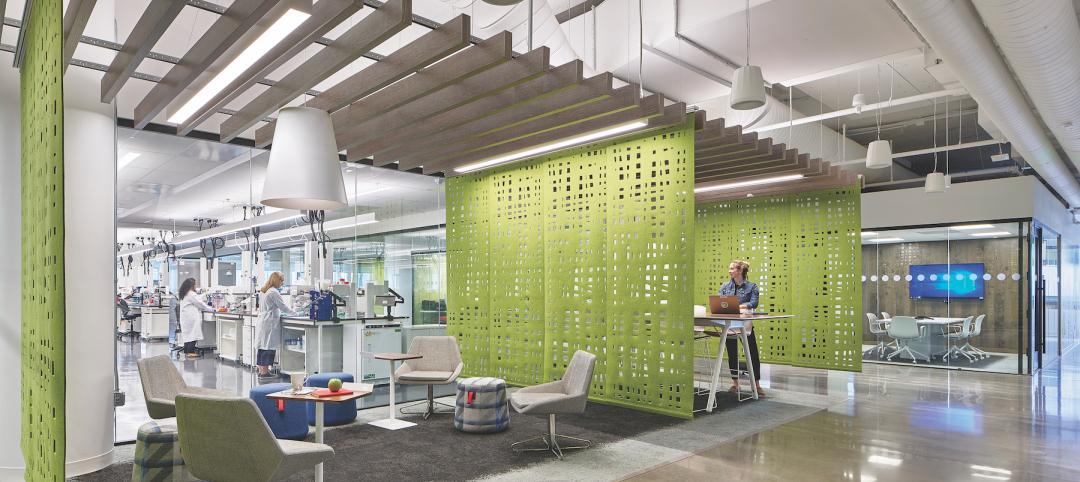
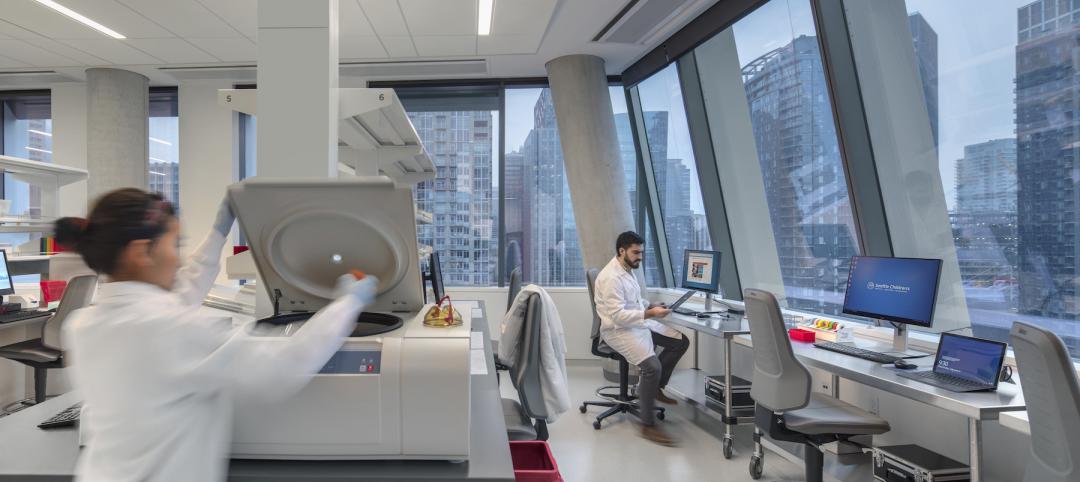
Imagine dozens of brilliant scientists and scientists-to-be working side by side in one large, open and fully equipped lab space — a shared space humming with the activity of curious minds as they interact with, learn from and inspire one another. I would describe such a setting as nothing short of super. In fact, as many in the industry know, laboratory facilities that facilitate learning/teaching and the exchange of ideas in a large group environment, as well as potentially running multiple sessions in parallel, are often referred to as ‘superlabs’.
Established in 2006, the London Metropolitan University’s Science Centre is home to one such superlab. At 280 individual workstations, this superlab is not only considered one of the largest and most advanced educational science facilities in Europe, but is also often credited as being the first open-plan superlab in the world to enable scientific research and learning to be carried out simultaneously at such a scale.
HDR is currently working on a number of superlabs, which while not necessarily an entirely new concept, do constantly offer interesting opportunities to explore and compare teaching pedagogies. The value of such opportunities are reflected in the Australian university sector’s increasing interest in and demand for the benefits of the superlab.
So what is the major benefit that superlabs have to offer? Efficiency. A superlab provides greater efficiency due to its generally contiguous, albeit large, space — particularly when compared to traditional teaching laboratories comprised of multiple smaller spaces. Superlabs drive a theoretical efficiency on real estate and ‘teaching and support’ head count, both of which help maximize cost efficiencies in a very competitive university sector.
But while the flexibility of having larger numbers of students sharing a space at any given time may be economically appealing, it won’t count for much if the quality of teaching is adversely affected. As a former biologist myself, I can attest — based on my own days as an undergraduate in a biology practical — that a quality teaching process is key to knowledge retention and to making the journey of learning and discovery more enjoyable and exciting. I would also argue that the camaraderie developed between students is an equally valuable life skill for life beyond graduation.
The question, therefore, is this: What factors should design teams address to ensure high levels of teaching quality in superlabs? To answer that, I created a superlab design quality checklist to prompt some thoughts at the initial stage.
Technology
Technology is a critical challenge because technologies evolve at rates that are far faster than that of a large construction project, hence the importance of seeking qualified expertise and establishing suitable budgets. It is important to determine how students will use this space. We live in a ‘bring your own device’ era; tablet and hybrid devices are becoming increasingly common; and apps have become part of the teaching process. Design thinking has to accommodate for evolving patterns of use while considering the type of laboratory — from computer or engineering to, for instance, chemistry or microbiology. For example, bracket mounts cannot be an afterthought and have to be carefully planned out as part of the overall design of the space. The opportunity of running several lessons simultaneously in the same space can only work with the right technology in place and operational.
 Monitor bracket mounts clear work surfaces and improve safety.
Monitor bracket mounts clear work surfaces and improve safety.
Acoustics
Noise is such a variable factor — the right amount of ‘good’ background noise can have a calming and comforting effect while stark silence can actually be quite confronting in a stressful environment. A ‘sound’ design (pun intended) considers the use of technology to address auditory quality that goes beyond volume control, for example through the use of directional speakers or more personal solutions such as headsets. Furthermore, when all is said and done, it is the architects’ and planners’ responsibility to ensure the spaces are compliant with all accreditation requirements and that the available materials and finishes have been utilized in the best manner possible.
 Sharing equipment and resources benefit an institution's bottom line.
Sharing equipment and resources benefit an institution's bottom line.
Equipment
One of the biggest benefits of superlabs, again from an efficiency perspective, is the possibility of sharing equipment and making valuable inventory readily accessible. Secondary benefits related to equipment in a large, open laboratory environment include more efficient troubleshooting and improved repair and maintenance operations that can positively impact operational expenditures. A superlab environment provides staff with increased opportunities to monitor students and educate them on the use of equipment. In the case of microbiology, for instance, it is essential that students learn about the principles underlying a sterile workplace, equipment and technique, since cell culture experiments are ruined once contaminated.
 Circulation and access to exits are important layout considerations.
Circulation and access to exits are important layout considerations.
Spatial Allowance
Safety in a laboratory setting is fundamental. Plenty of planning references and code requirements that influence lab planning and design address all issues from bench spacing to entrances and exits. Efficiency is by definition a key driver of superlab planning. That being said, a good layout will both maximize efficiency yet retain all aspects of sensible planning and rational layout of fixed items while allowing flexibility around loose items and equipment.
 Generous circulation spaces make it easier for large groups of students to enter and depart.
Generous circulation spaces make it easier for large groups of students to enter and depart.
Spatial Allocation
One of the operational challenges facing superlabs is managing the tidal flow of student arrivals and departures — where the student population is of course far greater than in a traditional teaching laboratory. An integrated system that clearly articulates students’ bench locations, such as colored light indicators at workstations, is of the utmost importance, especially when several activities are being held simultaneously. Scheduling needs to be coordinated to provide seamless access to personal protective equipment and pick up/drop off lockers.
 Large windows can improve lighting levels while providing a better backdrop.
Large windows can improve lighting levels while providing a better backdrop.
Environmental Quality and Quality of the Environment
Students deserve environments that encourage the exchange of ideas, promote a desire to learn, and that simply make them want to be there. Adequate lighting levels, air quality and thermal comfort are all basic requirements. A superlab environment should, however, aspire to improve on the limited palette and dreary backdrops typically associated with traditional laboratories. Just like other workplaces continuously evolve, so must laboratories. There are no excuses for a boring teaching environment.
Related Stories
University Buildings | Jan 11, 2022
Designing for health sciences education: supporting student well-being
While student and faculty health and well-being should be a top priority in all spaces within educational facilities, this article will highlight some key considerations.
Giants 400 | Dec 31, 2021
2021 Science and Technology Sector Giants: Top architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S. S+T facilities sector
HDR, CRB, Jacobs, Skanska USA, and Whiting-Turner Contracting Co. top the rankings of the nation's largest science and technology (S+T) sector architecture, engineering, and construction firms, as reported in the 2021 Giants 400 Report.
Laboratories | Nov 18, 2021
Tapping into the life sciences building boom
Paul Ferro of Form4 Architecture discusses how developers are pivoting to the life sciences sector, and what that means for construction and adaptive reuse.
2021 Building Team Awards | Nov 17, 2021
Caltech's new neuroscience building unites scientists, engineers to master the human brain
The Tianqiao and Chrissy Chen Institute for Neuroscience at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena wins a Gold Award in BD+C's 2021 Building Team Awards.
Laboratories | Nov 17, 2021
New report finds a biopharma industry being reshaped by disruption
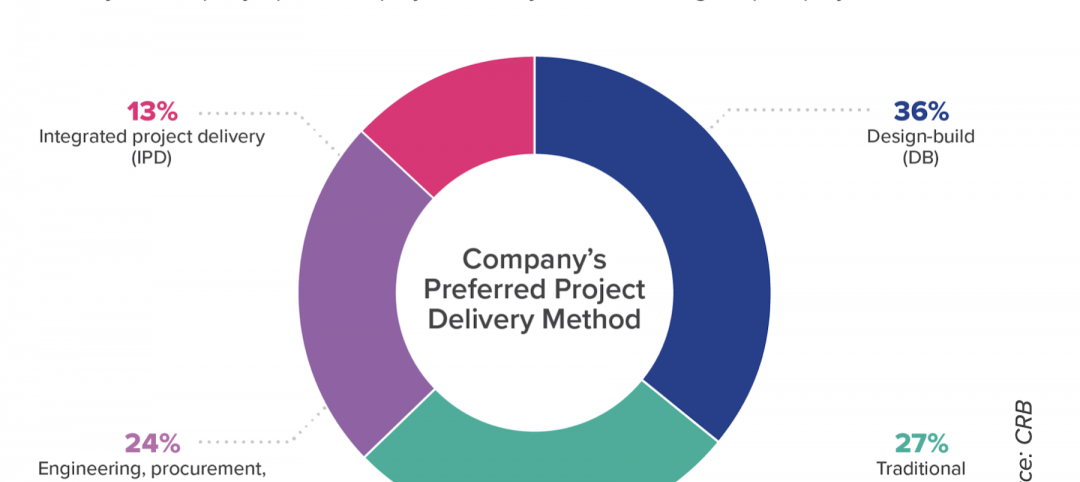
Industry respondents to CRB’s survey weigh in on project delivery, digitization, and off-site manufacturing for life sciences construction.
Laboratories | Oct 14, 2021
‘Next-generation’ Quest Diagnostics lab unveiled in New Jersey
Mark Cavagnero Associates designed the project.
Laboratories | Aug 31, 2021
Pandemic puts science and technology facilities at center stage
Expanding demand for labs and life science space is spurring new construction and improvements in existing buildings.
Giants 400 | Aug 30, 2021
2021 Giants 400 Report: Ranking the largest architecture, engineering, and construction firms in the U.S.
The 2021 Giants 400 Report includes more than 130 rankings across 25 building sectors and specialty categories.
Laboratories | Aug 30, 2021
Science in the sky: Designing high-rise research labs
Recognizing the inherent socioeconomic and environmental benefits of high-density design, research corporations have boldly embraced high-rise research labs.
Laboratories | Aug 25, 2021
Lab design strategies for renovations and adaptive reuse
Lab design experts in HOK’s Science + Technology group outline the challenges organizations must understand before renovating a lab or converting an existing building into research space.