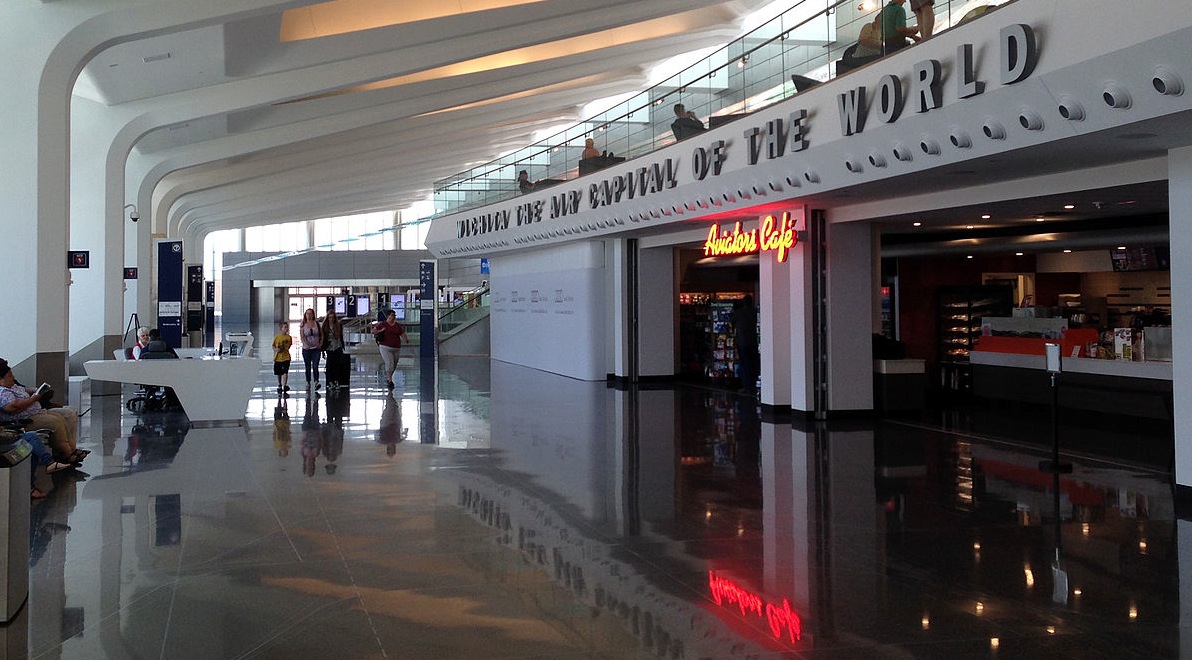
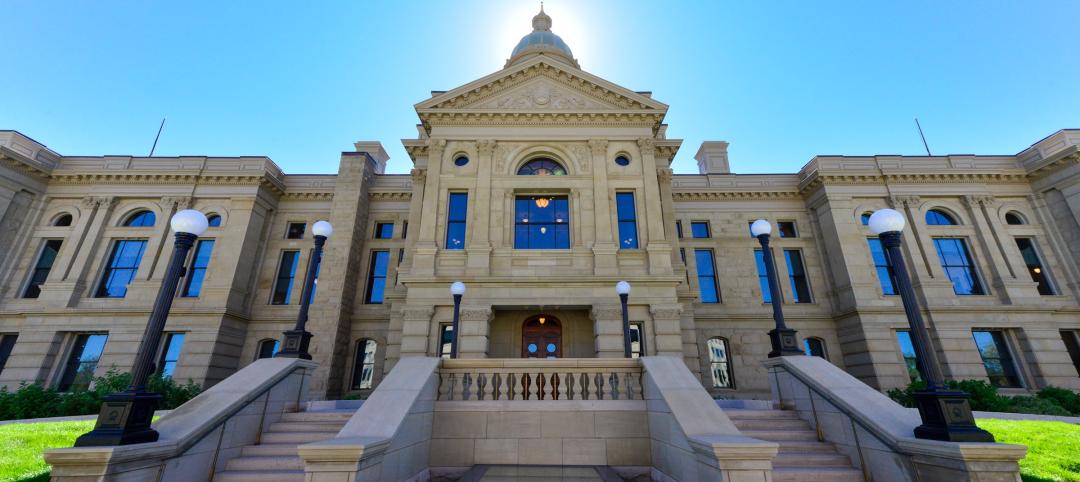
In June, the Dwight D. Eisenhower National Airport in Wichita, Kan., opened a new 275,000-sf, 12-gate terminal. According to an airport press release, the new facility “expresses …Wichita’s globally prominent position in Aviation as the Air Capital of the World.” The $200 million-plus terminal (which includes a new consolidated rental car facility) can handle two million passengers annually. It was designed (by HTNB) to support future growth up to 2.4 million.
Passenger traffic at the airport (formerly known as Wichita Mid-Continent Airport) was about 1.5 million in 2014, up 6% from the previous year. As of mid-2015, it is running about even with last year, says Victor White, Wichita Airport Authority’s Director of Airports.
Regional airports like Eisenhower National—which offers flights to and from Atlanta, Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Houston, Las Vegas, Los Angeles, Minneapolis-St. Paul, and Phoenix—are doing everything they can to hold onto business. But small-to-midsize airports are still battling for their lives, as big carriers are cut or eliminate service to non-hub cities.
A 2013 report from Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s International Center for Air Transportation found that small- and medium-sized airports ”have been disproportionally affected by reductions in service,” with medium-sized airports having felt “the biggest brunt” of airline network strategies.
This report predicts that smaller airports close to major hubs could be at risk of losing all of their carrier service by 2018. That’s bad news for local municipalities that see their airports as economic engines.
San Luis Obispo County (Calif.) Regional Airport is a case in point. In 2008 Delta ceased service to Salt Lake City, U.S. Air discontinued flights to Las Vegas, and American Airlines pulled out of the airport altogether. About 60% of travelers in this region now fly out of Los Angeles or the San Francisco Bay Area, according to The Tribune, a newspaper that covers this market.
County officials believe San Luis Obispo’s prosperity hinges on its airport’s growth. Despite ongoing discussions with several carriers, the airport has had trouble finding airlines willing to provide service to Dallas, Salt Lake, or Denver.
White says that over the past decade, Wichita’s airport has managed to grow through aggressive marketing and airline recruitment. Four of the nation’s largest carriers—American, Delta, United, and Southwest—all fly out of Eisenhower, as does Allegiant Air, which caters to leisure travelers.
Wichita’s airport was also one of the first to offer incentives to carriers in the form of guaranteeing revenue and other subsidies, a practice that is now common among small and medium size airports. “Southwest Airlines wouldn’t have come here if we hadn’t provided guarantees and subsidies,” White says.
Rent income from airlines is one of the revenue streams that Wichita tapped to pay for its new terminal, along with user fees, commissions on retail sales, and a $4.50 per passenger facility fee. It also received a $60 million FAA grant, and another $7 million from TSA, says White.
The MIT report noted that while airlines have been grounding their older, smaller turbo planes and moving to larger jets with more seats, they still aren’t offering small and midsize airports enough flights to match demand.
At Eisenhower, White says that carriers are mostly flying Airbus or Boeing jets. But, he’s quick to add, demand continues to outpace availability. “The biggest complaint that passengers have is that flights are too full and it is hard to find a seat at the time and price they want to fly.”
Related Stories
Giants 400 | Dec 12, 2023
Top 40 Military Facility Architecture Firms for 2023
Michael Baker International, HDR, Whitman, Requardt & Associates, and Stantec top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest military facility architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Office Buildings | Dec 12, 2023
Transforming workplaces for employee mental health
Lauren Elliott, Director of Interior Design, Design Collaborative, shares practical tips and strategies for workplace renovation that prioritizes employee mental health.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 150 Local Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Gensler, HOK, Stantec, and Skidmore, Owings & Merrill top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest local government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Giants 400 | Dec 11, 2023
Top 90 State Government Building Architecture Firms for 2023
Page Southerland Page, Skidmore, Owings & Merrill, Stantec, and NORR top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest state government building architecture and architecture/engineering (AE) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
Codes and Standards | Dec 11, 2023
Washington state tries new approach to phase out fossil fuels in new construction
After pausing a heat pump mandate earlier this year after a federal court overturned Berkeley, Calif.’s ban on gas appliances in new buildings, Washington state enacted a new code provision that seems poised to achieve the same goal.
Green | Dec 11, 2023
U.S. has tools to meet commercial building sector decarbonization goals early
The U.S. has the tools to reduce commercial building-related emissions to reach target goals in 2029, earlier than what it committed to when it signed the Paris Agreement, according to a report by the U.S. Green Building Council.
MFPRO+ News | Dec 11, 2023
U.S. poorly prepared to house growing number of older adults
The U.S. is ill-prepared to provide adequate housing for the growing ranks of older people, according to a report from Harvard University’s Joint Center for Housing Studies. Over the next decade, the U.S. population older than 75 will increase by 45%, growing from 17 million to nearly 25 million, with many expected to struggle financially.
Office Buildings | Dec 11, 2023
Believe it or not, there could be a shortage of office space in the years ahead
With work-from-home firmly established, many real estate analysts predict a dramatic reduction in office space leasing and plummeting property values. But the high-end of the office segment might actually be headed for a shortage, according to real estate intelligence company CoStar Group.
University Buildings | Dec 8, 2023
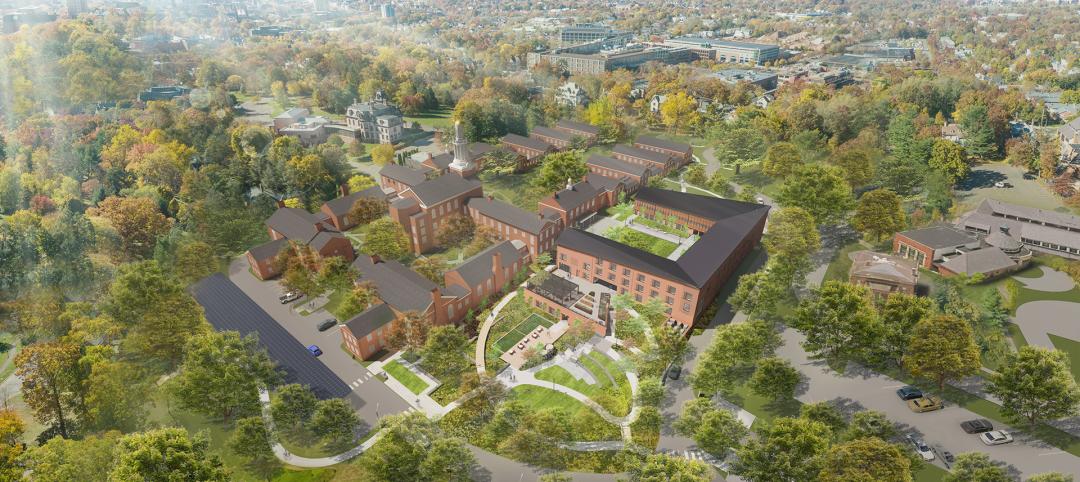
Yale University breaks ground on nation's largest Living Building student housing complex
A groundbreaking on Oct. 11 kicked off a project aiming to construct the largest Living Building Challenge-certified residence on a university campus. The Living Village, a 45,000 sf home for Yale University Divinity School graduate students, “will make an ecological statement about the need to build in harmony with the natural world while training students to become ‘apostles of the environment’,” according to Bruner/Cott, which is leading the design team that includes Höweler + Yoon Architecture and Andropogon Associates.
University Buildings | Dec 5, 2023
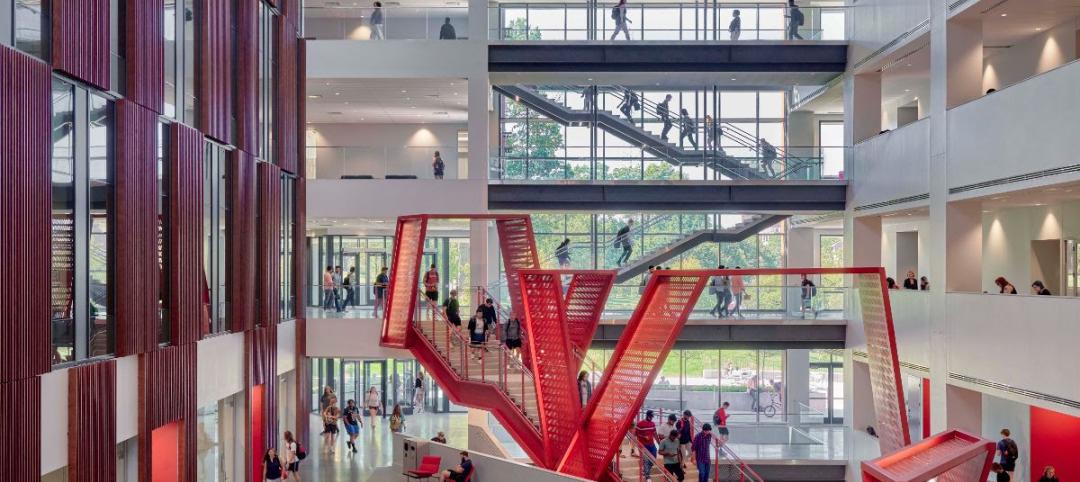
The University of Cincinnati builds its largest classroom building to serve its largest college
The University of Cincinnati’s recently completed Clifton Court Hall unifies the school’s social science programs into a multidisciplinary research and education facility. The 185,400-sf structure is the university’s largest classroom building, serving its largest college, the College of Arts and Sciences.