With security and sustainability becoming critical factors in nonresidential construction, design sometimes takes a back seat on projects.
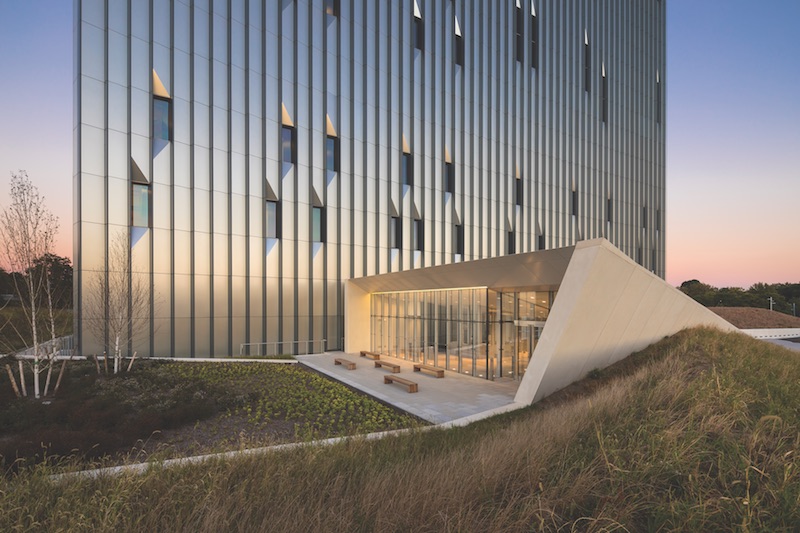
Case in point: New York City's second Public Safety Answering Center, known as PSAC II, which opened last June in the Bronx. The 450,000-sf facility, sitting on 8.75 acres along the Hutchinson River and Pelham Parkways, supplements PSAC I, located at the MetroTech Center in Brooklyn. The newer facility is set up to handle more than 11 million emergency 911 calls annually to the city’s police and fire departments.
As tall as a 24-story building, the cube-like PSAC II is a fortress protected by 15-inch-thick concrete walls, with a relatively limited number of windows for an edifice this size: 77 4x10-foot openings and 54 4x20-foot openings. There’s only one window on the west side of the facility, facing a train station. The main building’s overall window-to-wall ratio is 4%.
The windows and doors are blast- and tamper-proof. Computers, machinery, and mechanicals (often duplicated for security purposes) take up half the building’s floor space. Its 230 or so operators and dispatchers aren’t allowed to leave the building at any time during their work shifts, which sometimes last up to 14 hours.
“It was a challenge to take a vertical bunker and make it architecturally interesting, and a place where people working in a high-intensity environment could tolerate being inside of it,” recalls Gary Haney, FAIA, RIBA, Design Partner with Skidmore, Owings & Merrill. SOM, which also designed PSAC I, provided architectural services on the $800 million PSAC II. Jaros Baum & Bolles was the MEP Engineer, and Vidaris the sustainability consultant.
To make PSAC II something more than just a secure concrete box, SOM created what Haney describes as a “kind of camouflage” on the exterior with a sawtooth, two-color aluminum façade that has a “picket fence quality” and reflects sunlight.
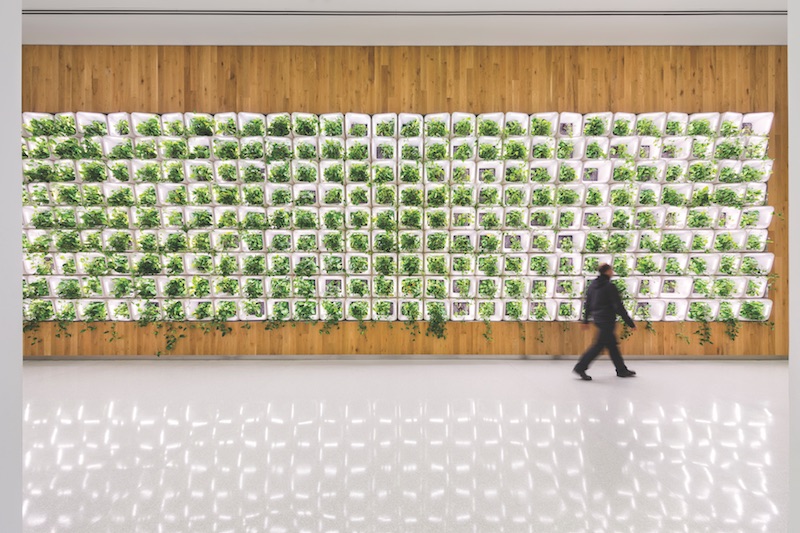 The plant wall is by CASE and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. Courtesy SOM/©Albert Vecerka|Esto.
The plant wall is by CASE and Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute. Courtesy SOM/©Albert Vecerka|Esto.
Working with landscape architect Thomas Balsley, FASLA, SOM further softened the building’s monolithic exterior by installing a wrap-around sculptural berm of wild grasses. Haney has described the berm as making the building appear to float. The berm also serves as security cover to help hide the facility, which has two floors underground and an attached entry pavilion. “When you view the berm from the inside, it creates an infinite landscape,” says Haney.
SOM laid out the building’s windows in an irregular pattern to give it design character. The firm paid particular attention to bringing natural light into the 50,000-sf, L-shaped call center, which has 30-foot-tall ceilings.
“We’ve gone back to the building almost every week since it opened, and what I’m most happy about is the amount of light that comes into the call center,” says Haney. “It’s a pleasant surprise.”
The same is true on the third floor, which is mostly office space. “From the inside, you hardly notice there aren’t a lot of windows,” he adds.
In order to fine-tune the mechanical systems, the project team took almost a year to commission the building. “That made a huge difference in controlling energy consumption,” says Haney. The effort helped PSAC II achieve LEED Gold certification.
The building earned LEED points for its use of a living wall in its lobby and cafeteria areas. The plant wall—developed by CASE, SOM’s design research laboratory, in partnership with Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute—acts as a natural air filter and a center of engagement for the building’s occupants.
“It became part of the idea of making the indoors more livable,” says Haney, who adds that the city was very receptive to including this design feature.
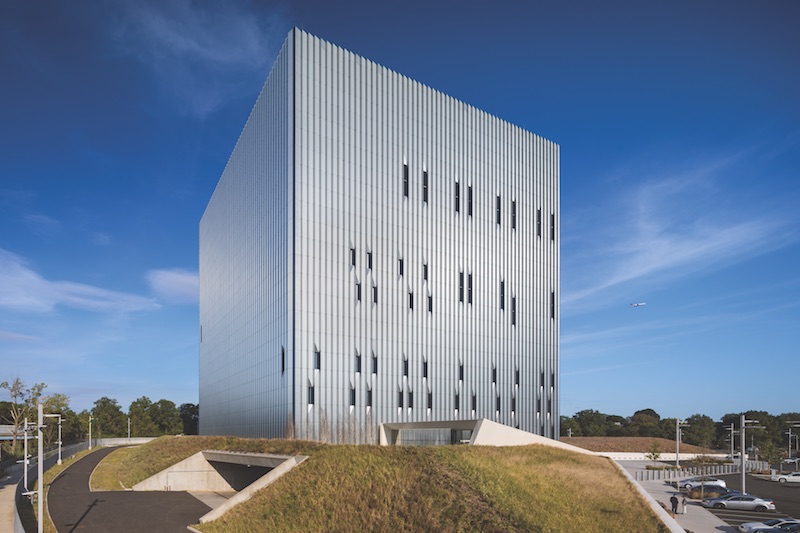 Landscape architect Thomas Balsley Associates created the grass berm. Courtesy SOM/©Albert Vecerka|Esto.
Landscape architect Thomas Balsley Associates created the grass berm. Courtesy SOM/©Albert Vecerka|Esto.
Related Stories
Wood | Nov 16, 2022
5 steps to using mass timber in multifamily housing
A design-assist approach can provide the most effective delivery method for multifamily housing projects using mass timber as the primary building element.
Energy-Efficient Design | Nov 14, 2022
How to achieve net zero energy in five steps
Martine Dion and Ethan Seaman share net zero energy best practices with owners and developers.
Green | Nov 13, 2022
USGBC updates LEED v4 to better address greenhouse gas emissions and climate change
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) will update the LEED v4 green building certification program to “more directly address greenhouse gas emissions and climate change” according to a USGBC news release.
Green | Nov 13, 2022
NREL report: Using photovoltaic modules with longer lifetimes is a better option than recycling
A new report from the U.S. National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) says PV module lifetime extensions should be prioritized over closed-loop recycling to reduce demand for new materials.
Green | Nov 13, 2022
Global building emissions reached record levels in 2021
Carbon-dioxide emissions from building construction and operations hit an all-time high in 2021, according to the most recent data compiled by the Global Alliance for Buildings and Construction.
University Buildings | Nov 13, 2022
University of Washington opens mass timber business school building
Founders Hall at the University of Washington Foster School of Business, the first mass timber building at Seattle campus of Univ. of Washington, was recently completed. The 84,800-sf building creates a new hub for community, entrepreneurship, and innovation, according the project’s design architect LMN Architects.
Industry Research | Nov 8, 2022
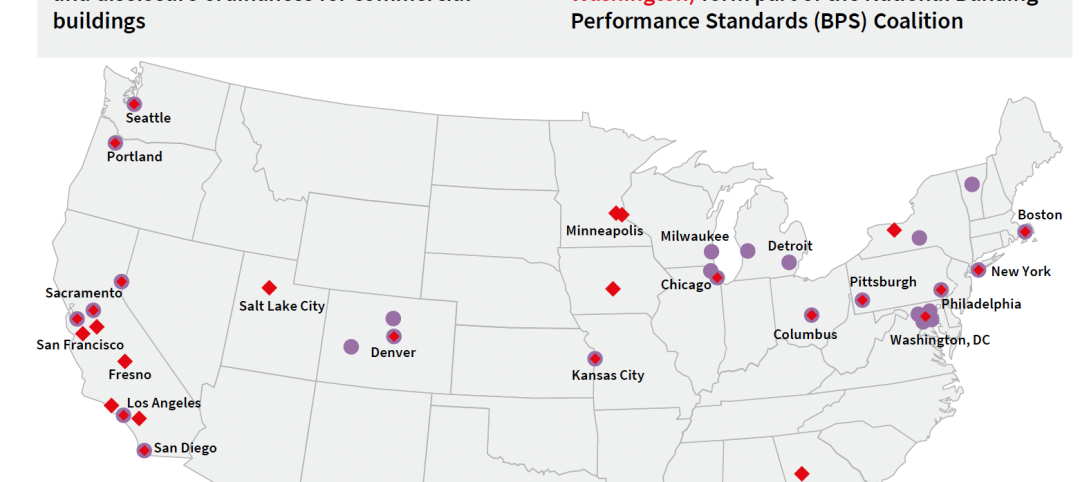
U.S. metros take the lead in decarbonizing their built environments
A new JLL report evaluates the goals and actions of 18 cities.
Green | Nov 8, 2022
USGBC and IWBI will develop dual certification pathways for LEED and WELL
The U.S. Green Building Council (USGBC) and the International WELL Building Institute (IWBI) will expand their strategic partnership to develop dual certification pathways for LEED and WELL.
Wood | Nov 1, 2022
A European manufacturer says its engineered wood products can store carbon for decades
Metsä Wood, a Finland-based manufacturer of engineered wood products, says its sustainable, material-efficient products can store carbon for decades, helping to combat climate change.
40 Under 40 | Oct 19, 2022
Meet the 40 Under 40 class of 2022
Each year, the editors of Building Design+Construction honor 40 architects engineers, contractors, and real estate developers as BD+C 40 Under 40 awards winners. These AEC professionals are recognized for their career achievements, passion for the AEC profession, involvement with AEC industry organizations, and service to their communities.