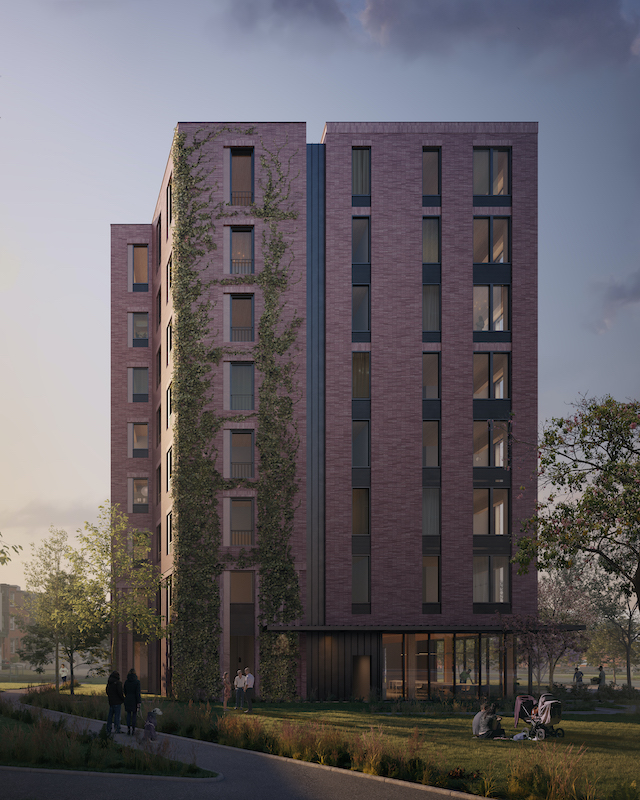
A team of AEC firms, assembled by Generate, an AEC technology company that advocates for the greater use of mass timber in construction, has developed a digital catalog of integrated design systems that focus on the structural application of mass timber as a carbon-conscious response to high-density urban building needs, especially for housing.
Meeting those needs within the status quo—where buildings currently account to two-fifths of greenhouse gas emissions—is at odds with many cities’ environmental aspirations. For example, Boston’s goal of reducing its carbon footprint 80% by 2050 would be unachievable if that metro also hits its parallel goal of building 300,000 more housing units and 40 million sf of commercial buildings over the next 30 years.
To bring down those CO2 emissions and streamline the construction process, an AEC coalition has developed Tallhouse, a digital catalog of customizable systems comprised of four mass timber structural solutions. That catalog illustrates a range of mass timber design options that are engineered for speedier delivery, sustainability, and cost savings.
Also see: San Jose affordable housing project will feature mass timber frame
The coalition includes Generate, Niles Bolton Associates (architect), Buro Happold (SE, MEP, sustainability consultant, embodied carbon analyst), Consigli Construction (GC), Arup (fire engineering, structural review), Code Red (code consultant), Urbanica (developer), and Olifant Market Development (carbon and forests).
The coalition’s work has been supported by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Agriculture, the Softwood Lumber Board, the Binational Softwood Lumber Council, and the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
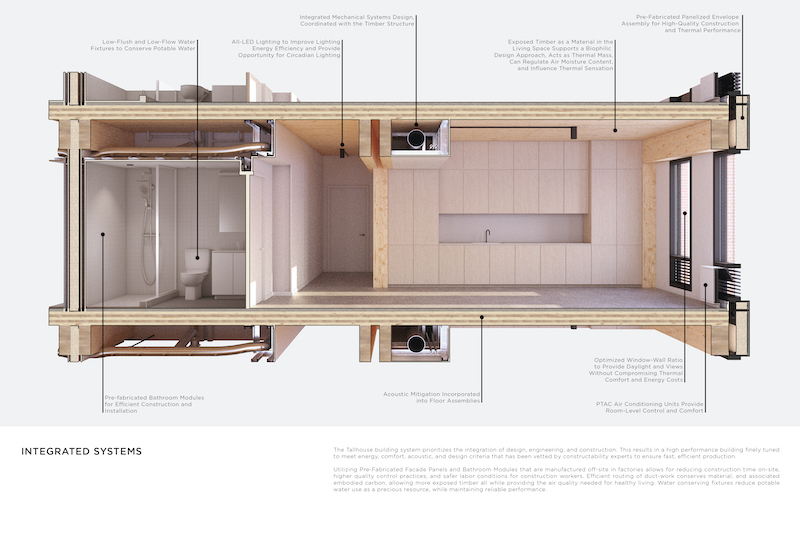
Tallhouse's systems are designed as kits of parts to accommodate most countries' products and transportation.
THE DESIGNS ANTICIPATE TALLER WOOD BUILDING CODES
Tallhouse’s four options are a hybrid steel/cross-laminated timber (CLT) structure, a mass-timber post, beam and plate structure; a hybrid light-gauge metal/CLT structure, and a full CLT plate honeycomb structure.
By “hybridizing” conventional construction materials with timber, the Tallhouse designs can offset near-term emissions by greatly reducing emissions from the manufacture of materials, while storing carbon in the timber structure over the lifetime of buildings. The team sees synergies between the steel and timber industries, as both materials lend themselves to digitization and carbon efficiency.
To evaluate each design, the coalition developed a Carbon Data Analysis tool that validated savings in embodied emissions ranging from 14% to 52%.
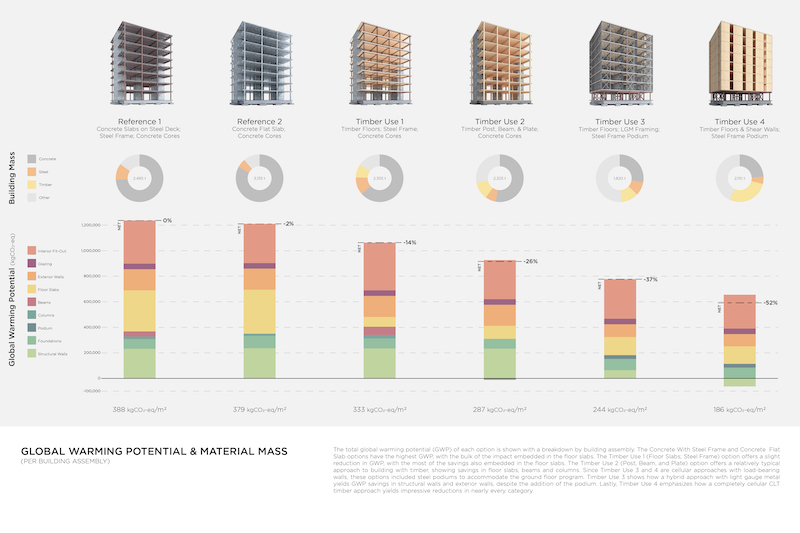
The coalition used a Carbon Data Analysis tool to gauge the impact of its designs on carbon emissions and global warming.
The Tallhouse system is adaptable for buildings eight to 18 stories, in line with the upcoming 2021 U.S. Tallwood Codes that would allow the use of mass timber for structures at those heights under the 2021 International Building Code. According to Generate, the systems are designed as kits of parts to accommodate most American, Canadian, and European manufacturers’ products and shipping logistics.
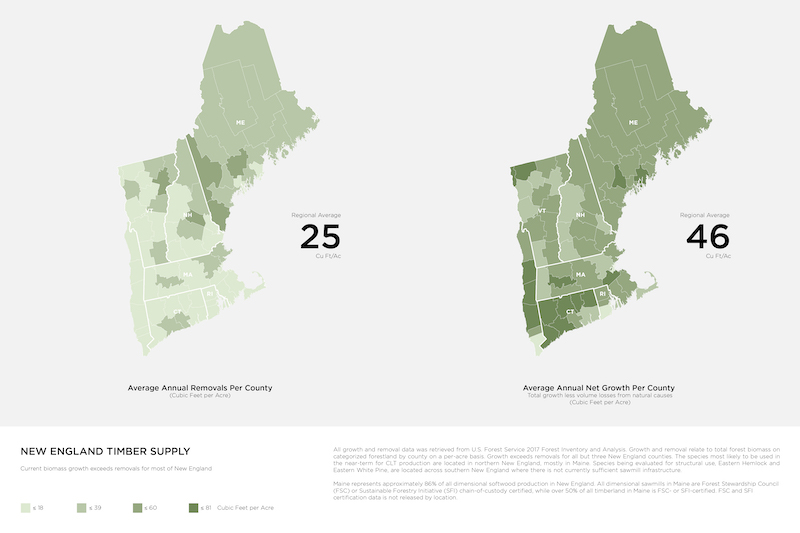
The U.S. Northeast is home to the highest percentage of sustainably managed timber in the U.S. Long-lived forest products such as mass timber building materials have longer timelines than paper or pulp products for keeping CO2 stored in wood post-harvesting.
The Tallhouse team is implementing these systems in over 1 million sf of construction in the U.S., and is looking for additional developers. The Tallhouse catalog, says John Klein, Generate’s CEO and project leader, “was developed with the specific intent of at once enabling our cities to achieve their ambitious CO2 footprint reduction goals, and to meet growing demand for affordable, biophilic housing.” As these systems become widely accessible to architectural communities globally, they will “serve as a vehicle to deploy sustainable materials at scale,” says Klein.
Related Stories
Modular Building | Mar 20, 2023
3 ways prefabrication doubles as a sustainability strategy
Corie Baker, AIA, shares three modular Gresham Smith projects that found sustainability benefits from the use of prefabrication.
Sustainability | Mar 16, 2023
Lack of standards for carbon accounting hamper emissions reduction
A lack of universally accepted standards for collecting, managing, and storing greenhouse gas emissions data (i.e., carbon accounting) is holding back carbon reduction efforts, according to an essay published by the Rocky Mountain Institute.
Affordable Housing | Mar 14, 2023
3 affordable housing projects that overcame building obstacles
These three developments faced certain obstacles during their building processes—from surrounding noise suppression to construction methodology.
Laboratories | Mar 9, 2023
5 laboratory design choices that accelerate scientific discovery
Stephen Blair, director of CannonDesign's Science & Technology Practice, identifies five important design strategies to make the most out of our research laboratories.
Sustainability | Mar 2, 2023
The next steps for a sustainable, decarbonized future
For building owners and developers, the push to net zero energy and carbon neutrality is no longer an academic discussion.
Sustainable Design and Construction | Feb 28, 2023
Architecture 2030 launches free carbon calculator for retrofit projects
Architecture 2030’s Carbon Avoided Retrofit Estimator (CARE) tool allows project teams and building owners to accurately quantify the carbon “savings” in retrofit or reuse projects versus new construction.
AEC Innovators | Feb 28, 2023
Meet the 'urban miner' who is rethinking how we deconstruct and reuse buildings
New Horizon Urban Mining, a demolition firm in the Netherlands, has hitched its business model to construction materials recycling. It's plan: deconstruct buildings and infrastructure and sell the building products for reuse in new construction. New Horizon and its Founder Michel Baars have been named 2023 AEC Innovators by Building Design+Construction editors.
Affordable Housing | Feb 22, 2023
Passive House, sustainability standards meet multifamily development
These multifamily developments are not only Passive House (PHIUS) certified, but affordable for tenants.
Senior Living Design | Feb 15, 2023
Passive House affordable senior housing project opens in Boston
Work on Phase Three C of The Anne M. Lynch Homes at Old Colony, a 55-apartment midrise building in Boston that stands out for its use of Passive House design principles, was recently completed. Designed by The Architectural Team (TAT), the four-story structure was informed throughout by Passive House principles and standards.
Affordable Housing | Feb 15, 2023
2023 affordable housing roundup: 20+ multifamily projects
In our latest call for entries, Building Design+Construction collected over 20 multifamily projects with a focus on affordable housing. Here is a comprehensive list of all projects in alphabetical order.

















