Cities interested in bolstering their economies through innovation should look beyond the typical formalized processes.
Instead, a new paper from the Brookings Anne T. and Robert M. Bass Initiative on Innovation and Placemaking pushes economic development leaders to recognize that different types of firms innovate through distinct actors and both market and non-market channels. As a result, regions require industry-tailored innovation-support strategies.
In “How Firms Learn: Industry specific strategies for urban economies,” Brookings Senior Policy Analyst and Associate Fellow Scott Andes examines how manufacturing and software services firms develop new products, processes, and ideas. He illustrates three archetypal innovation models, which correspond to three industry types:
- Classic Industries, such as pharmaceuticals, work primarily with universities and other traditional innovation actors and use market channels, including contracts and licensing agreements, as sources of invention.
- Unconventional Industries, exemplified by small-and medium-sized manufacturers, primarily source innovation from clients and suppliers and pursue informal innovation channels, such as joint research agreements and supplier contracts.
- Mixed Industries predominantly rely on non-traditional actors but formal market channels to acquire innovation. Example industries include semiconductors, chemicals, and textiles.
“In order to build strong regional economies, urban economic development leaders should stop carbon copying other cities’ approaches and instead align local economic strategies with the particular ways their dominant industries innovate,” Andes said.
Specifically, public, private, and institutional stakeholders should develop strategies that:
- Recognize that all industries can be innovative, not just software and medical technology startups, and identify the particular innovation pathways utilized by local firms.
- Eliminate institution-wide technology transfer practices at research universities that focus on licensing and allow specific departments and centers to cater to different industries.
- Establish partnerships with non-research colleges and universities to support firms seeking short-term process innovation.
- Modify the traditional accelerator model to respond to the innovation needs of startups in nontraditional growth sectors.
- Link designers, engineers, and software developers in urban centers to manufacturing supply chains in the surrounding regions.
- Advance appropriate place-based strategies to increase the density of innovative firms and support organizations.
Such industry-contextualized approaches will allow for urban economic development resources to be used to their best advantage and firms and other innovation actors to maximize learning and economic power.
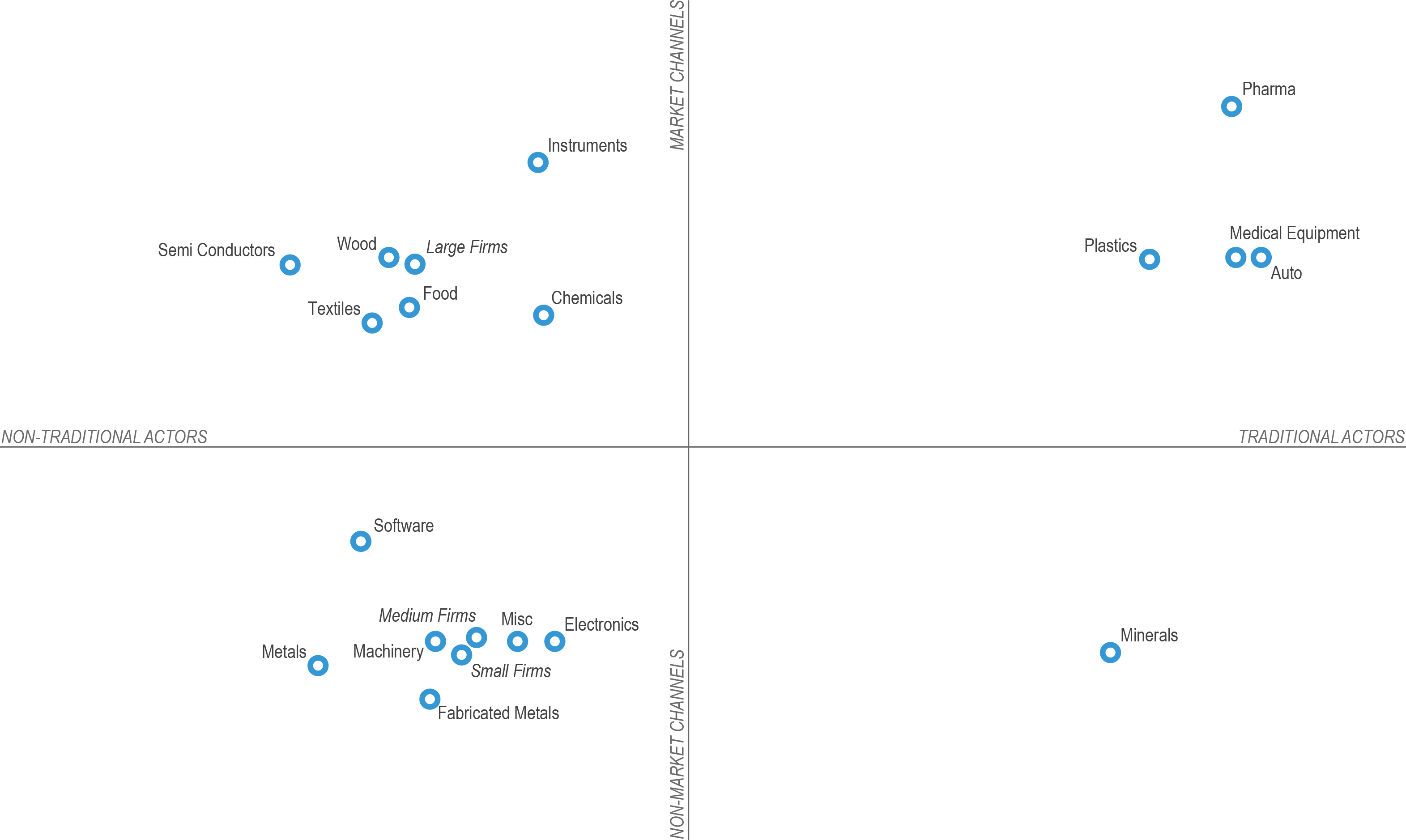 Sources of innovation and channels by which acquired, by industry. Source: Author’s analysis of Arora, Cohen, and Walsh (2014) and Graham (2009). Click image to enlarge.
Sources of innovation and channels by which acquired, by industry. Source: Author’s analysis of Arora, Cohen, and Walsh (2014) and Graham (2009). Click image to enlarge.
Related Stories
Mixed-Use | Aug 2, 2017
Redevelopment of Newark’s Bears Stadium site receives team of architects
Lotus Equity Group selected Michael Green Architecture, TEN Aquitectos, Practice for Architecture and Urbanism, and Minno & Wasko Architects and Planners to work on the project.
Urban Planning | Jul 21, 2017
Streets as storytellers: Defining places and connecting people
“In a city the street must be supreme. It is the first institution of the city. The street is a room by agreement, a community room, the walls of which belong to the donors, dedicated to the city for common use.” – Louis Kahn
Urban Planning | Jun 26, 2017
Convenience and community lead the suburban shift
As the demand for well-connected urban locales increases, so too has the cost of property and monthly rent; and as suburbs typically offer a bargain on both, more people are looking for a compromise.
Office Buildings | Jun 12, 2017
At 11.8 million-sf, LG Science Park is the largest new corporate research campus in the world
The project is currently 75% complete and on schedule to open in 2018.
Architects | May 26, 2017
Innovations in addressing homelessness
Parks departments and designers find new approaches to ameliorate homelessness.
Mixed-Use | May 24, 2017
Schmidt Hammer Lassen Architects will develop mixed-use project on former site of Carlsberg Brewery
The 36,000-sm project will cover a city block and include a residential tower.
Mixed-Use | May 23, 2017
45-story tower planned for Miami Worldcenter
Pickard Chilton Architects will design the 600,000-sf 110 10th Street.
Movers+Shapers | May 8, 2017
Movers + Shapers: Charm City's lucky charm
Under Armour’s Kevin Plank launches a $5.5 billion redevelopment to transform Baltimore into “the coolest city in America.”
Urban Planning | Apr 24, 2017
No Small Plans hopes to inspire Chicago teens to design the city they want
Launched with a Kickstarter campaign, the Chicago Architecture Foundation aims to get No Small Plans into the hands of thousands of Chicago teens.
Urban Planning | Apr 20, 2017
Times Square renovation officially opens
The Snøhetta-designed project nearly doubles the size of public space at one of the most visited attractions in the U.S.