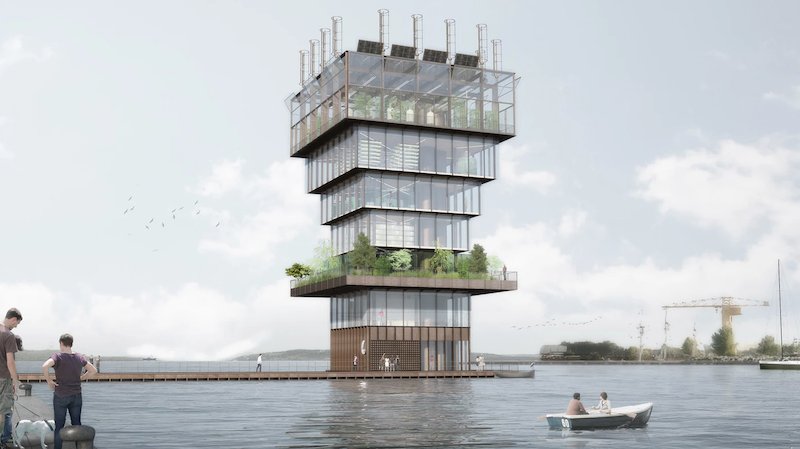
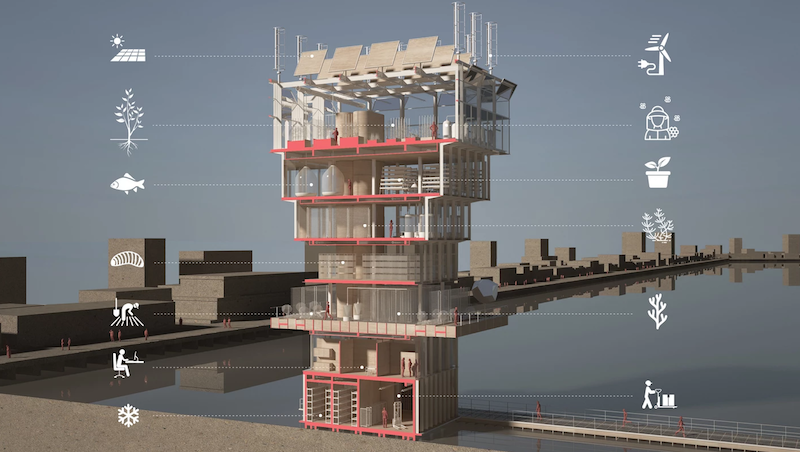
Studio NAB’s new Superfarm project is a 110-foot-tall vertical farm prototype that sits on a 40-foot by 40-foot platform built on the water in an urban area. The prototype goes beyond what typical vertical farms offer by creating an entire ecosystem across its six stories.
The Superfarm will use a combination of soil and soilless cropping techniques and will forgo the use of pesticides. Each floor will have its own specific function, but will work harmoniously with all the other floors to create a vertical ecosystem.
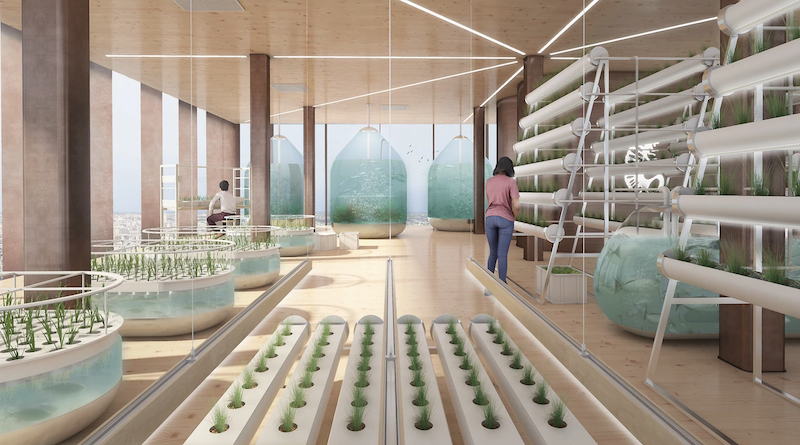 Aquaponics level.
Aquaponics level.
The ground level and Level 1 will be set aside for administration purposes. The Ground Level will include the entrance, cold rooms, storage, order preparation, and space for sale and delivery. Level 1 will include offices bathrooms, and a break room.
See Also: An apiary for the sanctuary
Level 2 is where the growing of plants begins. It is an open platform that will include ginseng, klamath, spirulina, and aloe vera cultures. Level 3 is reserved for insect breeding. Beetles, chenilles, locusts, and grasshoppers will all have a dedicated space on this floor. Level 4 will be dedicated to algae cultures, including chlorella and spirulina. Level 5 will be the aquaponics floor and will include tilapia and trout breeding and young plant cultures. The aquaponics floor will also feed the greenhouse on Level 6. The greenhouse will include an apiary, açaí berry cultures, acerola cultures, goji berry cultures, and aloe vera cultures. Above the greenhouse will be a series of wind turbines and solar panels that will power the farm.
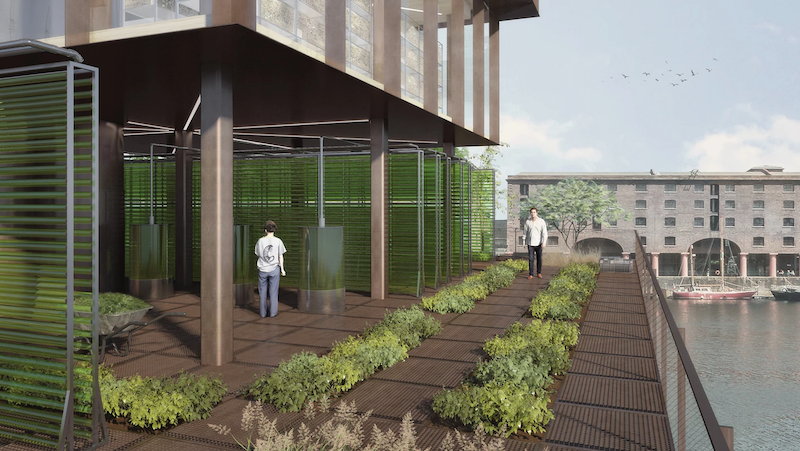 Level 2 platform.
Level 2 platform.
The goal of the Superfarm is to decrease the amount of land needed for agriculture while simultaneously feeding more people, and restore a social link between the produce and the consumer in the city, providing easier access to the products by allowing the consumer direct access to the farm.
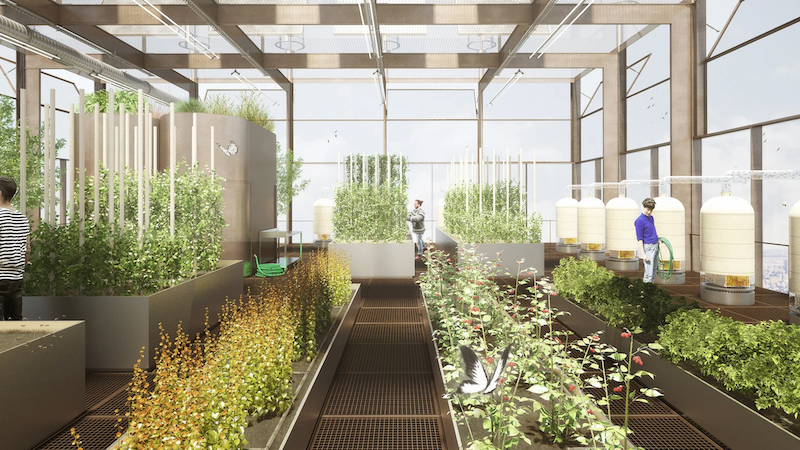 Level 6 greenhouse.
Level 6 greenhouse.

Related Stories
Mass Timber | Jul 11, 2023
5 solutions to acoustic issues in mass timber buildings
For all its advantages, mass timber also has a less-heralded quality: its acoustic challenges. Exposed wood ceilings and floors have led to issues with excessive noise. Mass timber experts offer practical solutions to the top five acoustic issues in mass timber buildings.
Adaptive Reuse | Jul 6, 2023
The responsibility of adapting historic university buildings
Shepley Bulfinch's David Whitehill, AIA, believes the adaptive reuse of historic university buildings is not a matter of sentimentality but of practicality, progress, and preservation.
Contractors | Jun 30, 2023
Construction industry task force aims for standardized carbon reporting
A newly formed Associated General Contractors of America (AGC) task force on decarbonization and carbon reporting will address the challenges around reporting and reducing carbon emissions in the construction industry.
Apartments | Jun 27, 2023
Dallas high-rise multifamily tower is first in state to receive WELL Gold certification
HALL Arts Residences, 28-story luxury residential high-rise in the Dallas Arts District, recently became the first high-rise multifamily tower in Texas to receive WELL Gold Certification, a designation issued by the International WELL Building Institute. The HKS-designed condominium tower was designed with numerous wellness details.
Green | Jun 26, 2023
Federal government will spend $30 million on novel green building technologies
The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies. The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance.
Industrial Facilities | Jun 20, 2023
A new study presses for measuring embodied carbon in industrial buildings
The embodied carbon (EC) intensity in core and shell industrial buildings in the U.S. averages 23.0 kilograms per sf, according to a recent analysis of 26 whole building life-cycle assessments. That means a 300,000-sf warehouse would emit 6,890 megatons of carbon over its lifespan, or the equivalent of the carbon emitted by 1,530 gas-powered cars driven for one year. Those sobering estimates come from a new benchmark study, “Embodied Carbon U.S. Industrial Real Estate.”
Mechanical Systems | Jun 16, 2023
Cogeneration: An efficient, reliable, sustainable alternative to traditional power generation
Cogeneration is more efficient than traditional power generation, reduces carbon emissions, has high returns on the initial investment, improves reliability, and offers a platform for additional renewable resources and energy storage for a facility. But what is cogeneration? And is it suitable for all facilities?
Resiliency | Jun 14, 2023
HUD offers $4.8 billion in funding for green and resilient building retrofit projects
The Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) recently released guidelines for its Green and Resilient Retrofit Program (GRRP) that has $4.8 billion for funding green projects.
Mass Timber | Jun 13, 2023
Mass timber construction featured in two-story mixed-use art gallery and wine bar in Silicon Valley
The Edes Building, a two-story art gallery and wine bar in the Silicon Valley community of Morgan Hill, will prominently feature mass timber. Cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glulam posts and beams were specified for aesthetics, biophilic properties, and a reduced carbon footprint compared to concrete and steel alternatives.
K-12 Schools | May 25, 2023
From net zero to net positive in K-12 schools
Perkins Eastman’s pursuit of healthy, net positive schools goes beyond environmental health; it targets all who work, teach, and learn inside them.