Global urbanization and densification are giving rise to new thinking about how design can lower the impact of buildings on the heating of the planet. This is particularly true of high-rise buildings with glass façades that get scalding hot and generate heat islands. On buildings and other sealed surfaces, only about 10% of any rainwater that hits them evaporates; the rest of that precipitation typically ends up running into sewer systems in volumes that increasingly are leading to flooding.
One design and engineering solution to these problems is being explored at the University of Stuttgart in Germany, where researchers last October presented what they claim is the first hydroactive façade that moderates the temperature of exterior walls and interiors of buildings by absorbing rainwater that the system releases on hot days for evaporative cooling.
“It’s a milestone in the adaptation of the built environment to the urgent challenges of our time,” proclaims Christina Eisenbarth, a Research Assistant at the university’s Institute of Lightweight Structures and Conceptual Design (ILEK), and the façade’s inventor.
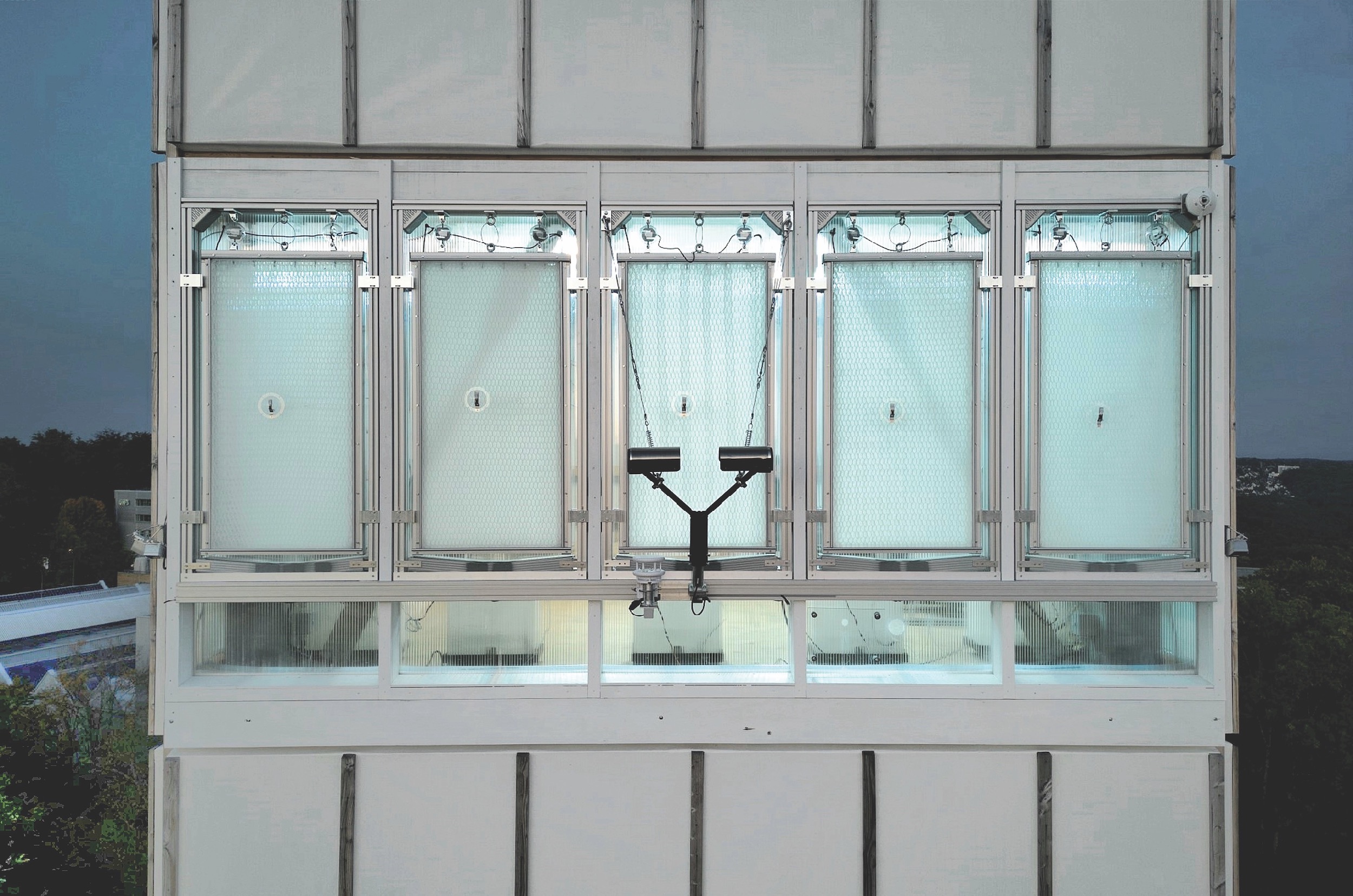
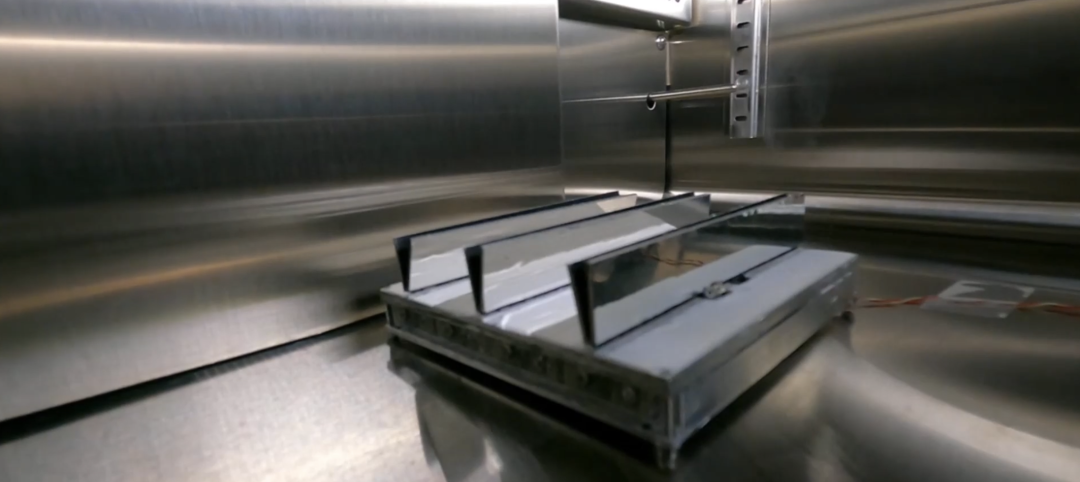
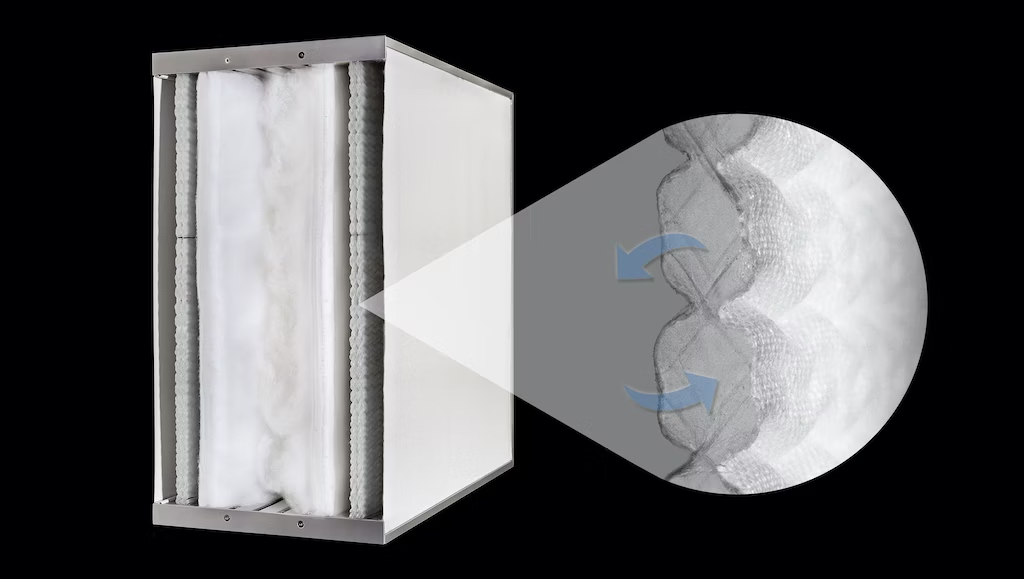
Dubbed HydroSKIN, the façade consists of an external, multilayered 3D textile that acts as a water collector and evaporator. Here’s how it works, according to research abstracts that ILEK released last fall:
- Its first layer is a water-permeable mesh or knitted fabric facing the outside that lets water in and filters out impurities and insects.
- A second inner layer is a water-transporting spacer fabric whose pile threads mobilize incoming and outgoing water and provide an open porous structure with a large surface area for air circulation and facilitating evaporation.
- A third layer can be integrated into the system to optimize water storage and evaporation performance. A water-bearing fourth layer, which might be a foil, is on the inside and provides water drainage and collection.
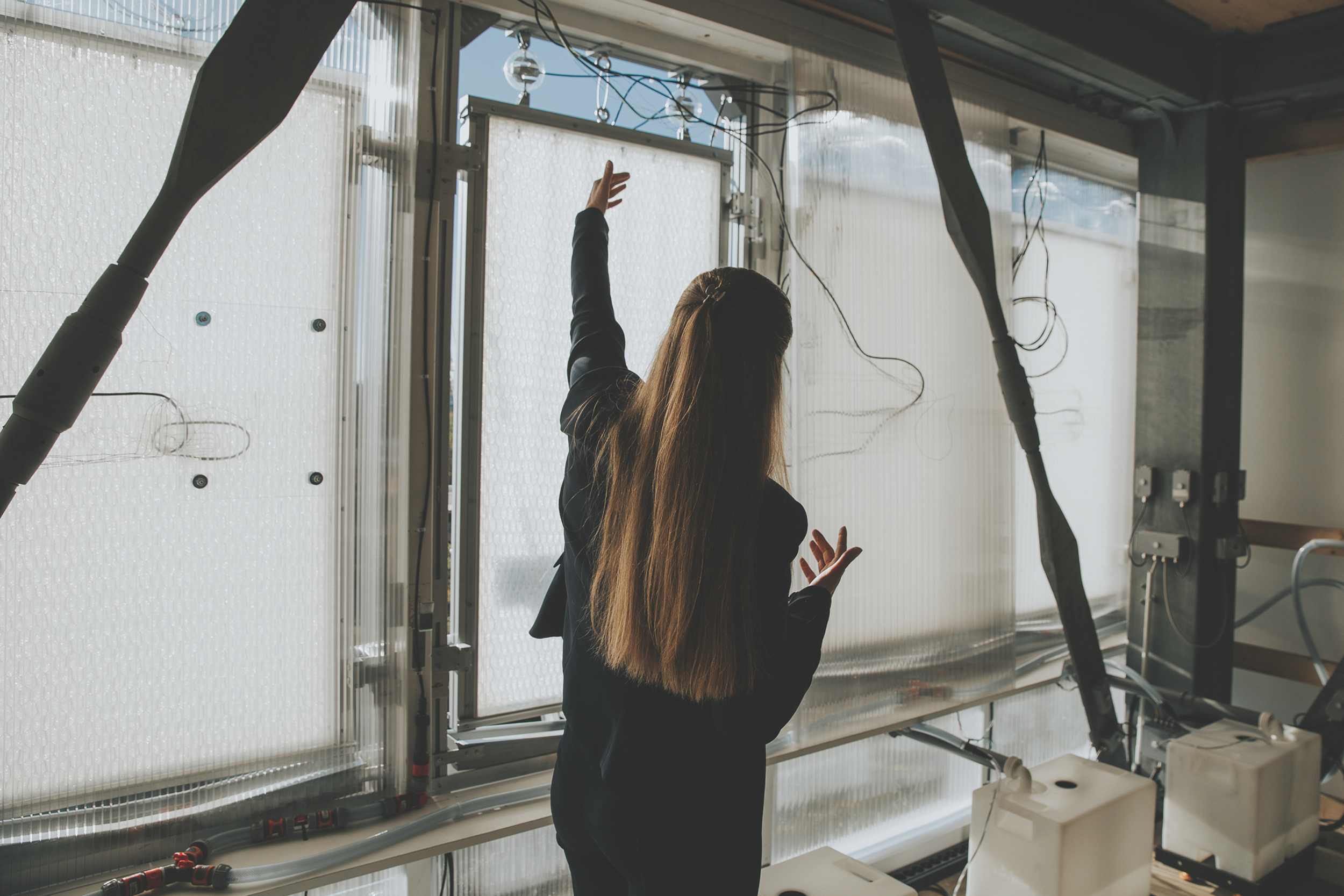

The layers are assembled by a force fit and are fixed into a frame profile by means of a waterproof Keder fabric.
The thickness of the textile- and film-based envelope system can vary between 20 and 60 mm, depending on environmental conditions and performance requirements. Depending on wind-driven rain yields, the depth of the frame profile’s water supply and discharge conduits might range from 50 to 100 mm.
HydroSKIN is well suited for high-rise buildings
Researchers have tested their concept in the lab and on buildings in Stuttgart and Singapore. At press time Eisenbarth was in Australia preparing to test HydroSKIN on buildings in Sydney.
The findings so far support the efficiency of the façade and its potential for high-rise buildings. For example, research found that above building heights of 29 meters, the total square-meter-related wind-driven-rain (WDR) yields striking a façade surface exceeded vertically falling precipitation yields per square meter. In other words, more rain can be absorbed by the façade than by a roof surface of the same size, and this disparity becomes even more pronounced at higher elevations.
In lab tests, researchers demonstrated a temperature reduction of about 10 degrees due to the effects of evaporation via HydroSKIN. Initial measurements last September on the world’s first adaptive high-rise building, at the University of Stuttgart’s Vaihingen campus, “suggest the cooling potential is even significantly higher,” says Eisenbarth.
Last year, a prototype installation and meteorological evaluation of five different HydroSKIN prototypes was conducted on the 10th level of this 12-floor, 36.5-meter campus high-rise. In 2023, there will be further testing of HydroSKIN on the building’s 9th level in combination with a unitized glass façade that will integrate textile insulation and other functional layers into the system.
BD+C was unable to ascertain how close HydroSKIN is to becoming commercially viable. (The results from the testing in Australia should be ready sometime this summer, says Dr. Walter Haase, ILEK’s Managing Director and Head of Working Groups.) But it is ILEK’s contention that this system could be retrofitted onto any façade surface of new or existing buildings.
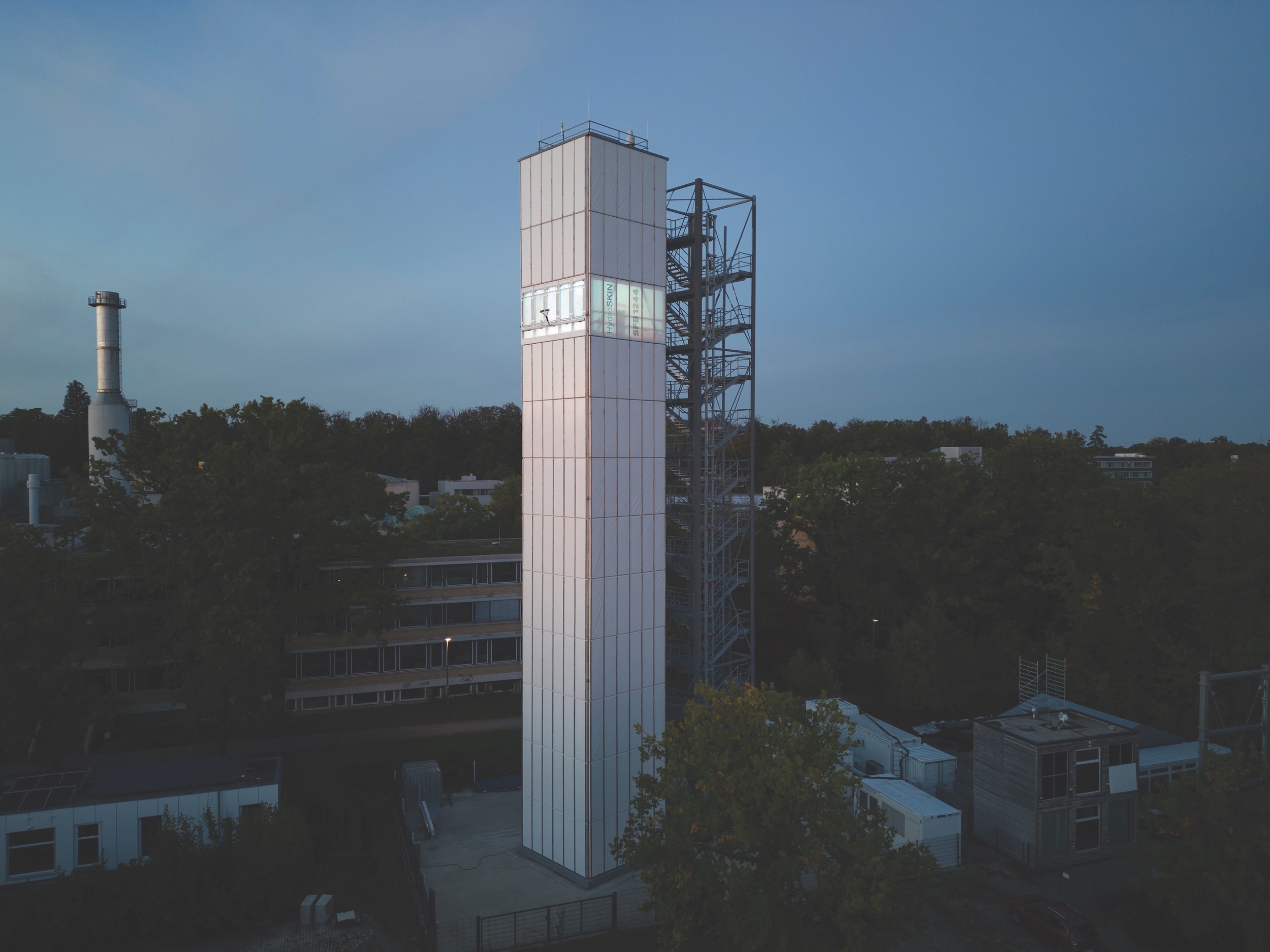

For one thing, its mass—between one kilogram per square meter dry to five kg/sm saturated—compares favorably to other façade infill materials such as cellular concrete (~150 kg/sm), wood-panel construction (~125 kg/sm), thermal insulation composite systems (~63 kg/sm), or even triple glazing (~45 kg/sm). In addition, HydroSKIN is designed to be aesthetically unobtrusive, and its layers are framed in a profile that allows for easy disassembly and recycling of all components.
While HydroSKIN’s long-term suitability has yet to be proven, ILEK has manufacturers lined up to make it, says Eisenbarth.
Related Stories
AEC Tech | Jan 8, 2024
What's driving the surge of digital transformation in AEC today?
For centuries, the AEC industry has clung to traditional methods and legacy processes—seated patterns that have bred resistance to change. This has made the adoption of new technologies a slow and hesitant process.
Giants 400 | Jan 8, 2024
Top 60 Senior Living Facility Construction Firms for 2023
Whiting-Turner, Ryan Companies US, Weis Builders, Suffolk Construction, and W.E. O'Neil Construction top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest senior living facility general contractors and construction management (CM) firms for 2023, as reported in the 2023 Giants 400 Report.
K-12 Schools | Jan 8, 2024
Video: Learn how DLR Group converted two big-box stores into an early education center
Learn how the North Kansas City (Mo.) School District and DLR Group adapted two big-box stores into a 115,000-sf early education center offering services for children with special needs.
Green | Jan 8, 2024
DOE releases RFI on developing national definition for a Zero Emissions Building
The Department of Energy released a Request for Information (RFI) for feedback from industry, academia, research laboratories, government agencies, and other stakeholders on a draft national definition for a Zero Emissions Building.
Codes and Standards | Jan 8, 2024
Australia to be first country to ban engineered stone countertops
In 2024, Australia will be the first country to ban engineered stone countertops. The ban came after a years-long campaign supported by doctors, trade unions, and workers over concerns that the material was causing increased silicosis cases among workers cutting and handling it.
Roofing | Jan 8, 2024
Researchers devise adaptive roof tile concept that adjusts to ambient temperatures
Scientists at the University of California Santa Barbara published a paper that proposes adaptive roof tile technology that can adjust to ambient temperatures. Using a wax motor, tiles could switch from a heating or cooling state enabling savings on heating and cooling costs.
MFPRO+ Special Reports | Jan 4, 2024
Top 10 trends in multifamily rental housing
Demographic and economic shifts, along with work and lifestyle changes, have made apartment living preferable for a wider range of buyers and renters. These top 10 trends in multifamily housing come from BD+C's 2023 Multifamily Annual Report.
Giants 400 | Jan 2, 2024
Top 80 Hotel Construction Firms for 2023
Suffolk Construction, STO Building Group, PCL Construction Enterprises, AECOM, and Brasfield & Gorrie top BD+C's ranking of the nation's largest hotel and resort general contractors and construction management (CM) firms for 2023, as reported in Building Design+Construction's 2023 Giants 400 Report.
MFPRO+ News | Jan 2, 2024
New York City will slash regulations on housing projects
New York City Mayor Eric Adams is expected to cut red tape to make it easier and less costly to build housing projects in the city. Adams would exempt projects with fewer than 175 units in low-density residential areas and those with fewer than 250 units in commercial, manufacturing, and medium- and high-density residential areas from environmental review.
Contractors | Dec 22, 2023
DBIA releases two free DEI resources for AEC firms
The Design-Build Institute of America (DBIA) has released two new resources offering guidance and provisions on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) on design-build projects.

















