The tuned mass damper used in Taiwan’s Taipei 101 tower represents an engineering feat that is so impressive the designers decided to make it publicly visible for all to see. Taipei 101’s 730-ton tuned mass damper may represent an extreme, but its purpose is the same as much smaller dampers that may be used in an office building or mall: to mitigate vibrations or sway that may otherwise alarm or cause discomfort to building occupants.
As building materials get lighter and designs push the limits of what is possible in architecture, structural vibrations are becoming more worrisome. A vibrating floor may not be dangerous, but it can certainly cause some unease among building occupants.
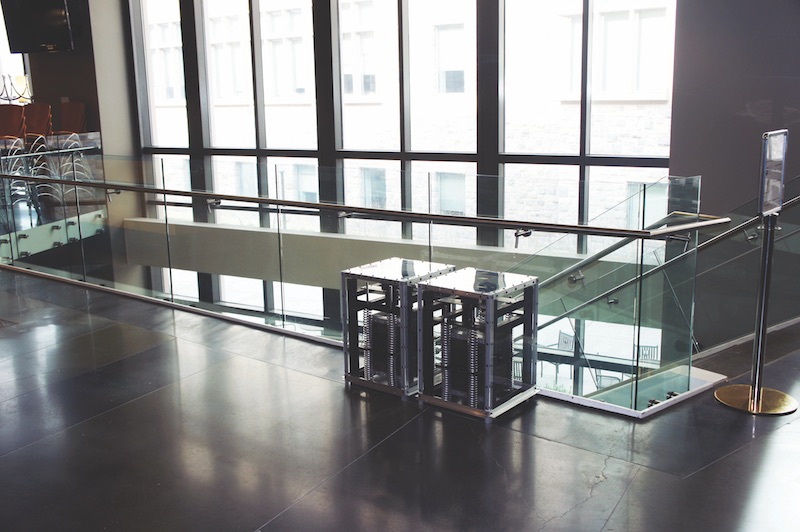
That’s where Mehdi Setareh, PhD, Professor, School of Architecture + Design at Virginia Tech’s College of Architecture and Urban Studies, comes in. With the help of a small team of students, he has created a portable tuned mass damper (PTMD) that weighs less than 275 pounds and is about the size of a shop vac. The device reduced vibrations by 40-75% in tests at Virginia Tech’s Vibration Testing Lab.
 Mehdi Setareh next to an early version of the Portable Tuned Mass Damper. Courtesy Virginia Tech.
Mehdi Setareh next to an early version of the Portable Tuned Mass Damper. Courtesy Virginia Tech.
The PTMD can be incorporated in new construction or added as a corrective measure in an existing building. Even nontechnical personnel can tune the device, using a $5 iTunes application and Setareh’s instructions. Because of the device’s small size, it can be easily hidden in a cabinet or even within furniture.
Plates, springs, and dampers that are built into the two-foot-tall, 15-inch-wide box are tuned to the natural frequency of a structure and reduce vibrations by moving in the opposite direction of that structure, but at 10 to 20 times higher acceleration rates.
Currently, the unit shows the most promise for use in structures with high foot traffic, such as theaters, malls, nightclubs, and monumental staircases, or in settings that have vibration-sensitive equipment, such as hospitals and labs.
Setareh has applied for a patent on the device. He plans to place it on the market as a kit of parts with instructions on how to assemble, install, and tune the damper.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Apr 13, 2022
A robot automates elevator installation
Schindler—which manufactures and installs elevators, escalators, and moving walkways—has created a robot called R.I.S.E. (robotic installation system for elevators) to help install lifts in high-rise buildings.
Building Tech | Apr 6, 2022
Autodesk Construction Cloud Introduces New Data Sharing Capabilities to Transform Construction Collaboration
Autodesk, Inc. (NASDAQ: ADSK) today launched Bridge, a new collaboration capability that empowers construction teams to share only relevant data with project stakeholders, regardless of whether they are on the same team or building project within Autodesk Construction Cloud.
Modular Building | Mar 31, 2022
Rick Murdock’s dream multifamily housing factory
Modular housing leader Rick Murdock had a vision: Why not use robotic systems to automate the production of affordable modular housing? Now that vision is a reality.
Codes and Standards | Mar 22, 2022
Dept. of Energy awards $32 million for next-generation building retrofits
The U.S. Dept. of Energy has awarded a total of $32 million for more than 30 next-generation building retrofit projects that will dramatically improve affordable housing technologies, according to a DOE news release.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Feb 17, 2022
Metal roofing trends
New ideas in design and constructability are radically changing how metal systems are used as roofing for commercial and institutional buildings. Behind the investment in these new kinds of expressions and construction approaches is a growing interest in improved performance and reduced environmental impact. Metal roofing systems can cut cooling and heating loads significantly, according to the EPA.
Sponsored | Reconstruction & Renovation | Jan 25, 2022
Concrete buildings: Effective solutions for restorations and major repairs
Architectural concrete as we know it today was invented in the 19th century. It reached new heights in the U.S. after World War II when mid-century modernism was in vogue, following in the footsteps of a European aesthetic that expressed structure and permanent surfaces through this exposed material. Concrete was treated as a monolithic miracle, waterproof and structurally and visually versatile.
Sponsored | Resiliency | Jan 24, 2022
Blast Hazard Mitigation: Building Openings for Greater Safety and Security
Coronavirus | Jan 20, 2022
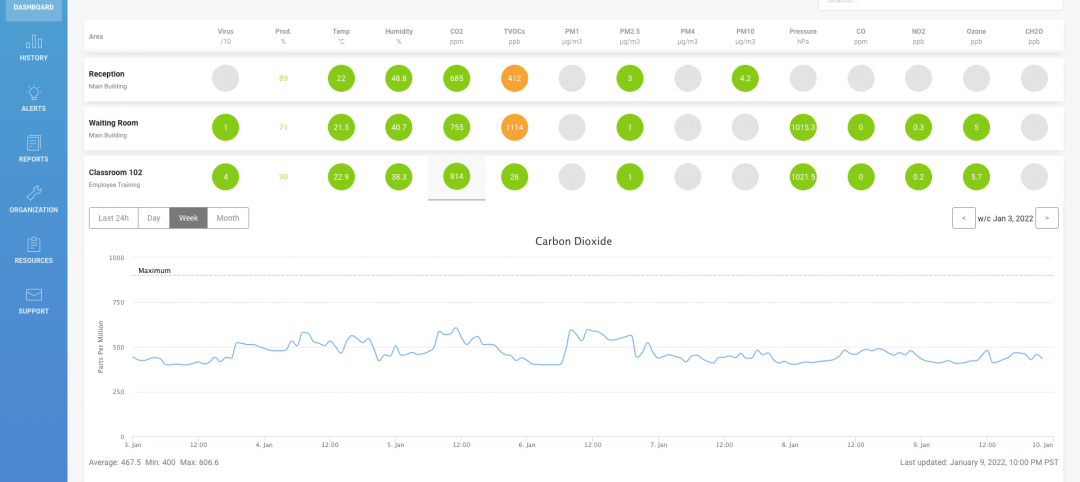
Advances and challenges in improving indoor air quality in commercial buildings
Michael Dreidger, CEO of IAQ tech startup Airsset speaks with BD+C's John Caulfield about how building owners and property managers can improve their buildings' air quality.
3D Printing | Jan 12, 2022
Using 3D-printed molds to create unitized window forms
COOKFOX designer Pam Campbell and Gate Precast's Mo Wright discuss the use of 3D-printed molds from Oak Ridge National Lab to create unitized window panels for One South First, a residential-commercial high-rise in Brooklyn, N.Y.
Sponsored | BD+C University Course | Jan 12, 2022
Total steel project performance
This instructor-led video course discusses actual project scenarios where collaborative steel joist and deck design have reduced total-project costs. In an era when incomplete structural drawings are a growing concern for our industry, the course reveals hidden costs and risks that can be avoided.