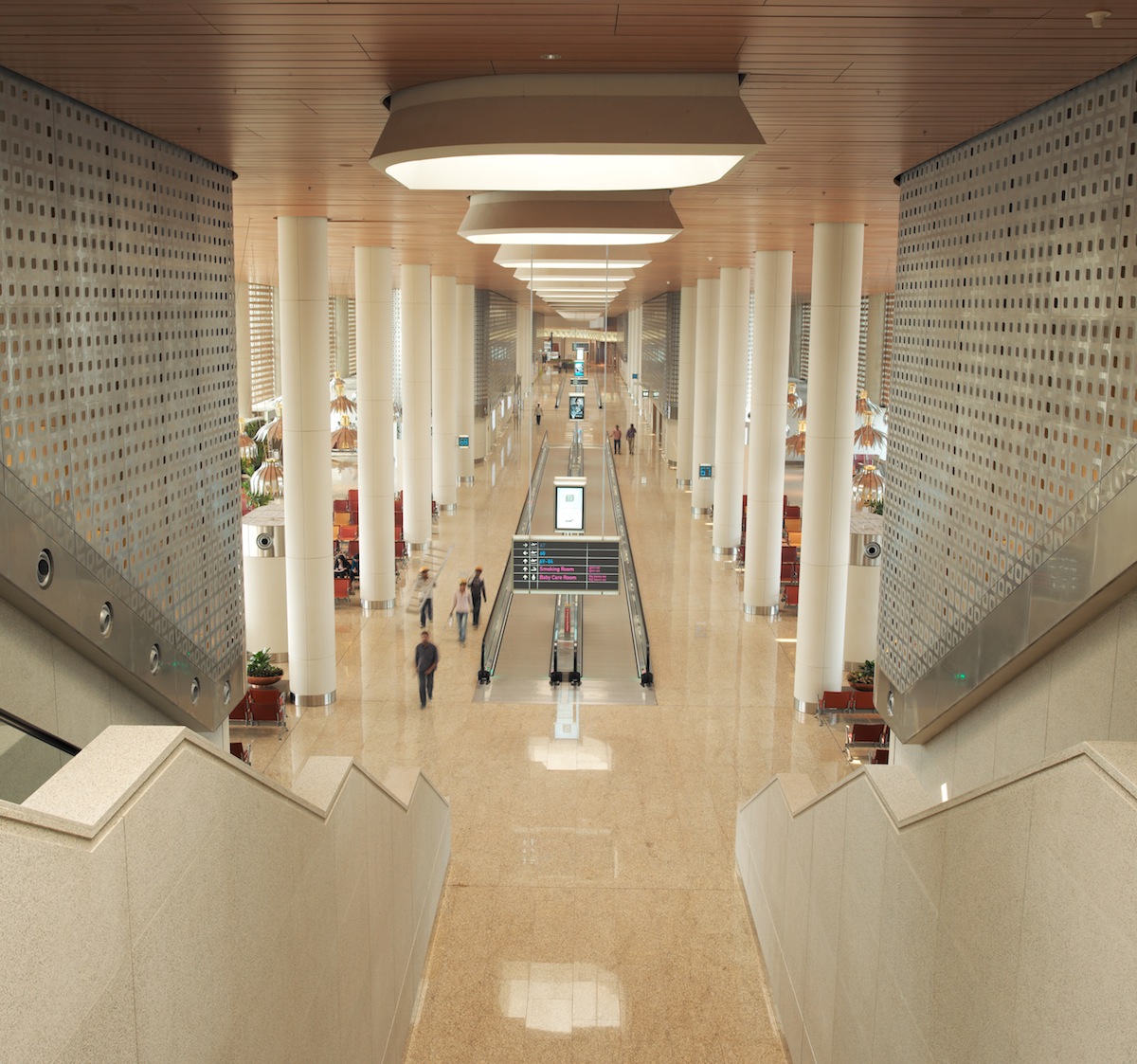

Terminal 2's perforated metal panels on curtain walls filter low sun angles in order to make spaces more comfortable for passengers during the daytime. Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
This innovative form also allows for the consolidation of important passenger processing, baggage handling, and retail/dining functions at the center of the terminal. On each floor, radiating piers permit the shortest possible walking distances from the center of the terminal to boarding areas, while also maximizing the terminal’s perimeter for aircraft gates.
The terminal’s roof—one of the largest in the world without an expansion joint—ensures further terminal flexibility. The long-span capabilities of the steel truss structure allow for the spacing of the thirty 40-meter columns to be far enough apart to not only give a feeling of openness to the large processing areas below but also to allow for maximum flexibility in the arrangement of ticket counters and other necessary processing facilities.
A Hub of Energy Efficiency
Terminal 2 uses a high-performance glazing system with a custom frit pattern to achieve optimal thermal performance and mitigate glare. Perforated metal panels on the terminal’s curtain wall filter the low western and eastern sun angles, creating a comfortable day-lit space for waiting passengers, and responsive daylight controls balance outdoor and indoor light levels for optimal energy savings. Strategically-placed skylights throughout the check-in hall will reduce the terminal’s energy usage by 23%.
At Terminal 2, modern materials and technologies are used to powerful effect. But while cutting-edge strategies set a new standard for sustainable, modern airport design, the terminal is as much a showpiece of the history and traditions of India and Mumbai as it is an unprecedented structural and technological achievement. Rising from the Mumbai cityscape, Chhatrapati Shivaji International Airport celebrates both India’s rich cultural heritage and the country’s increasingly global future.
The chandeliers pay homage to the lotus flower, native to this region. Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
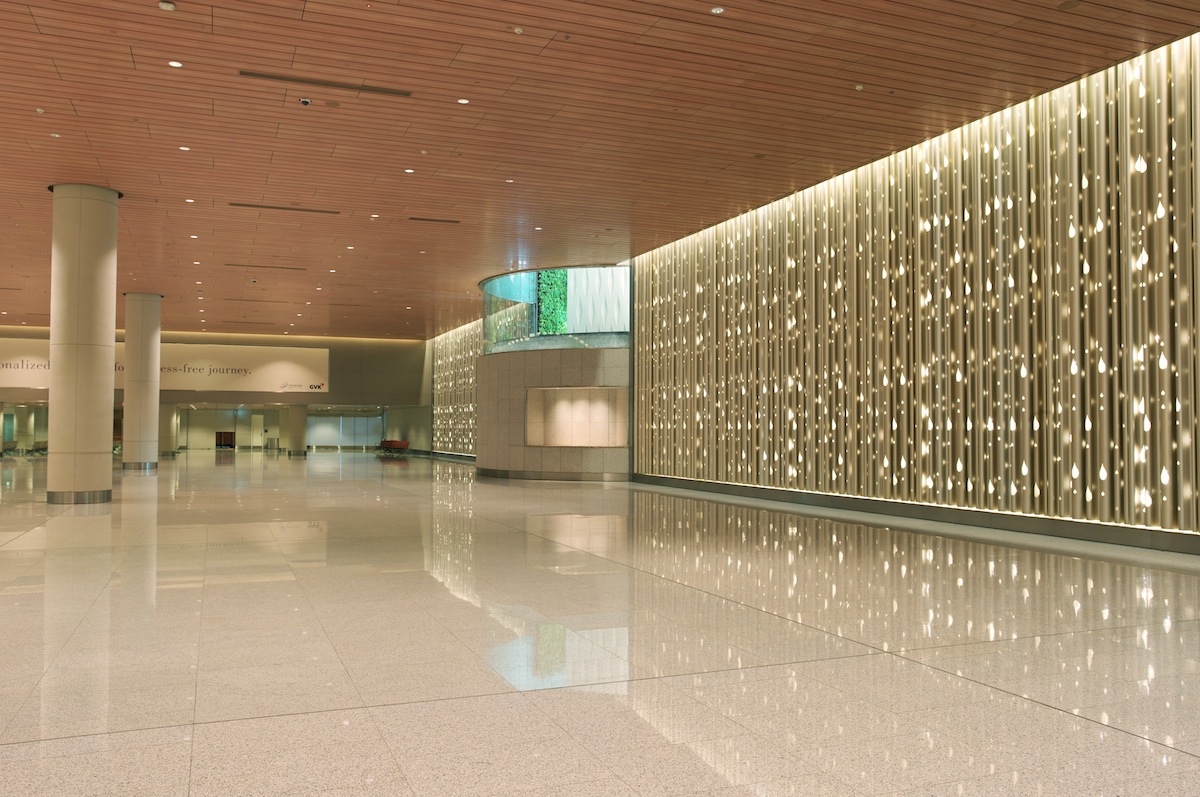

Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
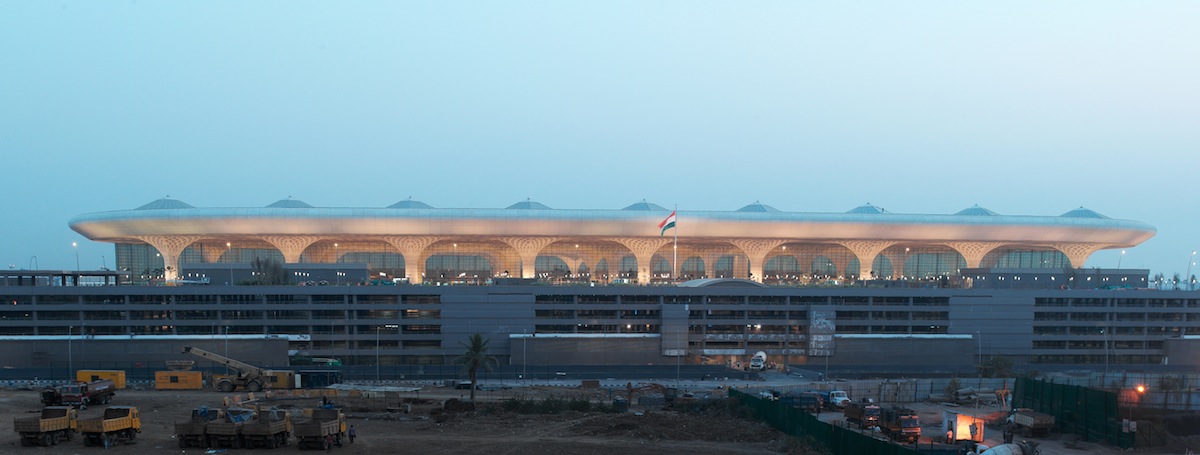

Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
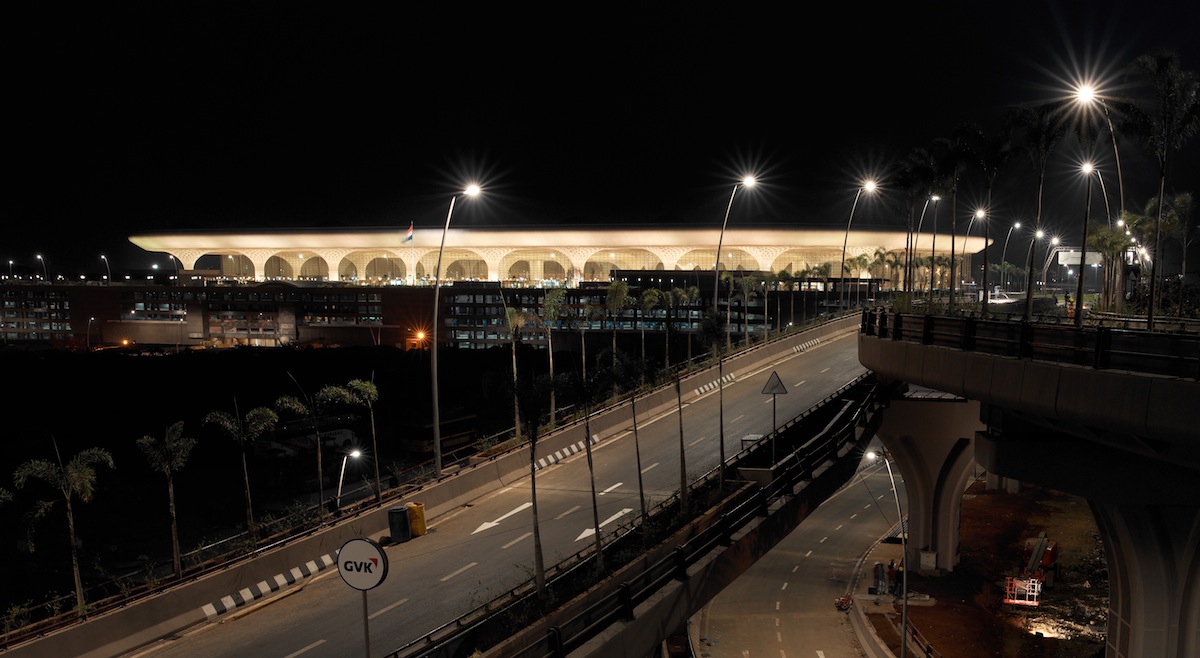

Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
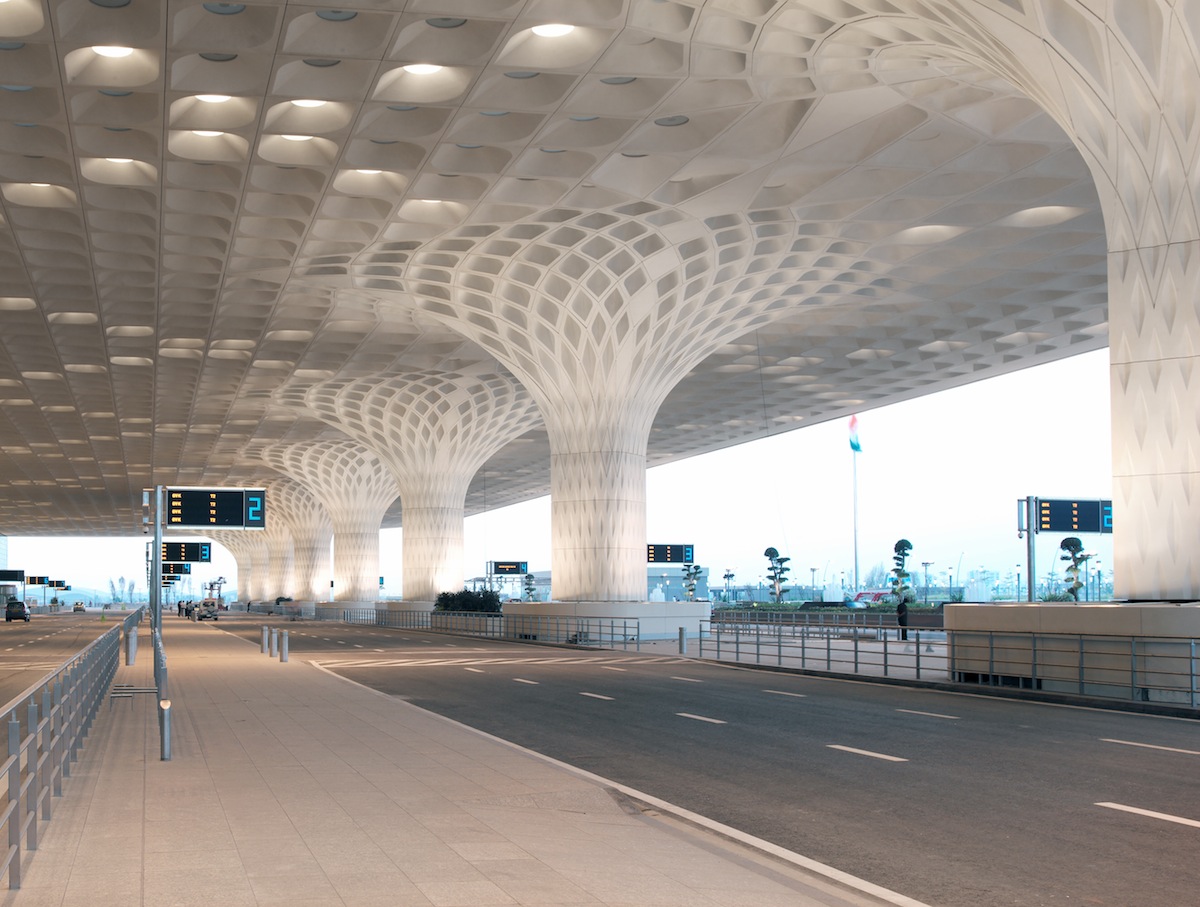

The fractal canopy extends over the roadway for arrivals in order to protect travelers from the weather. Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori / © Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
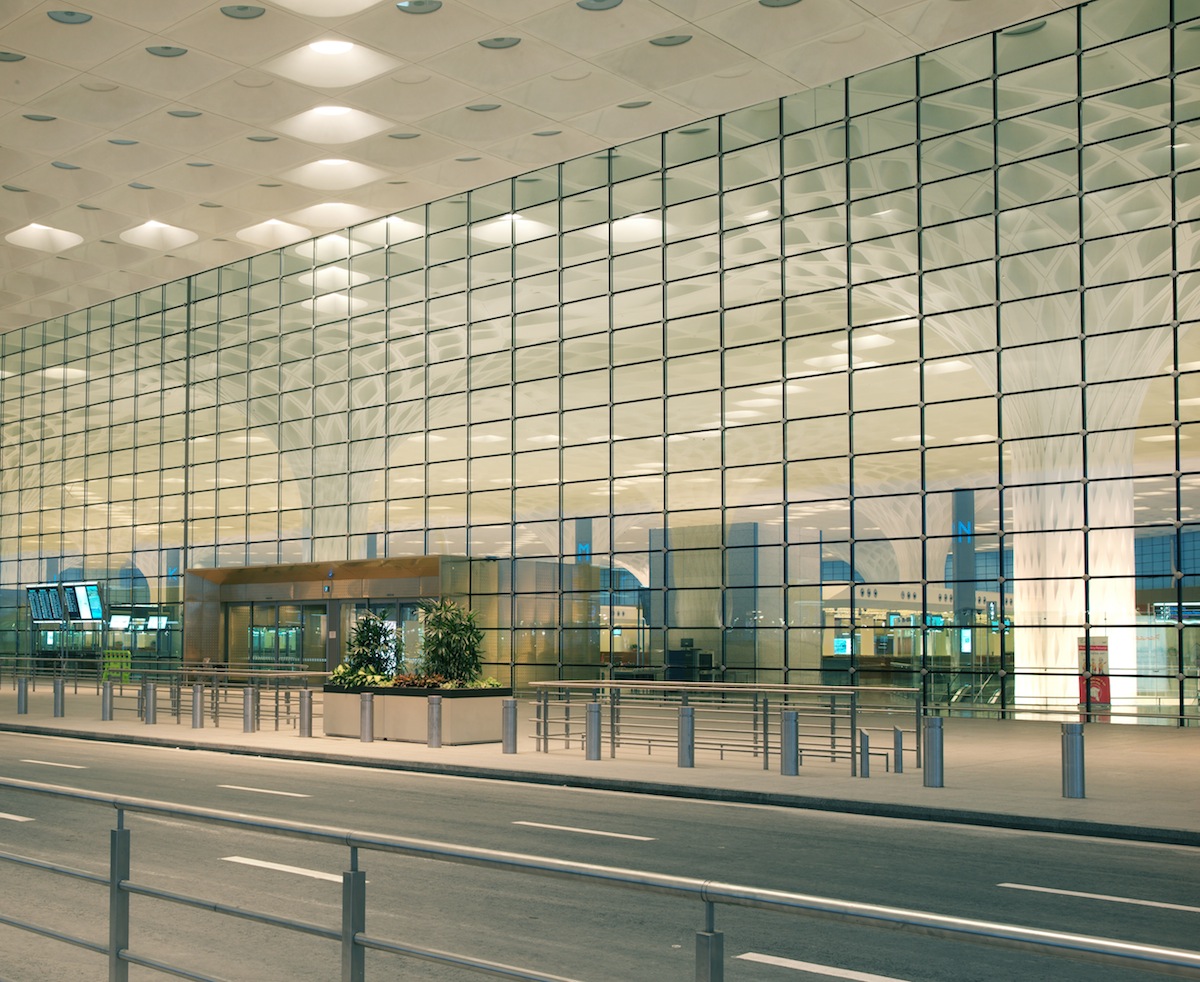

Image courtesy of SOM; Photographer, Robert Polidori /© Mumbai International Airport Pvt. Ltd.
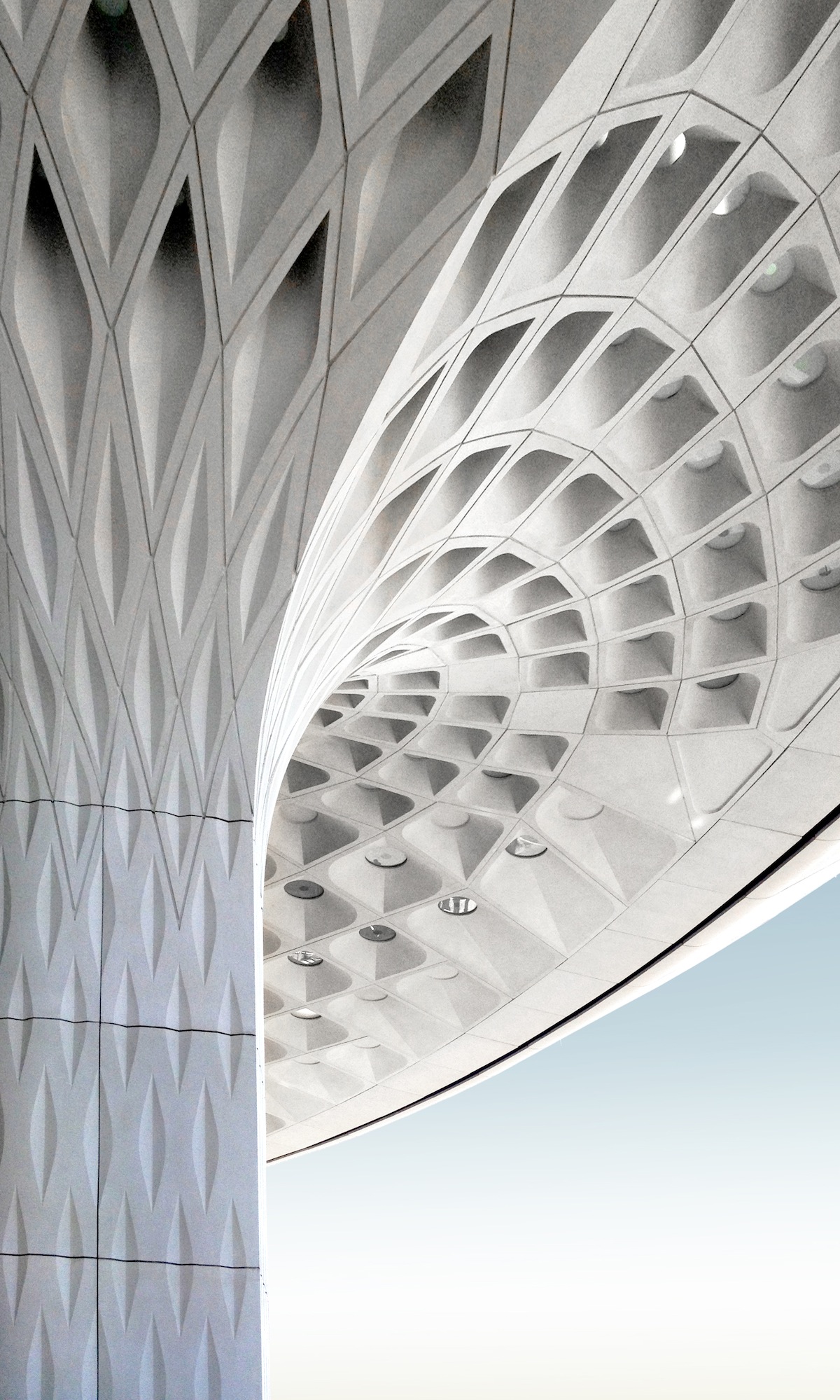

Image courtesy SOM / © SOM
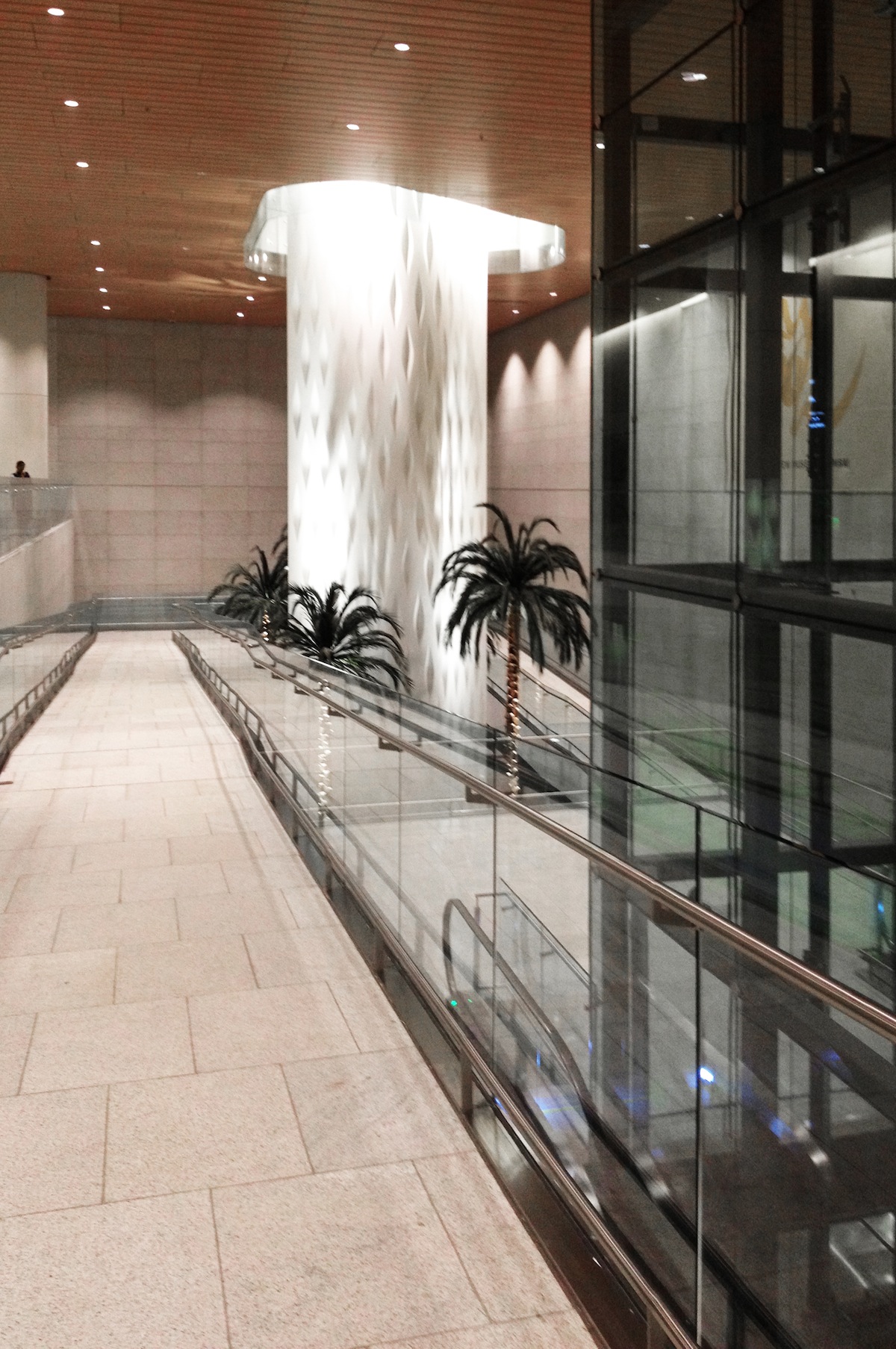

Image courtesy SOM / © SOM
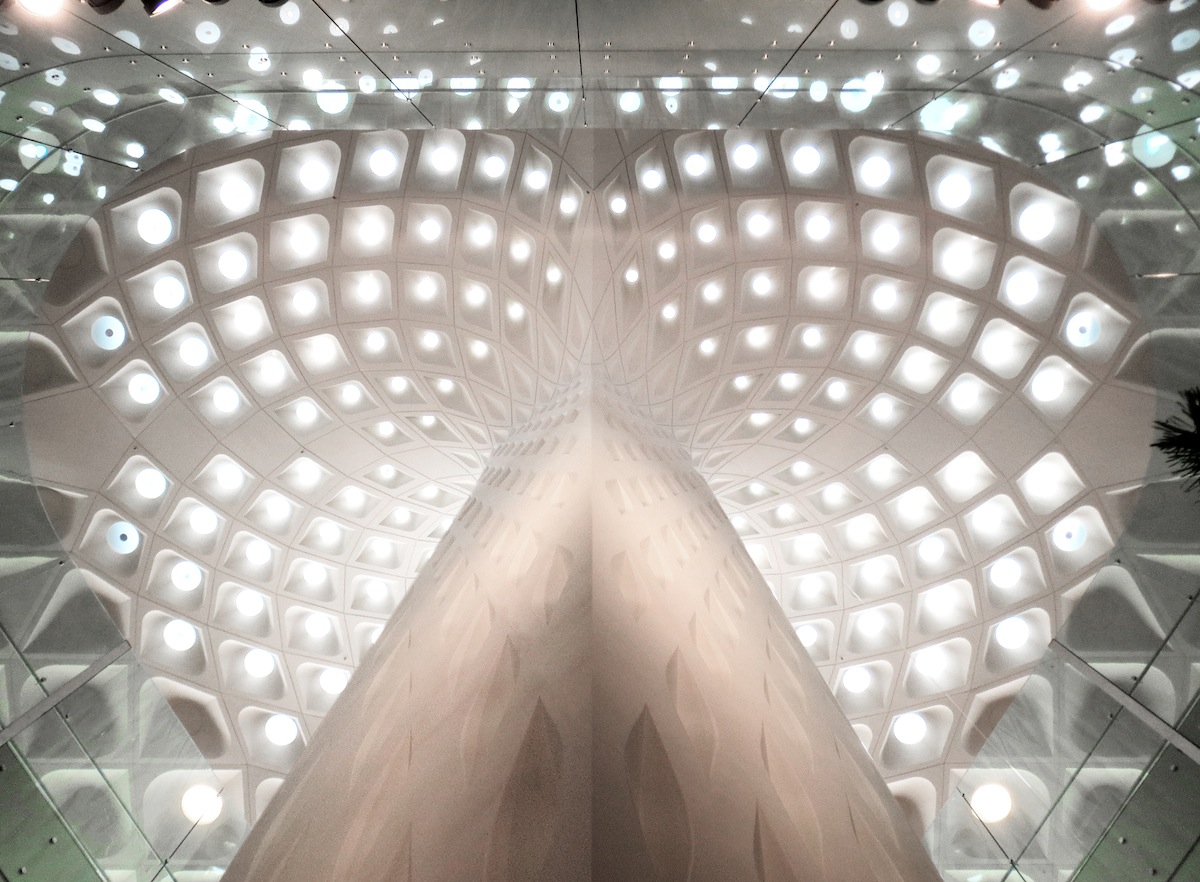

Image courtesy SOM / © SOM
Related Stories
| Nov 19, 2013
Top 10 green building products for 2014
Assa Abloy's power-over-ethernet access-control locks and Schüco's retrofit façade system are among the products to make BuildingGreen Inc.'s annual Top-10 Green Building Products list.
| Nov 15, 2013
Metal makes its mark on interior spaces
Beyond its long-standing role as a preferred material for a building’s structure and roof, metal is making its mark on interior spaces as well.
| Nov 13, 2013
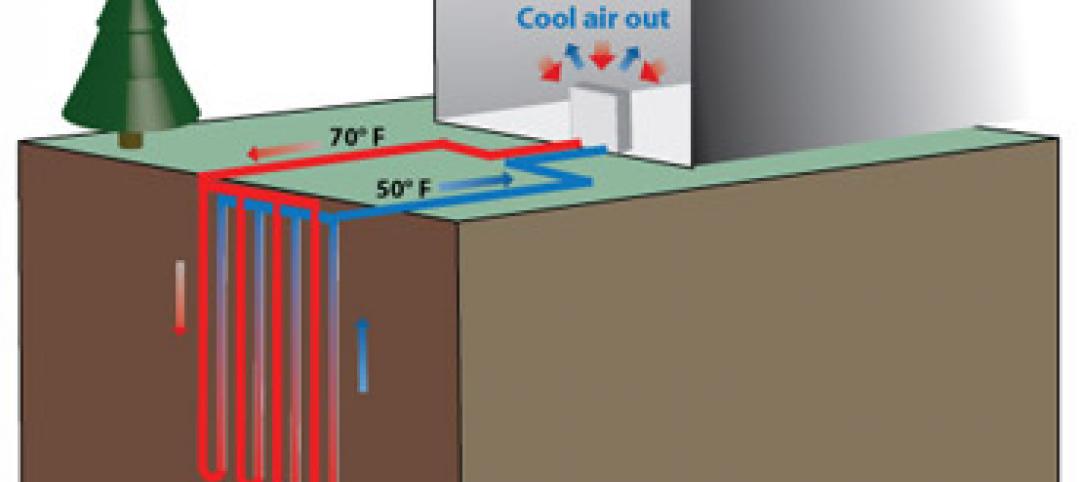
Installed capacity of geothermal heat pumps to grow by 150% by 2020, says study
The worldwide installed capacity of GHP systems will reach 127.4 gigawatts-thermal over the next seven years, growth of nearly 150%, according to a recent report from Navigant Research.
| Oct 30, 2013
11 hot BIM/VDC topics for 2013
If you like to geek out on building information modeling and virtual design and construction, you should enjoy this overview of the top BIM/VDC topics.
| Oct 18, 2013
Researchers discover tension-fusing properties of metal
When a group of MIT researchers recently discovered that stress can cause metal alloy to fuse rather than break apart, they assumed it must be a mistake. It wasn't. The surprising finding could lead to self-healing materials that repair early damage before it has a chance to spread.
| Sep 30, 2013
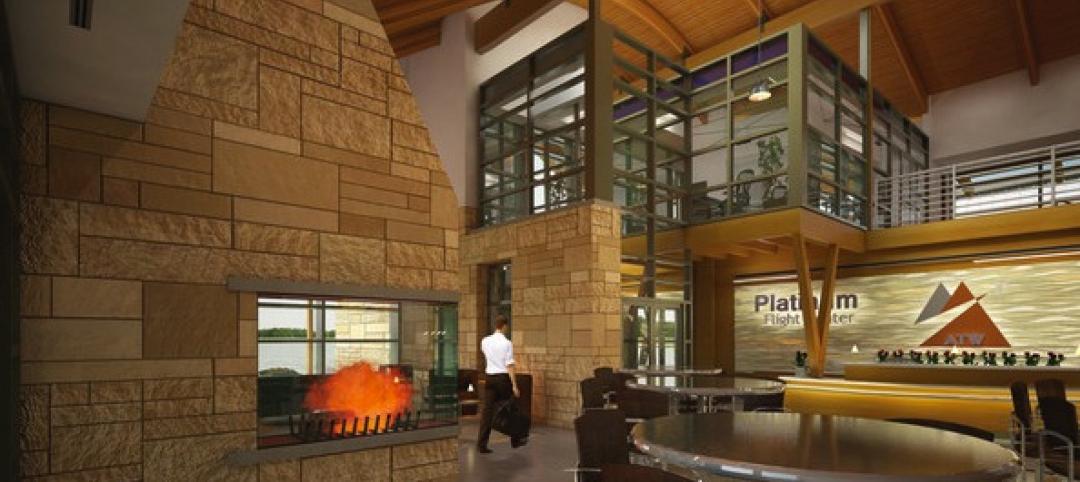
Smart building systems key to new Wisconsin general aviation terminal’s net zero target
The Outagamie County Regional Airport’s new 8,000 sf general aviation terminal was designed to achieve net zero.
| Sep 19, 2013
What we can learn from the world’s greenest buildings
Renowned green building author, Jerry Yudelson, offers five valuable lessons for designers, contractors, and building owners, based on a study of 55 high-performance projects from around the world.
| Sep 19, 2013
6 emerging energy-management glazing technologies
Phase-change materials, electrochromic glass, and building-integrated PVs are among the breakthrough glazing technologies that are taking energy performance to a new level.
| Sep 11, 2013
BUILDINGChicago eShow Daily – Day 3 coverage
Day 3 coverage of the BUILDINGChicago/Greening the Heartland conference and expo, taking place this week at the Holiday Inn Chicago Mart Plaza.
| Sep 10, 2013
BUILDINGChicago eShow Daily – Day 2 coverage
The BD+C editorial team brings you this real-time coverage of day 2 of the BUILDINGChicago/Greening the Heartland conference and expo taking place this week at the Holiday Inn Chicago Mart Plaza.