The U.S. General Services Administration (GSA), and the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will invest $30 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to increase the sustainability of federal buildings by testing novel technologies.
The vehicle for that effort, the Green Proving Ground (GPG) program, will invest in American-made technologies to help increase federal electric vehicle supply equipment, protect air quality, reduce climate pollution, and enhance building performance. This year the GPG program has selected 20 emerging and sustainable technologies for real-world evaluation in GSA’s real-estate portfolio.
The number of technologies tested this year increased four-fold increase over previous years with added funding from the Inflation Reduction Act.
This year’s GPG program focuses on seven technology areas:
- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment: Turnkey electric vehicle charging infrastructure from Loop Global, optimized charging through charge management software from bp pulse, a battery-buffered DC fast charger from ADS-TEC Energy, and vehicle grid integration (VGI) technology from General Motors LLC.
- Germicidal Ultraviolet technologies: Next-generation LEDs and Far-UVC light to disinfect air without increasing ventilation. The GPG program will evaluate technologies that support healthier buildings while reducing energy use from Far UV Technologies, R-Zero, and PURO (subsidiary of Applied UV Inc.) with the Academy Energy Group.
- Greenhouse Gas Accounting: Technologies essential to achieving 24/7 carbon-free electricity and net zero operational emissions. Cambio AI and nZero will aim to go beyond annual greenhouse gas reporting to operationally focused carbon management, including near-real-time 24/7 carbon-free electricity insights and impacts.
- Grid-Interactive Efficient Buildings: Delivering cost savings by leveraging technologies and strategies that provide continuous demand management and load flexibility. The energy management platform from COI Energy aims to optimize energy use through machine learning.
- High-Performance technologies: Helping reduce operational and embodied carbon emissions by evaluating automated aerosol-based duct sealing from Aeroseal; an Internet-of-Things (IoT) lighting system from Signify North America Corporation; and bio-engineered, low-embodied-carbon concrete from Biomason. DOE will seek commercial partners to validate Toggled, a plug load control solution, and a thermostatic radiator cover and hybrid electrification solution from Kelvin.
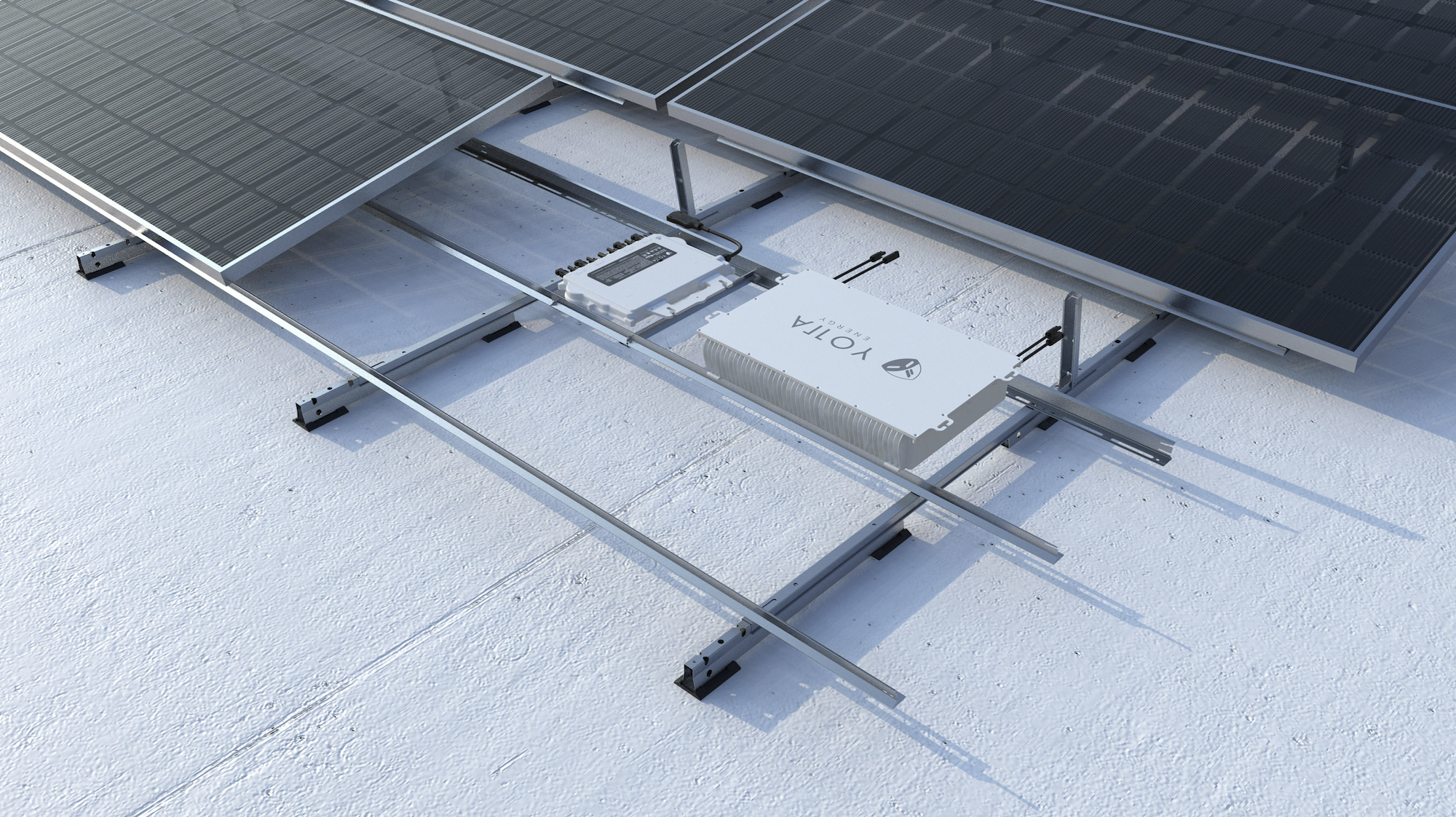
- Onsite Renewables: Technology essential to meeting the Administration’s net zero operational emission goals. The GPG program will evaluate an energy storage technology from Yotta Energy that is the size of a large laptop and installed in place of ballast beneath a rooftop photovoltaic system. The program will also pilot a wind turbine from Accelerate Wind that can be installed at the edge of the building roof and complement rooftop solar.
- Window Retrofit technologies: Help improve the performance of a building’s exterior envelope by evaluating three technologies: vacuum-insulated glazing from Pilkington; R14 interior window retrofit system from Vitro Architectural Glass; and, a secondary window framing system from Indow.
Some of these technologies will be tested at GSA’s Applied Innovation Learning Labs to identify replicable combinations of technologies that deliver net-zero operational emissions.
Related Stories
Green | Sep 11, 2018
Chicago becomes seventh city in the world to achieve LEED for Cities Platinum certification
It is the highest level of certification available from the U.S. Green Building Council.
Green | Aug 28, 2018
Chattanooga’s Miller Park set to open after $10.3 million overhaul
Spackman Mossop Michaels and Eskew Dumez Ripple partnered on the project.
Green | Aug 16, 2018
Vertical gardens: Wellness oases in the urban jungle
When there’s only so much real estate available in urban centers for parks, how’s a developer to bring in more green with biophilic design?
Green | Aug 15, 2018
What if your neighborhood could make you healthier?
The WELL Community Standard equips planners to build health promotion into the very fabric of neighborhoods.
Green | Jul 26, 2018
St. Paul aims for zero carbon in all buildings by 2050
The city is working for better efficiency and sourcing green power to reach its goal.
Green | Jul 26, 2018
DOE releases updated version of Better Buildings Financing Navigator
Version 2.0 provides renewable energy financing options, sector-specific and location-specific financing resources, and a smart database of financing providers.
Green | Jul 24, 2018
Cincinnati’s green approach to sewer discharge expected to save $100 million
Environmentally strategy does have its limits, though.
Codes and Standards | Jul 17, 2018
NIMBYism, generational divide threaten plan for net-zero village in St. Paul, Minn.
The ambitious redevelopment proposal for a former Ford automotive plant creates tension.
Sponsored | Energy Efficiency | Jul 2, 2018
Going solar has never been easier
There is an efficient system for mounting solar panels to roofs and turning roof real estate into raw power.
Multifamily Housing | Jun 27, 2018
To take on climate change, go passive
If you haven’t looked seriously at “passive house” design and construction, you should.